TITA Based Questions: Grouping and Selections | Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT PDF Download
As TITA (Type In The Answer) based questions are gaining prominence in the CAT exam, it’s important to build accuracy without relying on options. The following are carefully curated TITA-based questions on the topic Grouping and Selections to help you practice exact value-based problem solving.
Que 1: Instructions for Set 1
Three reviewers Amal, Bimal, and Komal are tasked with selecting questions from a pool of 13 questions (Q01 to Q13). Questions can be created by external “subject matter experts” (SMEs) or by one of the three reviewers. Each of the reviewers either approves or disapproves a question that is shown to them. Their decisions lead to eventual acceptance or rejection of the question in the manner described below.
If a question is created by an SME, it is reviewed first by Amal, and then by Bimal. If both of them approve the question, then the question is accepted and is not reviewed by Komal. If both disapprove the question, it is rejected and is not reviewed by Komal. If one of them approves the question and the other disapproves it, then the question is reviewed by Komal. Then the question is accepted only if she approves it.
A question created by one of the reviewers is decided upon by the other two. If a question is created by Amal, then it is first reviewed by Bimal. If Bimal approves the question, then it is accepted. Otherwise, it is reviewed by Komal. The question is then accepted only if Komal approves it. A similar process is followed for questions created by Bimal, whose questions are first reviewed by Komal, and then by Amal only if Komal disapproves it. Questions created by Komal are first reviewed by Amal, and then, if required, by Bimal.
The following facts are known about the review process after its completion.
1. Q02, Q06, Q09, Q11, and Q12 were rejected and the other questions were accepted.
2. Amal reviewed only Q02, Q03, Q04, Q06, Q08, Q10, Q11, and Q13.
3. Bimal reviewed only Q02, Q04, Q06 through Q09, Q12, and Q13.
4. Komal reviewed only Q01 through Q05, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q11, and Q12.
Q1: How many questions were DEFINITELY created by Amal?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 3
For a question created by externals(SME), the minimum number of reviews required is two and the maximum number of reviews is three to confirm the acceptance or the rejection.
For a question created by anyone among Amal, Bimal, Komal a question can be reviewed after one review or two reviews.
The information provided states :
Q02, Q06, Q09, Q11, and Q12 were rejected. Q01, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q10, Q13 were accepted.
For the questions :
Amal - Q02, Q03, Q04, Q06, Q08, Q10, Q11, and Q13.
Bimal - Q02, Q04, Q06, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q12, and Q13.
Komal - Q01, Q02, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q11, and Q12.
Q01 is reviewed by only Komal and is accepted hence Bimal must have prepared the question as it was accepted in a single review. (Bimal)
Q02-is reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and was rejected this has a possibility of being prepared by an external person and faced rejection by one among Amal and Bimal and Komal. (SME).
Q03-Was accepted and reviewed by Amal, Komal and hence must have been prepared by Bimal(Bimal).
Q04- Accepted and reviewed by the three of them and hence must have been prepared by an external expert. (SME).
Q05-Only reviewed by Komal and is accepted and hence must be prepared by Bimal. (Bimal)
Q06-Rejected and reviewed by Amal and Bimal. Hence could have been prepared by Komal or External and rejected by Bimal and Amal. (Komal/SME).
Q07-Accepted and reviewed by Bimal and Komal. Hence must have been prepared by Amal. (Amal).
Q08- Reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and is accepted. Hence must have been prepared by SME. (SME)
Q09- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and is rejected. It must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both of them. (Amal).
Q10- Was reviewed by Amal and was accepted. Must have been prepared by Komal. (Komal)
Q11- Reviewed by Amal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Bimal and rejected by both Amal and Komal. (Bimal)
Q12- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both Bimal and Komal. (Amal).
Q13- Reviewed by Amal and Bimal and was accepted. The question could have been prepared by Komal or SME. (Komal/SME).
Amal definitely prepared questions Q07, Q09, Q12.
Q2: How many questions were DEFINITELY created by Komal?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 1
For a question created by externals(SME), the minimum number of reviews required is two and the maximum number of reviews is three to confirm the acceptance or the rejection.
For a question created by anyone among Amal, Bimal, Komal a question can be reviewed after one review or two reviews.
The information provided states :
Q02, Q06, Q09, Q11, and Q12 were rejected. Q01, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q10, Q13 were accepted.
For the questions :
Amal - Q02, Q03, Q04, Q06, Q08, Q10, Q11, and Q13.
Bimal - Q02, Q04, Q06, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q12, and Q13.
Komal - Q01, Q02, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q11, and Q12.
Q01 is reviewed by only Komal and is accepted hence Bimal must have prepared the question as it was accepted in a single review. (Bimal)
Q02-is reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and was rejected this has a possibility of being prepared by an external person and faced rejection by one among Amal and Bimal and Komal. (SME).
Q03-Was accepted and reviewed by Amal, Komal and hence must have been prepared by Bimal(Bimal).
Q04- Accepted and reviewed by the three of them and hence must have been prepared by an external expert. (SME).
Q05-Only reviewed by Komal and is accepted and hence must be prepared by Bimal. (Bimal)
Q06-Rejected and reviewed by Amal and Bimal. Hence could have been prepared by Komal or External and rejected by Bimal and Amal. (Komal/SME).
Q07-Accepted and reviewed by Bimal and Komal. Hence must have been prepared by Amal. (Amal).
Q08- Reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and is accepted. Hence must have been prepared by SME. (SME)
Q09- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and is rejected. It must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both of them. (Amal).
Q10- Was reviewed by Amal and was accepted. Must have been prepared by Komal. (Komal)
Q11- Reviewed by Amal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Bimal and rejected by both Amal and Komal. (Bimal)
Q12- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both Bimal and Komal. (Amal).
Q13- Reviewed by Amal and Bimal and was accepted. The question could have been prepared by Komal or SME. (Komal/SME).
Q10 was definitely prepared by Komal.
Q3: How many questions were DEFINITELY created by the SMEs?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 3
For a question created by externals(SME), the minimum number of reviews required is two and the maximum number of reviews is three to confirm the acceptance or the rejection.
For a question created by anyone among Amal, Bimal, Komal a question can be reviewed after one review or two reviews.
The information provided states :
Q02, Q06, Q09, Q11, and Q12 were rejected. Q01, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q10, Q13 were accepted.
For the questions :
Amal - Q02, Q03, Q04, Q06, Q08, Q10, Q11, and Q13.
Bimal - Q02, Q04, Q06, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q12, and Q13.
Komal - Q01, Q02, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q11, and Q12.
Q01 is reviewed by only Komal and is accepted hence Bimal must have prepared the question as it was accepted in a single review. (Bimal)
Q02-is reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and was rejected this has a possibility of being prepared by an external person and faced rejection by one among Amal and Bimal and Komal. (SME).
Q03-Was accepted and reviewed by Amal, Komal and hence must have been prepared by Bimal(Bimal).
Q04- Accepted and reviewed by the three of them and hence must have been prepared by an external expert. (SME).
Q05-Only reviewed by Komal and is accepted and hence must be prepared by Bimal. (Bimal)
Q06-Rejected and reviewed by Amal and Bimal. Hence could have been prepared by Komal or External and rejected by Bimal and Amal. (Komal/SME).
Q07-Accepted and reviewed by Bimal and Komal. Hence must have been prepared by Amal. (Amal).
Q08- Reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and is accepted. Hence must have been prepared by SME. (SME)
Q09- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and is rejected. It must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both of them. (Amal).
Q10- Was reviewed by Amal and was accepted. Must have been prepared by Komal. (Komal)
Q11- Reviewed by Amal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Bimal and rejected by both Amal and Komal. (Bimal)
Q12- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both Bimal and Komal. (Amal).
Q13- Reviewed by Amal and Bimal and was accepted. The question could have been prepared by Komal or SME. (Komal/SME).
Q02, Q04, Q08 were prepared SME
Q4: How many questions were DEFINITELY disapproved by Bimal?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 4
For a question created by externals(SME), the minimum number of reviews required is two and the maximum number of reviews is three to confirm the acceptance or the rejection.
For a question created by anyone among Amal, Bimal, Komal a question can be reviewed after one review or two reviews.
The information provided states :
Q02, Q06, Q09, Q11, and Q12 were rejected. Q01, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q10, Q13 were accepted.
For the questions :
Amal - Q02, Q03, Q04, Q06, Q08, Q10, Q11, and Q13.
Bimal - Q02, Q04, Q06, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q12, and Q13.
Komal - Q01, Q02, Q03, Q04, Q05, Q07, Q08, Q09, Q11, and Q12.
Q01 is reviewed by only Komal and is accepted hence Bimal must have prepared the question as it was accepted in a single review. (Bimal)
Q02-is reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and was rejected this has a possibility of being prepared by an external person and faced rejection by one among Amal and Bimal and Komal. (SME).
Q03-Was accepted and reviewed by Amal, Komal and hence must have been prepared by Bimal(Bimal).
Q04- Accepted and reviewed by the three of them and hence must have been prepared by an external expert. (SME).
Q05-Only reviewed by Komal and is accepted and hence must be prepared by Bimal. (Bimal)
Q06-Rejected and reviewed by Amal and Bimal. Hence could have been prepared by Komal or External and rejected by Bimal and Amal. (Komal/SME).
Q07-Accepted and reviewed by Bimal and Komal. Hence must have been prepared by Amal. (Amal).
Q08- Reviewed by Amal, Bimal, and Komal and is accepted. Hence must have been prepared by SME. (SME)
Q09- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and is rejected. It must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both of them. (Amal).
Q10- Was reviewed by Amal and was accepted. Must have been prepared by Komal. (Komal)
Q11- Reviewed by Amal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Bimal and rejected by both Amal and Komal. (Bimal)
Q12- Reviewed by Bimal and Komal and was rejected. Must have been prepared by Amal and was rejected by both Bimal and Komal. (Amal).
Q13- Reviewed by Amal and Bimal and was accepted. The question could have been prepared by Komal or SME. (Komal/SME).
Q06 irrespective of the question prepared by Komal/SME Bimal must reject the question.
Q07, Q09, Q12 are prepared by Amal and were reviewed by Bimal first and Komal next for this to happen Bimal must reject these questions.
Hence a total of four questions were rejected by Bimal.
Que 2: Instruction for Set 2
K, L, M, N, P, Q, R, S, U and W are the only ten members in a department. There is a proposal to form a team from within the members of the department, subject to the following conditions:
- A team must include exactly one among P,R and S.
- A team must include either M or Q, but not both.
- If a team includes K, then it must also include L, and vice versa.
- If a team includes one among S, U and W, then it should also include the other two.
- L and N cannot be members of the same team.
- L and U cannot be members of the same team.
The size of a team is defined as the number of members in the team.
Q1: In how many ways a team can be constituted so that the team includes N?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 6
Since N is in the team, L and K cannot be in the team.
The team can have one of M and Q. So, 2 ways of selection.
If the team has S, then it should have U and W as well.
If the team has no S, then it should have one of P or R.
So, the number of ways of forming the team is 2*(1+2) = 6 ways
Q2: What would be the size of the largest possible team?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 5
Out of P, R and S only 1 can be in the team. If S is there, U and W will also be there. So, P and R should not be in the team for its size to be maximum.
Out of M and Q, only 1 can be there.
If L is there in the team, N and U cannot be in the team.
If L is not there in the team, then K is also not there in the team but N and U can be in the team.
So, the maximum team size is 5 consisting of S, U, W, (M or Q), N.
Q3: Who can be a member of a team of size 5?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: M
Out of P, R and S only 1 can be in the team. If S is there, U and W will also be there. So, P and R should not be in the team for its size to be maximum.
Out of M and Q, only 1 can be there.
If L is there in the team, N and U cannot be in the team.
If L is not there in the team, then K is also not there in the team but N and U can be in the team.
So, the maximum team size is 5 consisting of S, U, W, (M or Q), N.
So, M can be a member of team size 5.
Q4: Who cannot be a member of a team of size 3?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: L
If L is in the team, the team should include K also. The team should have one among P, R and S and one among M and Q.
So, the team size cannot be 3 if L is in the team.
Que 3 : Instructions for Set 3
Two traders, Chetan and Michael, were involved in the buying and selling Of MCS shares over five trading days. At the beginning of the first day, the MCS share was priced at Rs 100, while at the end of the fifth day it was priced at Rs 110. At the end of each day, the MCS share price either went up by Rs 10, or else, it came down by Rs 10. Both Chetan and Michael took buying and selling decisions at the end of each trading day. The beginning price of MCS share on a given day was the same as the ending price of the previous day. Chetan and Michael started with the same number of shares and amount of cash, and had enough of both. Below are some additional facts about how Chetan and Michael traded over the five trading days.
- Each day if the price went up, Chetan sold 10 shares of MCS at the closing price. On the other hand, each day if the price went down, he bought 10 shares at the closing price.
- If on any day, the closing price was above Rs 110, then Michael sold 10 shares of MCS, while if it was below Rs 90, he bought 10 shares, all at the closing price.
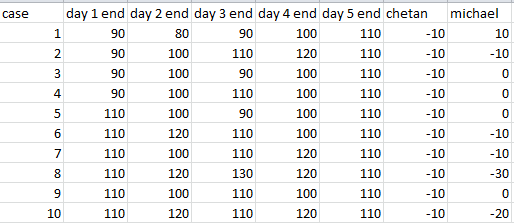
Q1: If Chetan sold 10 shares of MCS on three consecutive days, while Michael sold 10 shares only once during the five days, what was the price of MCS at the end of day 3?
Ans: Rs 110
The above table includes the values of the share price at the end of each day. Chetan and Michael column shows the number of shares at the end of 5th day with Chetan and Michael respectively. (-10 means he has sold 10 shares, +10 means he has bought 10 shares) there are 10 different possible cases according to the initial and final share price.
The question asks about the case where Chetan has sold 3 times and Michael sells only once.
Starting with Michael, for exactly one sell, the price should touch 120 only once as Michael sells the share only at price greater than 110.
if the price touches 120 twice or more, Michael will sell the share more than once which is not a desirable case.
Also, chetan has to sell thrice consecutively which is only possible if the share price is 90 at one instance and rises to 120 in straight 3 days.
This is only possible in case 2. Hence the price on 3rd day's end in case 2 is 110.
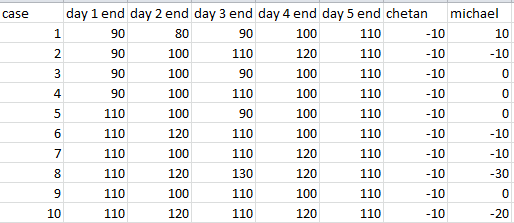
Q2: If Chetan ended up with Rs 1300 more cash than Michael at the end of day 5, what was the price of MCS share at the end of day 4?
Ans: Rs 100
The above table includes the values of the share price at the end of each day. Chetan and Michael column shows the number of shares at the end of 5th day with Chetan and Michael respectively. (-10 means he has sold 10 shares, +10 means he has bought 10 shares) there are 10 different possible cases according to the initial and final share price.
Please note that Chetan will always be having -10 shares(10 shares sold) and 1300 as cash.
This is because Chetan buys for every fall in price and sells for every rise in price. But the fluctuation in share price is constant as it starts from 100 and closes at 110 on day 5. So, in total Chetan will always sell 10 shares in all 5 days combined.
As Chetan has sold 10 shares, he'll get 110*10 =1100 cash because of it in every case. Also, Chetan earns Rs. 200 in every case because of buying at low and selling at high. So total cash Chetan will always have after 5 days = 1100+200 =1300.
The question asks about the case where Michael ended up with Rs 1300 cash less than Chetan.
As Chetan will have exactly 1300 cash in every case; we have to look for the cases where Michael does not make any profit and also does not have any sold shares at the end of 5 days.
This is possible in 4 cases ie. 3,4,5 and 9.
In each of these cases, the price fluctuates in the range 90-110 which does not allow Michael to buy or sell any shares.
Also, in all these cases the price of MCS is 100 at the end of day 4.
So the answer is 100.
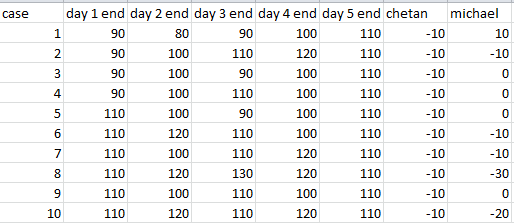
Q3: What could have been the maximum possible increase in combined cash balance of Chetan and Michael at the end of the fifth day?
Ans: Rs 5000
The above table includes the values of the share price at the end of each day. Chetan and Michael column shows the number of shares at the end of 5th day with Chetan and Michael respectively. (-10 means he has sold 10 shares, +10 means he has bought 10 shares) there are 10 different possible cases according to the initial and final share price.
Please note that Chetan will always be having -10 shares(10 shares sold) and 1300 as cash.
This is because Chetan buys for every fall in price and sells for every rise in price. But the fluctuation in share price is constant as it starts from 100 and closes at 110 on day 5. So, in total Chetan will always sell 10 shares in all 5 days combined.
As Chetan has sold 10 shares, he'll get 110*10 =1100 cash because of it in every case. Also, Chetan earns Rs. 200 in every case because of buying at low and selling at high. So total cash Chetan will always have after 5 days = 1100+200 =1300.
The question asks about the case where there has been the maximum possible increase in the combined cash balance of Chetan and Michael at the end of the fifth day.
As we know chetan has 1300 cash in all the cases , so we have to maximize the case where Michael has the most cash.
Also, if we see clearly, the profit made by selling and buying is in hundreds while the cash received by selling the shares is much far in terms of cash.
As 10 shares sold give = 10*110 = 1100 cash. So we have to look at the case where Michael has sold most shares which is case 8.
In case 8 the price rises from 100 to 110 ->120 ->130 ->120 ->110
in this case 110(0 new shares)->120(Michael sold 10 shares)->130(Michael sold 10 shares)120(Michael sold 10 shares)->110(Michael does nothing) = 30 shares sold in total
Cash = 20 shares at 120 and 10 shares at 130 = 120*20+130*10 = 2400+1300 =3700
As Chetan has 1300 cash and Michael has 3700 cash;
total cash they have is : 3700+1300 =5000
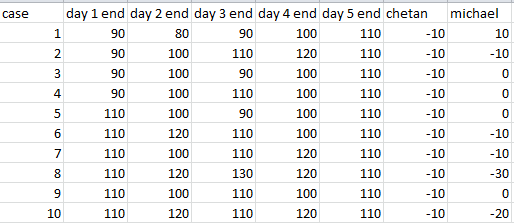
Q4: If Michael ended up with 20 more shares than Chetan at the end of day 5, what was the price of the share at the end of day 3?
Ans: Rs 90
The above table includes the values of the share price at the end of each day. Chetan and Michael column shows the number of shares at the end of 5th day with Chetan and Michael respectively. (-10 means he has sold 10 shares, +10 means he has bought 10 shares) there are 10 different possible cases according to the initial and final share price.
Please note that Chetan will always be having -10 shares(10 shares sold) and 1300 as cash.
To have 20 more shares than Chetan, Michael has to buy 10 shares which is case 1.
In case 1, the share price at the end of day 3 is 90.
|
77 videos|180 docs|96 tests
|
FAQs on TITA Based Questions: Grouping and Selections - Logical Reasoning (LR) and Data Interpretation (DI) - CAT
| 1. What are the key topics covered in the 2006 TITA exam related to Italian? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the grouping and selections portion of the 2006 TITA exam? |  |
| 3. Are there any recommended resources for studying Italian for the TITA exam? |  |
| 4. What are the common mistakes to avoid when taking the 2006 TITA exam? |  |
| 5. How is the scoring system structured for the 2006 TITA exam in Italian? |  |