Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 > Mind Map: Lines and Angles
Mind Map: Lines and Angles | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
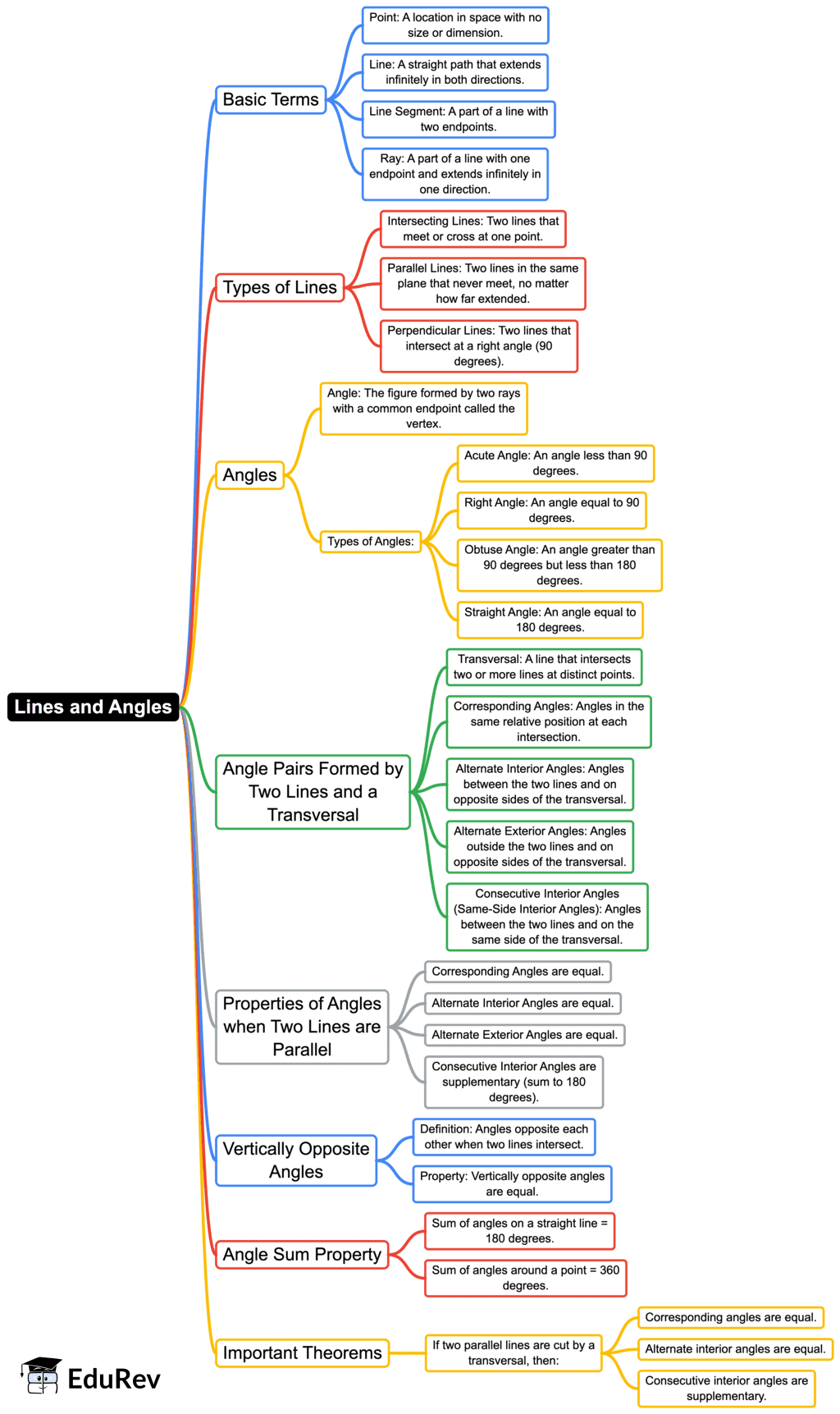
The document Mind Map: Lines and Angles | Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Mathematics (Maths) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
40 videos|563 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Lines and Angles - Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What are the different types of angles? |  |
Ans. The different types of angles include acute angles (less than 90 degrees), right angles (exactly 90 degrees), obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees), straight angles (exactly 180 degrees), reflex angles (greater than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees), and full angles (exactly 360 degrees).
| 2. How do you identify complementary and supplementary angles? |  |
Ans. Complementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 90 degrees. For example, if one angle measures 30 degrees, its complementary angle would measure 60 degrees. Supplementary angles are two angles whose measures add up to 180 degrees. For instance, if one angle measures 110 degrees, its supplementary angle would measure 70 degrees.
| 3. What is the relationship between parallel lines and angles? |  |
Ans. When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, several pairs of angles are formed. The corresponding angles are equal, alternate interior angles are equal, and consecutive interior angles are supplementary. This means that these relationships can help determine the measures of unknown angles when working with parallel lines.
| 4. How can you use a protractor to measure angles accurately? |  |
Ans. To measure an angle using a protractor, place the midpoint of the protractor at the vertex of the angle. Align one side of the angle with the zero line of the protractor. Then, read the measurement on the scale where the other side of the angle crosses the protractor. Make sure to take note of whether to use the inner or outer scale, depending on the direction of the angle.
| 5. What are vertically opposite angles, and how are they formed? |  |
Ans. Vertically opposite angles are the angles that are opposite each other when two lines intersect. They are formed when the two lines cross each other, creating pairs of angles that are equal in measure. For example, if two lines intersect and one angle measures 50 degrees, the angle directly opposite it will also measure 50 degrees.
Related Searches
















