Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT > Mnemonics : Heat Transfer in Nature
Mnemonics : Heat Transfer in Nature | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Heat Transfer Processes |

|
| Sea Breeze and Land Breeze |

|
| Water Cycle |

|
| Seepage of Water Beneath the Earth's Surface |

|
Heat Transfer Processes
1. Mnemonic: “Conduction – Direct Contact Does the Trick”
- Conduction → Direct Contact
- Explanation: Heat travels through solids by direct contact. In metals, vibrating particles pass energy along without moving from place to place.
2. Mnemonic: “Convection – Currents Carry Heat”
- Convection → Currents
- Explanation: In liquids and gases, heat moves as warm, less dense particles rise and cooler, denser particles sink, forming currents.
3. Mnemonic: “Radiation – Rays Race Through Space”
- Radiation → Rays Race
- Explanation: Heat travels in waves through space without any medium. For example, sunlight reaches Earth via radiation.
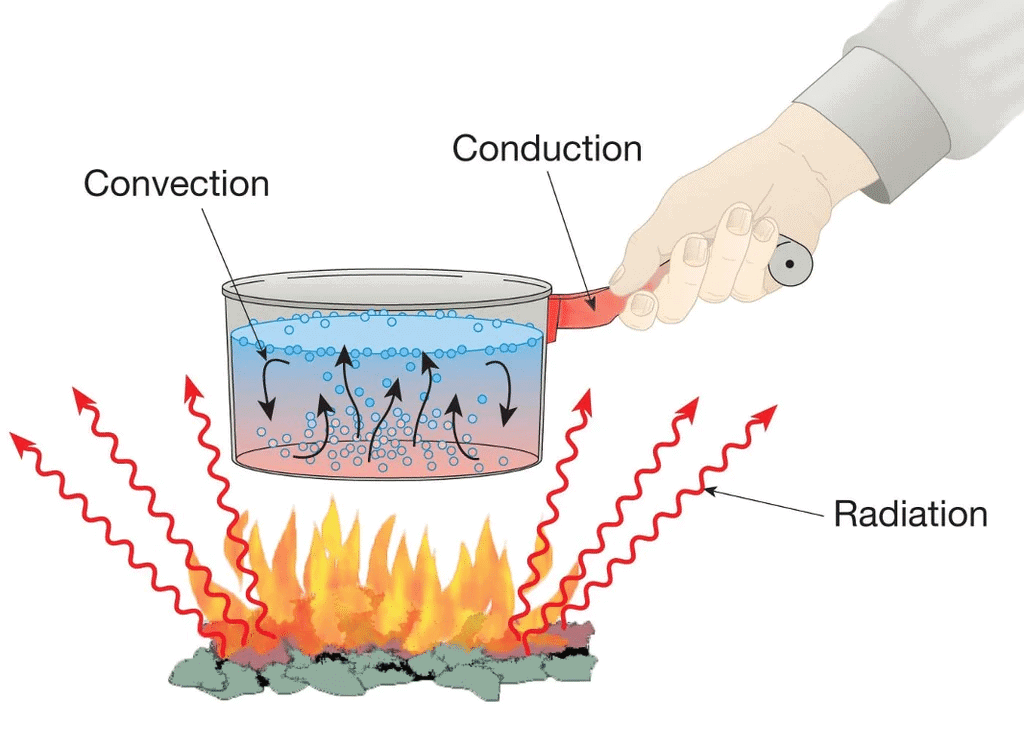
Overall Mnemonic to remember Heat Transfer Processes : Pan Cooking is C.C.R” – Conduction, Convection, Radiation
- Conduction: Heat moves from flame to pan
- Convection: Water circulates inside pan
- Radiation: Heat felt around the pan
Explanation: All three types work when you heat water in a pan.
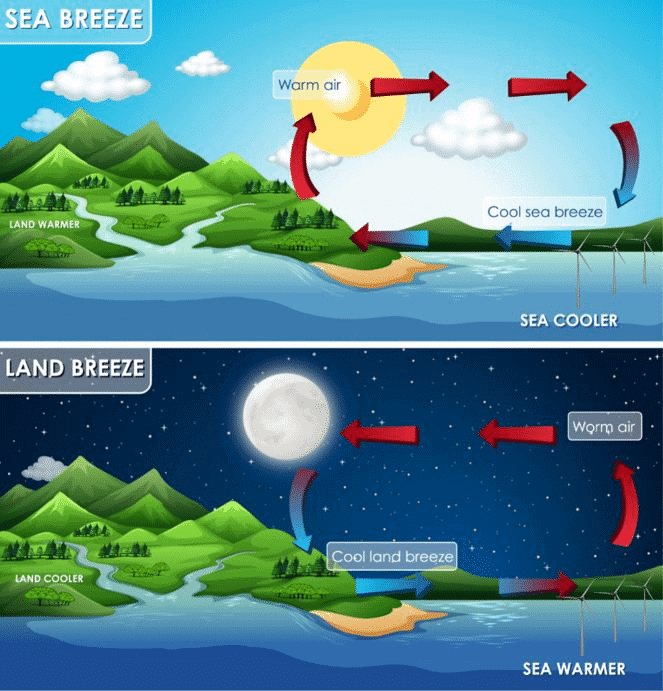
Sea Breeze and Land Breeze
Sea Breeze Mnemonic : Cool Sea Comes During Sun
Mnemonic Explanation: Cool air from sea comes during the day (sun is out), Warm air rises over land → cool air from sea replaces it
Land Breeze Mnemonic : Lazy Land Blows at Moonlight
Mnemonic Explanation: Cool air from land blows to sea at night (moon is out), Warm air over sea → cool land air moves in
Water Cycle
Mnemonic : “E.C.P.T.I.R” – Every Cloud Produces The Important Rain
- Every - Evaporation
- Cloud - Condensation
- Produces - Precipitation
- The - Transpiration
- Important - Infiltration
- Rain - Runoff
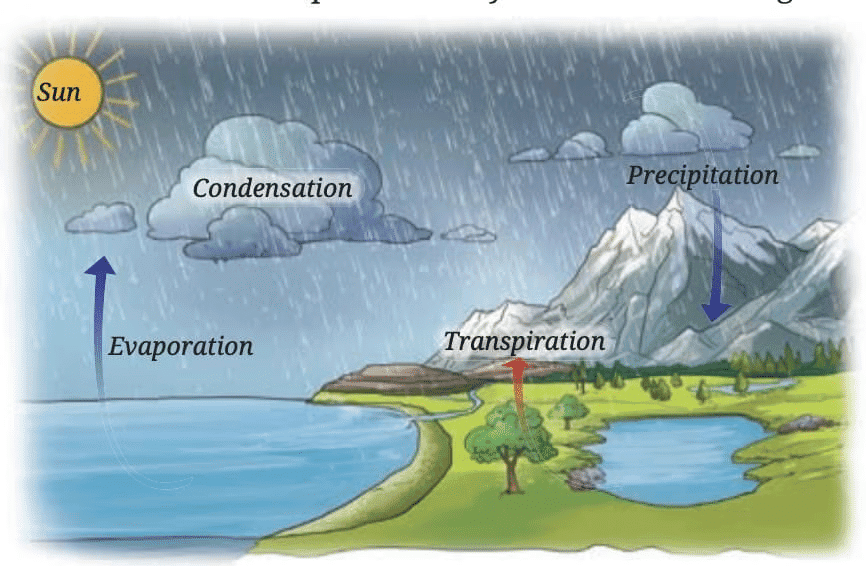
Explanation:
- During summer, snow and ice melt due to the Sun’s radiation, forming rivers that flow into oceans. Fresh snow replenishes the ice in winter.
- Water in oceans, rivers, and lakes evaporates due to the Sun’s heat. Plants also release water vapor through transpiration.
- Water vapor rises, cools, and condenses to form clouds. Clouds cause precipitation (rain, snow, hail).
- This continuous movement of water—evaporation, condensation, precipitation, infiltration, and runoff—is called the water cycle
Seepage of Water Beneath the Earth's Surface
Mnemonic : “Gravel Slips, Sand Sips, Clay Clings”
- Gravel: Water slips through quickly
- Sand: Water sips through slowly
- Clay: Water clings, moves very slowly
Explanation: Based on particle size and pore space, affecting infiltration speed.
The document Mnemonics : Heat Transfer in Nature | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT is a part of the Class 7 Course Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics : Heat Transfer in Nature - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between a sea breeze and a land breeze? |  |
Ans. A sea breeze occurs during the day when the land heats up faster than the sea, causing the warm air over the land to rise and cooler air from the sea to move in to replace it. In contrast, a land breeze occurs at night when the land cools down more quickly than the sea, resulting in cooler air from the land moving towards the warmer sea.
| 2. How does the water cycle work? |  |
Ans. The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It includes processes such as evaporation (water turning into vapor), condensation (vapor forming clouds), precipitation (rain or snow falling), and collection (water gathering in bodies of water). This cycle helps maintain the Earth's water supply.
| 3. What is seepage of water beneath the Earth's surface? |  |
Ans. Seepage refers to the process where water moves through soil and rock layers underground. It can occur due to rainfall, irrigation, or melting snow. This water can replenish groundwater supplies, which are important for drinking water and agriculture.
| 4. Why is heat transfer important in nature? |  |
Ans. Heat transfer is crucial in nature as it regulates temperatures, influences weather patterns, and affects ecosystems. It helps in the distribution of heat from the sun, which warms the Earth, and contributes to processes like evaporation and convection, impacting climate and living organisms.
| 5. What are some examples of heat transfer processes in nature? |  |
Ans. Examples of heat transfer processes in nature include conduction (heat transfer through direct contact), convection (heat transfer through fluid movement, like air or water currents), and radiation (heat transfer through electromagnetic waves, like sunlight). These processes are fundamental in phenomena such as weather changes and ocean currents.
Related Searches




















