Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids - 1 | Biochemistry - NEET PG PDF Download
Chemistry of Amino Acids
General Structure of Alpha Amino Acids
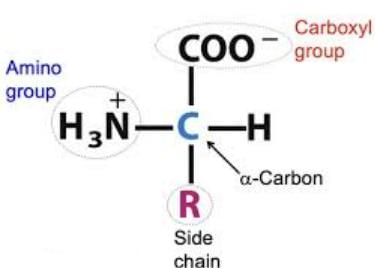
Structure: An alpha amino acid consists of:
A central alpha carbon (Cα) bonded to:
- A carboxyl group (-COOH)
- An amino group (-NH₂)
- A hydrogen atom
- A variable side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid
Non-Alpha Amino Acids
Definition: Amino acids where the amino group is not attached to the alpha carbon (e.g., beta, gamma, or other positions).
Example from PDF: Beta-Alanine(explicitly discussed on PAGE5 and PAGE6):
- A non-alpha amino acid with the amino group on the beta carbon.
- Sources:
- Formed from degradation of cytosine and uracil.
- Hydrolysis of beta-alanyl dipeptides.
- Found in:
- Pantothenic Acid
- Coenzyme A
- Acyl Carrier Protein
- Beta-Alanyl Dipeptides (e.g., Carnosine, Anserine)
- Note: Beta-alanine is highlighted as a "very important topic for national board pattern exams."
- Other Non-Alpha Amino Acids: Not explicitly listed in the PDF excerpt but implied in the context of beta-alanine’s unique structure compared to alpha amino acids.
Imino Acids
- Definition: Amino acids with a secondary amine group, where the nitrogen is part of a ring structure, technically making them imino acids.
- Example from PDF: Proline(explicitly classified as an imino acid on PAGE2):
- Contains a pyrrolidine ring, where the alpha amino group is a secondary amine.
- Classified as a nonpolar (hydrophobic) amino acid.
- Special group: Pyrrolidine.
- Note: Proline is unique due to its cyclic structure, affecting protein folding.
- Color Reaction: Proline gives a yellow color with ninhydrin (unlike the purple color of most alpha amino acids).
Classification of Amino Acids
Based on Chemical Structure
Branched Chain Amino Acids:
- Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
- Mnemonic: LIV Amino Acids
Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids:
- Cysteine, Methionine
Amino Acids with Hydroxyl Group:
- Serine, Threonine
Amino Acids with Amide Group:
- Asparagine, Glutamine
Acidic Amino Acids:
- Aspartic Acid (Aspartate), Glutamic Acid (Glutamate)
Basic Amino Acids:
- Arginine (most basic), Lysine, Histidine
Aromatic Amino Acids:
- Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan, Histidine
- Notes:
- Tryptophan and Histidine have heterocyclic aromatic rings (contain more than one atom type).
- Tyrosine has a hydroxyl group.
- Histidine has basic properties.
Imino Acid:
- Proline (explicitly noted as an imino acid).
Based on Side Chain Characteristics (Polarity)
Polar Amino Acids (Hydrophilic):
Charged:
- Acidic: Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid
- Basic: Histidine, Arginine, Lysine
Uncharged:
- Aliphatic with hydroxyl group: Serine, Threonine
- Aliphatic with amide group: Asparagine, Glutamine
- Simple: Glycine
- Sulfur-containing: Cysteine
Nonpolar Amino Acids (Hydrophobic):
- Simple: Alanine
- Sulfur-containing: Methionine
- Aromatic (except Histidine): Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
- Branched Chain: Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
- Imino Acid: Proline
Concepts:
- Learn polar and nonpolar amino acids by group classification.
- Mnemonic: ABC (Acidic and Basic are Charged).
- All branched chain amino acids are nonpolar.
- All aromatic amino acids except Histidine are nonpolar.
Based on Metabolic Fate
Ketogenic:
- Purely Ketogenic: Leucine
- Predominantly Ketogenic: Lysine
Both Glucogenic and Ketogenic:
- Phenylalanine, Isoleucine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan
- Mnemonic: LPITT (Lysine, Phenylalanine, Isoleucine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan)
- Glucogenic: All other amino acids not listed above.
- Concept: Learn ketogenic amino acids first, then those that are both glucogenic and ketogenic; the rest are glucogenic.
Based on Nutritional Requirement
Essential:
- Methionine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Phenylalanine, Lysine, Histidine
- Mnemonic: MeTT VIL PHLY
Semiessential:
- Arginine (required for growing children)
Nonessential:
- All other amino acids.
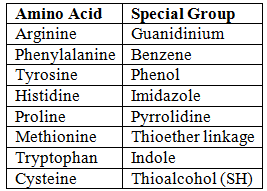
Special Groups Present in Amino Acids
Conservative (Homologous) Substitution
Definition: Replacement of an amino acid with another of similar characteristics.
Groups:
- Hydrophilic, Acidic: Aspartate, Glutamate
- Hydrophilic, Basic: Histidine, Arginine, Lysine
- Polar, Uncharged: Serine, Threonine, Glutamine, Asparagine
- Hydrophobic: Alanine, Phenylalanine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
Nonconservative (Nonhomologous) Substitution
- Definition: Replacement of an amino acid with another of different characteristics.
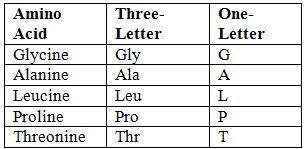
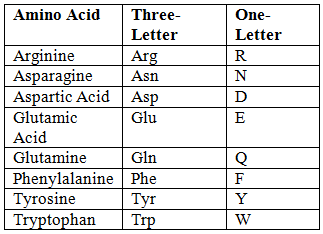
Abbreviations of Amino Acids
- Unique First Letter:
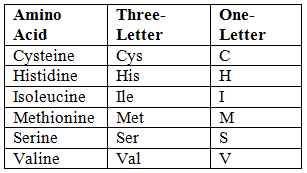
- Non-Unique First Letter:
- Phonetic Abbreviations:
- Close to Initial Letter:

21st and 22nd Amino Acids
Selenocysteine:
- 21st amino acid, coded by UGA stop codon.
- Precursor: Serine, modified to cysteine with selenium replacing sulfur.
- Found in ~24 selenoproteins (e.g., Thioredoxin reductase, Glutathione peroxidase).
Pyrrolysine:
- 22nd amino acid, coded by UAG stop codon.
- Found in some archaea and bacteria.
Properties of Amino Acids
Optical Activity and Isomerism
- Chirality: Most amino acids have a chiral alpha carbon, forming L- and D-enantiomers.
- L-Isomers: Predominant in proteins.
- D-Amino Acids:
- Free D-Aspartate, D-Serine (brain tissue).
- D-Alanine, D-Glutamate (bacterial cell walls).
- Bacillus subtilis: D-Methionine, D-Tyrosine, D-Leucine, D-Tryptophan.
- Vibrio cholerae: D-Leucine, D-Methionine.
- Glycine: No chiral carbon, optically inactive.
Charge at Physiological pH (7.4)
- Carboxyl group: Negatively charged.
- Amino group: Positively charged.
- At pH > pI: Amino acid is negatively charged.
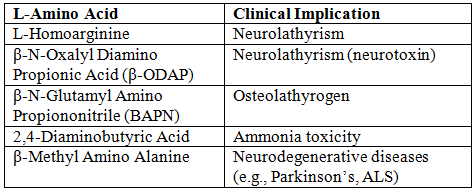
Potentially Toxic L-Amino Acids
UV Light Absorption
- Aromatic amino acids (Tryptophan, Phenylalanine, Tyrosine) absorb UV light (250–290 nm, max at 280 nm).
- Tryptophan has the highest absorption.
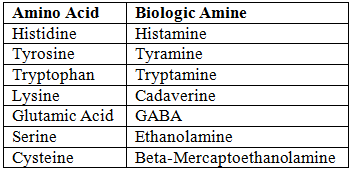
Decarboxylation of Amino Acids
- Process: Alpha decarboxylation forms biologic amines.
- Coenzyme: Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP).
- Examples:
Color Reactions
- Biuret Test: Detects proteins (requires ≥ 2 peptide bonds).
- Ninhydrin Test: Detects alpha amino acids (purple complex, except Proline: yellow, Glutamine/Asparagine: brown).
- Other Tests:
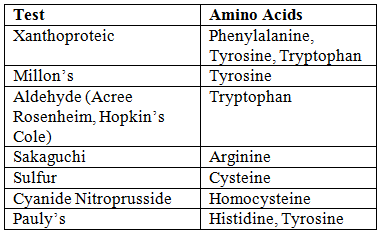
Buffering Action
- Henderson-Hasselbalch: pH = pKa + log([Base]/[Acid]).
- pKa Ranges:
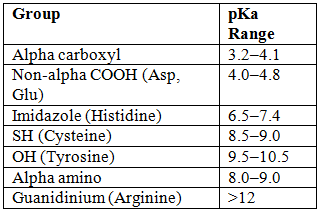
- Histidine has maximum buffering capacity at pH 7.4.
High-Yielding Facts
- Simplest: Glycine
- Most hydrophobic: Isoleucine
- Second most hydrophobic: Valine
- Most polar: Arginine
- Most abundant in proteins: Alanine
- Most abundant in plasma: Glutamine
Amino Acids as Neurotransmitters
- Glycine: Inhibitory (brainstem, spinal cord).
- Glutamate: Excitatory.
- Derivatives: Dopamine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, Serotonin, GABA.
Digestion of Proteins
- Endopeptidases: Pepsin, Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Elastase.
- Exopeptidases: Carboxypeptidases, Aminopeptidases, Dipeptidases, Tripeptidases.
- Zymogen Activation: Pepsinogen → Pepsin; Trypsinogen → Trypsin (by enteropeptidase).
Biosynthesis of Urea (Urea Cycle)
- Site: Liver (mitochondria and cytoplasm).
- Reactions:
- Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase-I (CPS-I)
- Ornithine Transcarbamoylase (OTC)
- Argininosuccinate Synthetase
- Argininosuccinate Lyase
- Arginase
- N-Acetylglutamate Synthase
- Energetics: 4 high-energy phosphates, 3 ATPs directly.
- Urea Bicycle: Linked to TCA cycle via fumarate and aspartate.
Transamination
- Enzyme: Transaminase.
- Coenzyme: PLP.
- Examples: ALT (Alanine + α-Ketoglutarate → Pyruvate + Glutamate), AST (Aspartate + α-Ketoglutarate → Oxaloacetate + Glutamate).
- Exceptions: Proline, Hydroxyproline, Threonine, Lysine.
Oxidative Deamination
- Enzyme: Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH).
- Coenzymes: NAD⁺, NADP⁺.
- Minor Pathway: L-Amino Acid Oxidase (FMN, H₂O₂).
Nonoxidative Deamination
- Dehydrases (Serine, Threonine), Histidase (Histidine), Desulfhydrases (Cysteine, Homocysteine).
Transdeamination
- Transamination + Oxidative Deamination.
Transport of Ammonia
- From Tissues/Brain: As glutamine (Glutamine Synthetase).
- From Skeletal Muscle: As alanine.
Urea Cycle Disorders
Disorders:
- Hyperammonemia Type I (CPS-I)
- Hyperammonemia Type II (OTC, most common, X-linked)
- Citrullinemia Type I
- Arginosuccinic Aciduria
- Hyperargininemia
- Citrullinemia Type II (Citrin)
- HHH Syndrome (Ornithine Transporter)
Biochemical Investigation
- Ammonia: Berthelot, Glutamate Dehydrogenase, Electrodes.
- Urea: Diacetyl Monoxime, Urease.
- Tool: Tandem Mass Spectrometry.
Treatment
- Arginine: Provides ornithine, contraindicated in arginase deficiency.
- Acylation: Sodium Benzoate (hippuric acid), Sodium Phenylacetate (phenylacetylglutamine).
Individual Amino Acid Metabolism
Phenylalanine
- Aromatic, essential, hydrophobic, partly glucogenic/ketogenic.
Tyrosine
- Aromatic, nonessential, partly glucogenic/ketogenic.
Synthesis of Tyrosine
- Enzyme: Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (monooxygenase, tetrahydrobiopterin, NADPH).
Catabolism of Tyrosine
- Pathway:
- Tyrosine → p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate → Homogentisate → Maleylacetoacetate → Fumarylacetoacetate → Fumarate + Acetoacetate.
- Enzymes: Tyrosine Transaminase, p-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Hydroxylase, Homogentisate Oxidase, Maleylacetoacetate Isomerase, Fumarylacetoacetate Hydrolase.
Specialized Products
- Melanin, Catecholamines, Thyroxine.
|
48 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids - 1 - Biochemistry - NEET PG
| 1. What are the different classifications of amino acids based on their side chains? |  |
| 2. What are the common abbreviations for the 20 standard amino acids? |  |
| 3. How do amino acids undergo decarboxylation, and what is its significance? |  |
| 4. What is the process of protein digestion in the human body? |  |
| 5. What are the key metabolic pathways involving individual amino acids? |  |