Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids - 2 | Biochemistry - NEET PG PDF Download
Synthesis of Melanin
- Location: Occurs in the melanosome of melanocytes in deeper epidermis layers.
- Regulation: Influenced by Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormone (MSH).
- Function: Melanin provides pigmentation to skin and hair.
- Key Enzyme: Tyrosinase
- Role: Rate-limiting step in melanin synthesis.
- Type: Monooxygenase.
- Cofactor: Copper (Cu²⁺).
- Function: Catalyzes two reactions converting tyrosine to DOPA and then to dopaquinone.
Synthesis of Catecholamines
- Catecholamines: Dopamine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine.
- Structure: Contain a catechol nucleus.
- Synthesis Sites: Chromaffin cells of adrenal medulla and sympathetic ganglia.
- Adrenal Medulla: Primarily produces epinephrine (80%).
- Sympathetic Nerves: Primarily produces norepinephrine (80%).
- Note: Epinephrine is also known as adrenaline.
- Steps of Synthesis from Tyrosine to Epinephrine:
- Ring Hydroxylation: Tyrosine to DOPA by tyrosine hydroxylase.
- Decarboxylation: DOPA to dopamine by DOPA decarboxylase.
- Side Chain Hydroxylation: Dopamine to norepinephrine.
- N-Methylation: Norepinephrine to epinephrine.
- Key Enzyme: Tyrosine Hydroxylase
- Role: Rate-limiting step.
- Type: Monooxygenase.
- Cofactor: Tetrahydrobiopterin.
- Similarity: Similar to phenylalanine hydroxylase.
- Tyrosinase vs. Tyrosine Hydroxylase:
- Tyrosinase: Expressed in melanocytes, uses Cu²⁺, produces DOPA for melanin.
- Tyrosine Hydroxylase: Expressed in catecholamine synthesis sites, uses tetrahydrobiopterin, produces DOPA for catecholamines.
- DOPA Decarboxylase:
- Location: Present in all tissues.
- Coenzyme: Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP).
Degradation of Catecholamines
Half-Life: 2–5 minutes.
Enzymes:
- Catechol O-Methyl Transferase (COMT): Initial catabolism of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
- Monoamine Oxidase (MAO): Further degradation.
End Products:
- Epinephrine/Norepinephrine: Vanillyl Mandelic Acid (VMA).
- Urinary Excretion: 2–6 mg/24 hours.
- Dopamine: Homovanillic Acid (HVA).
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormones
Substrate: Thyroglobulin (large iodinated glycosylated protein with 115 tyrosine residues).
Process:
- Tyrosine residues iodinated to form Mono-IodoTyrosine (MIT) and Di-IodoTyrosine (DIT).
- Coupling reactions:
- MIT + DIT → Tri-iodothyronine (T3).
- DIT + DIT → Tetra-iodothyronine (T4, Thyroxine).
Clinical Correlations: Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism
Metabolic Disorders of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Catabolism
Phenylketonuria (PKU):
- Type: Classic PKU (Type I).
- Prevalence: Most common amino acid metabolic disorder.
- Biochemical Defect: Phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
- Phenylalanine cannot be converted to tyrosine.
- Leads to elevated phenylalanine levels in blood.
- Alternate pathways produce phenylketones (phenylpyruvate, phenylacetate), excreted in urine.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Normal at birth.
- Untreated: Progressive intellectual disability, vomiting (may mimic pyloric stenosis), hyperactivity, autistic behaviors (hand movements, rocking, athetosis).
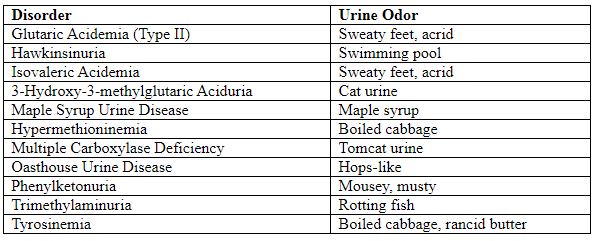
- Lighter complexion due to reduced melanin synthesis.
- Musty/mousey odor from phenylacetic acid.
- CNS damage due to high phenylalanine levels inhibiting transport of other large neutral amino acids (tyrosine, tryptophan) across the blood-brain barrier.
- Lab Diagnosis:
- Guthrie’s Test: Bacterial inhibition assay, rapid blood screening using Bacillus subtilis (growth proportional to phenylalanine).
- Ferric Chloride Test: Detects phenylketones in urine (outdated in developed countries).
- Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Method of choice, identifies all hyperphenylalaninemia forms.
- Other Methods: Molecular biology (phenylalanine hydroxylase probes), quantitative blood phenylalanine (>20 mg/dl), enzyme assay in dry blood spots.
- Treatment:
- Low-phenylalanine diet.
- Large Neutral Amino Acids (LNAAs) supplementation to compete with phenylalanine for transport across blood-brain barrier.
- Sapropterin dihydrochloride (Kuvan): Synthetic tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) for patients with residual phenylalanine hydroxylase activity.
- Recombinant phenylalanine ammonia lyase trials.
- Nonclassical PKU:
- Biochemical Defect: Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency.
- Type II & III: Dihydrobiopterin reductase defect.
- Type IV & V: Defects in tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis enzymes (6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase, GTP cyclohydrolase).
- Lab Diagnosis:
- Measurement of neopterin and biopterin in urine.
- Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) loading test normalizes plasma phenylalanine.
- Enzyme assay in dry blood spots.
- Genetic mutation analysis.
- Biochemical Defect: Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency.
- Alkaptonuria:
- Inheritance: Autosomal recessive, part of Garrod’s Tetrad (Alkaptonuria, Albinism, Pentosuria, Cystinuria).
- Biochemical Defect: Homogentisate oxidase deficiency.
- Accumulation of homogentisic acid, polymerizes to alkaptone bodies.
- Clinical Presentation:
- Normal until 3rd/4th decade.
- Children: Urine darkens on standing.
- Adults: Ochronosis (alkaptone deposition in intervertebral disks, cartilage), arthritis.
- No mental retardation.
- Lab Diagnosis:
- Alkalinization darkens urine.
- Positive Benedict’s, ferric chloride, silver nitrate tests (homogentisic acid is a reducing agent).
- Treatment:
- Nitisinone (NTBC): Inhibits para-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase to reduce homogentisic acid.
- Symptomatic treatment.
Tyrosinemia:
- Type I (Hepatorenal Tyrosinemia):
- Biochemical Defect: Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase deficiency.
- Affected Organs: Liver, kidney, peripheral nerves.
- Cause of Damage: Accumulation of fumarylacetoacetate and succinylacetone.
- Odor: Cabbage-like due to succinylacetone.
- Diagnosis: Elevated succinylacetone in urine/blood (plasma tyrosine less diagnostic).
- Treatment: Low phenylalanine/tyrosine diet, Nitisinone.
- Type II (Oculocutaneous Tyrosinemia):
- Biochemical Defect: Tyrosine transaminase deficiency.
- Clinical Features: Palmar/plantar hyperkeratosis, herpetiform corneal ulcers, intellectual disability.
- Type III (Neonatal Tyrosinemia):
- Biochemical Defect: Para-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase (4-HPPD) deficiency.
Hawkinsinuria:
- Inheritance: Autosomal dominant.
- Biochemical Defect: Missense mutations in para-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase.
- Mutant enzyme forms hawkinsin (reacts with cysteine) instead of homogentisic acid.
- Secondary glutathione deficiency.
- Odor: Swimming pool-like.
Segawa Syndrome:
- Biochemical Defect: GTP cyclohydrolase deficiency (tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency).
- Features: No hyperphenylalaninemia, autosomal dominant, dystonia with diurnal variation, females more affected.
Albinism:
- Biochemical Defect: Tyrosinase deficiency (melanin synthesis).
- Types:
- Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA):
- OCA-1: Tyrosinase deficient.
- OCA-2: Tyrosinase positive (most common).
- OCA-3: Rufous/red OCA.
- Syndromes: Prader-Willi, Angelman, Hermansky-Pudlak, Chédiak-Higashi.
- Ocular Albinism: Nettleship-Falls type.
- Localized Albinism: Piebaldism, Waardenburg syndrome.
- Oculocutaneous Albinism (OCA):
Pheochromocytoma:
- Description: Catecholamine-producing tumors (adrenal/extra-adrenal).
- Clinical Triad: Palpitations, headaches, profuse sweating, associated with hypertension.
- Biochemical Testing:
- Elevated plasma/urinary catecholamines, metanephrines, VMA.
- Tests:
- Urinary: VMA, catecholamines, fractionated/total metanephrines.
- Plasma: Catecholamines, free metanephrines.
- Associated Syndromes: Neurofibromatosis type 1, Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) 2A/2B.
Tryptophan Metabolism
Characteristics:
- Aromatic, essential amino acid.
- Contains indole group.
- Glucogenic and ketogenic.
Catabolic Pathway: Kynurenine-Anthranilate Pathway.
- Key Enzyme: Tryptophan Pyrrolase (Tryptophan Oxygenase).
- Type: Dioxygenase, heme-containing.
- Kynureninase:
- Coenzyme: PLP.
- Deficiency: Leads to reduced NAD+ synthesis, niacin deficiency, pellagra-like symptoms, xanthurenate excretion in urine.
Specialized Products:
Niacin (Nicotinic Acid):
- 3% of tryptophan enters this pathway.
- 60 mg tryptophan → 1 mg niacin.
- Rate-Limiting Enzyme: Quinolinate Phosphoribosyl Transferase.
Serotonin (5-Hydroxytryptamine):
- Synthesis Sites: Argentaffin cells (intestine), mast cells, platelets, brain.
- Functions: Neurotransmitter, mood elevation, GI motility, temperature regulation, vasoconstriction.
- Key Enzyme: Tryptophan Hydroxylase.
- Role: Rate-limiting step, converts tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan.
- Cofactor: Tetrahydrobiopterin.
- Amino Acid Decarboxylase: Converts 5-hydroxytryptophan to serotonin (PLP coenzyme).
- Catabolism: By monoamine oxidase, produces 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid (5-HIAA).
- Urinary Excretion: <5 mg/day.
Melatonin:
- Synthesis Site: Pineal gland.
- Process: N-acetylation of serotonin followed by N-methylation (methyl donor: S-Adenosyl Methionine).
- Functions: Diurnal variation, biological rhythm, sleep-wake cycle.
Metabolic Disorders:
Carcinoid Syndrome:
- Description: Gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumor of argentaffin cells, overproduces serotonin.
- Symptoms: Intermittent diarrhea (32–84%), flushing (63–75%), sweating, fluctuating hypertension, pellagra-like symptoms.
- Diagnosis: Elevated serum serotonin, urinary 5-HIAA, neuroendocrine markers (chromogranin A, neuron-specific enolase, synaptophysin).
- Typical Carcinoid:
- Midgut tumor, increased serotonin synthesis, elevated blood/platelet serotonin, urinary 5-HIAA.
- Atypical Carcinoid:
- Foregut tumor, aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency.
- 5-Hydroxytryptophan secreted, normal plasma serotonin, increased urinary 5-HTP/5-HT, slightly elevated 5-HIAA.
Hartnup Disorder:
- Inheritance: Autosomal recessive.
- Biochemical Defect: Defective absorption of tryptophan and neutral amino acids (BOAT1 transporter, SLC6A19 gene).
- Clinical Features: Asymptomatic, cutaneous photosensitivity, intermittent ataxia, pellagra-like symptoms (due to niacin deficiency).
- Diagnosis: Positive Obermeyer test (indole compounds in urine).
- Treatment: Lipid-soluble amino acid esters, nicotinic acid/nicotinamide (50–300 mg/24 hr), high-protein diet.
Blue Diaper Syndrome:
- Biochemical Defect: Tryptophan malabsorption in intestine (not kidney).
- Feature: Blue diaper staining due to bacterial breakdown of unabsorbed tryptophan to indican and indigoblue.
Simple Amino Acids
Glycine
Characteristics: Simplest, nonessential, glucogenic, optically inactive.
Biosynthesis:
- From glyoxylate, glutamate, alanine by glycine aminotransferase.
- From serine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (reversible, requires PLP and folic acid).
- From threonine by threonine aldolase.
- In invertebrates: Glycine synthase system.
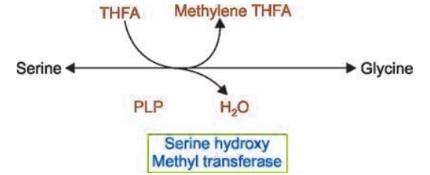
Catabolism: Glycine Cleavage System (liver mitochondria).
- Components:
- Glycine dehydrogenase.
- Aminomethyltransferase.
- Dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase.
- H protein (dihydrolipoyl moiety).
- Reaction: Glycine + THFA + NAD⁺ → CO₂ + NH₃ + N5,N10-Methenyl THFA + NADH + H⁺.
- Specialized Products:
- Creatine, creatine phosphate, creatinine.
- Heme.
- Purine nucleotides (C4, C5, N7 of purine ring).
- Glutathione.
- Functions:
- Conjugation: Bile acids (glycocholic acid), benzoic acid (hippuric acid).
- Neurotransmitter: Excitatory and inhibitory.
- Collagen: Every third amino acid is glycine.
- Creatinine Synthesis:
- Amino Acids: Glycine, arginine, methionine.
- Steps:
- Kidney: Glycine + arginine → guanidinoacetic acid (glycine arginine amidotransferase).
- Liver: Guanidinoacetic acid → creatine (guanidinoacetate methyltransferase, SAM as methyl donor).
- Muscle: Creatine → creatine phosphate (creatine kinase).
- Spontaneous: Creatine phosphate → creatinine.
Glutathione:
Composition: Gamma-glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine (tripeptide, pseudopeptide).
- Functions:
- Meister’s cycle: Amino acid transport (intestine, kidney, brain, 3 ATP/mol).
- Free radical scavenging (RBC membrane integrity).
- Reduction of methemoglobin (keeps heme iron ferrous).
- Conjugation in phase II xenobiotic reactions (glutathione S-transferase).
- Coenzyme for some reactions.
- Derivatives:
- Sarcosine: N-methyl glycine.
- Betaine: Trimethyl glycine.
- Metabolic Disorders:
- Primary Hyperoxaluria Type I:
- Biochemical Defect: Alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase deficiency (liver peroxisomes, pyridoxine cofactor).
- Feature: Protein targeting defect.
- Primary Hyperoxaluria Type II:
- Biochemical Defect: D-glycerate dehydrogenase/glyoxylate reductase deficiency.
- Secondary Hyperoxaluria:
- Pyridoxine deficiency.
- Ethylene glycol ingestion.
- High vitamin C doses.
- Methoxyflurane anesthesia.
- Inflammatory bowel disease/ bowel resection.
- Nonketotic Hyperglycinemia:
- Biochemical Defect: Glycine cleavage system deficiency.
Alanine
- Characteristics: Simple, nonessential, principal glucogenic amino acid.
- Functions:
- Transports amino groups from skeletal muscle.
- Participates in glucose-alanine cycle (Cahill cycle).
- Biosynthesis: From pyruvate by transamination.
Serine
- Characteristics: Hydroxyl group-containing, glucogenic, nonessential, polar.
- Biosynthesis:
- From glycine by serine hydroxymethyltransferase (PLP coenzyme).
- From 3-phosphoglycerate (glycolytic intermediate).
- Vitamins: Folic acid, pyridoxine for serine-to-glycine conversion.
- Metabolic Functions:
- Primary donor of one-carbon groups.
- Precursor for cysteine (serine + homocysteine → cysteine + homoserine).
- Phospholipid synthesis (phosphatidylserine).
- Drug analogs: Cycloserine (antituberculous), azaserine (anticancer).
- Synthesis of ethanolamine, choline, betaine.
- Precursor of selenocysteine.
- O-glycosylation at serine/threonine residues.
- Phosphorylation sites (serine/threonine).
- Sphingosine synthesis (serine + palmitoyl CoA → ceramide → sphingolipids).
Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids
Methionine
Characteristics: Essential, glucogenic.
Metabolism:
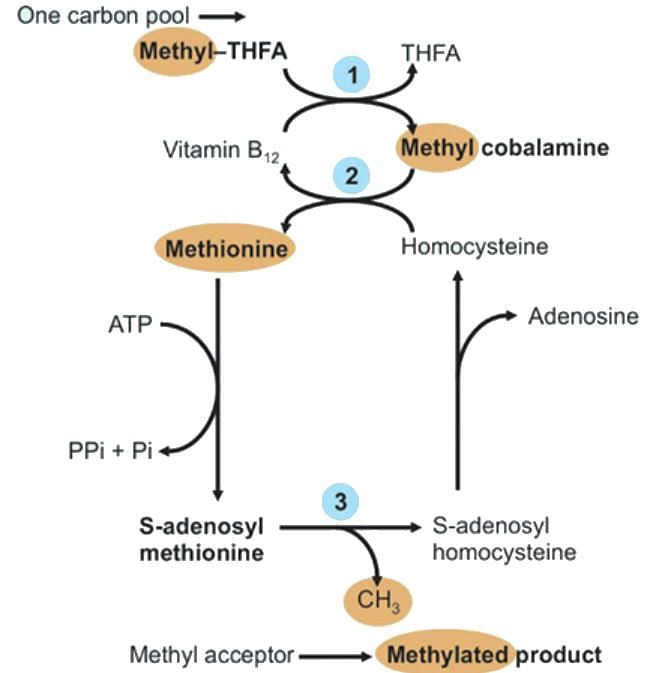
- Step 1: Conversion to S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) by methionine adenosyl transferase (MAT).
- Isoenzymes: MAT-I, MAT-III (liver), MAT-II (extrahepatic).
- Function: SAM is the principal methyl donor (methyl group labile due to adenosyl group).
- Step 2: SAM to homocysteine.
Fates of Homocysteine:
- Resynthesis of Methionine: Methyl group transfer from N5-methyl THFA (vitamin B12, folate).
- Cysteine Synthesis (Transsulfuration):
- Homocysteine + serine → cystathionine (cystathionine beta synthase, PLP).
- Cystathionine → cysteine + homoserine (cystathionase, PLP).
- Homoserine → propionyl CoA → succinyl CoA.
Functions of SAM:
- Transmethylation (e.g., guanidinoacetate → creatine, norepinephrine → epinephrine).
- DNA methylation.
- Polyamine synthesis:
- Ornithine → putrescine (ornithine decarboxylase, rate-limiting).
- SAM (decarboxylated) donates carbons/amino group to form spermidine, spermine.
- Polyamine Functions: DNA/RNA stabilization, cell proliferation, growth, membrane stabilization, carcinogenesis.
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin B12, folic acid: Methionine synthase.
- Vitamin B6: Cystathionine beta synthase, cystathionase.
- Folate Trap:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency blocks N5-methyl THFA to THFA conversion.
- Folate trapped as N5-methyl THFA, causing THFA starvation and impaired one-carbon metabolism.
- Homocysteine accumulates (risk for acute coronary syndrome).
Cysteine
- Characteristics: Nonessential, glucogenic.
- Specialized Products:
- Cystine (condensation of two cysteines).
- Taurine.
- Glutathione.
- Betamercaptoethanolamine (from decarboxylation).
- Coenzyme A.
- Role in Aging:
- Cysteine and taurine decrease aging (aging as cysteine deficiency syndrome).
- Homocysteine accelerates aging.
Metabolic Disorders
Classic Homocystinuria:
Biochemical Defect: Cystathionine beta synthase deficiency.
- Homocysteine not converted to cysteine (cysteine deficiency).
- Excess homocysteine → methionine (hypermethioninemia).
Clinical Features:
- Normal at birth, nonspecific infancy symptoms (failure to thrive, developmental delay).
- After age 3: Ectopia lentis (severe myopia, iridodonesis), intellectual disability, Marfan-like skeletal abnormalities, fair complexion, malar flush, thromboembolism.
Diagnosis:
- Elevated methionine, homocystine; low cystine in plasma.
- Cyanide nitroprusside test (urine, homocystine unstable).
- Enzyme analysis (liver, fibroblasts), DNA mutation analysis.
Treatment:
- High-dose vitamin B6 (200–1000 mg/24 hr).
- Folic acid (1–5 mg/24 hr) for non-responders.
- Methionine restriction, cysteine supplementation.
- Betaine (remethylates homocysteine to methionine).
- Vitamin C (1 g/day) for endothelial function.
Nonclassic Homocystinuria:
Causes:
- Methylcobalamin Formation Defect:
- Methionine synthase cofactor deficiency.
- Homocysteine accumulation, hypomethioninemia, megaloblastic anemia.
- Treatment: Hydroxycobalamin (1–2 mg/24 hr).
- Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Deficiency:
- Blocks N5,N10-methylene THFA to N5-methyl THFA.
- Hypomethioninemia, homocystinemia, no megaloblastic anemia.
- Treatment: Folic acid, vitamin B6, B12, methionine, betaine.
Cystathioninuria:
- Biochemical Defect: Cystathionase deficiency.
- Features: Mental retardation, anemia, thrombocytopenia.
- Diagnosis: Negative cyanide nitroprusside test.
Cystinuria:
- Description: Part of Garrod’s Tetrad.
- Biochemical Defect: Defective dibasic amino acid transporter (cystine, ornithine, lysine, arginine; COLA).
- Features: Cystine stones in urine.
- Diagnosis: Positive cyanide nitroprusside test.
- Treatment: Hydration, urine alkalinization.
Oasthouse Syndrome:
- Biochemical Defect: Malabsorption of methionine and neutral amino acids.
Hypermethioninemia:
- Biochemical Defect: Hepatic methionine adenosyl transferase (MAT I, III) deficiency.
- Feature: Boiled cabbage odor.
Cystinosis:
- Description: Lysosomal storage disorder.
- Biochemical Defect: CTNS gene mutation (cystinosin, H⁺-driven cystine transporter).
- Features: Cystine crystal accumulation in kidney, liver, eye, brain.
- Diagnosis: Corneal cystine crystals, elevated leukocyte cystine.
- Treatment: Cysteamine (converts cystine to cysteine), kidney transplantation.
Branched Chain Amino Acids
- Amino Acids:
- Valine: Glucogenic.
- Leucine: Ketogenic.
- Isoleucine: Glucogenic and ketogenic.
- Characteristics: All essential.
- Common Metabolic Steps:
- Transamination: Branched chain amino acid transaminase (PLP).
- Oxidative Decarboxylation: Branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase (thiamine pyrophosphate, FAD, NAD⁺, lipoamide, CoA).
- Dehydrogenation: Acyl CoA dehydrogenase (FAD).
- Metabolic Fates:
- Leucine: Ketogenic pathway.
- Valine: Glucogenic pathway.
- Isoleucine: Both pathways.
- Metabolic Disorders:
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD):
- Biochemical Defect: Branched chain ketoacid dehydrogenase deficiency (defective decarboxylation).
- Components:
- Type IA: E1α (decarboxylase, TPP).
- Type IB: E1β (decarboxylase).
- Type II: E2 (dihydrolipoyl transacylase, lipoamide).
- Type III: E3 (dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase, FAD).
- Clinical Features:
- Normal at birth, poor feeding, vomiting in first week.
- Lethargy, coma, convulsions, metabolic acidosis, hypertonicity, opisthotonos, alternating flaccidity.
- Maple syrup odor in urine, sweat, cerumen.
- Mental retardation.
- Diagnosis:
- Elevated plasma leucine, isoleucine, valine, alloisoleucine.
- Urinary leucine, isoleucine, valine, ketoacids.
- Dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) test, Rothera’s test.
- Enzyme analysis (leukocytes, fibroblasts), tandem mass spectrometry.
- Treatment: Restrict branched chain amino acids, high-dose thiamine.
- Isovaleric Aciduria:
- Biochemical Defect: Isovaleryl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (leucine metabolism).
- Feature: Sweaty feet odor.
- Isovaleric Aciduria:
- Intermittent Branched Chain Ketonuria:
- Partial activity of branched chain α-ketoacid decarboxylase.
Basic Amino Acids
Lysine
- Characteristics: Essential, predominantly ketogenic, represented by letter K.
- Functions:
- Hydroxylysine: Collagen cross-links, desmosine in elastin.
- Forms Schiff’s bases.
- Precursor of carnitine (with methionine).
- Decarboxylation forms cadaverine.
- Histone proteins are lysine-rich.
- Catabolism: Saccharopine intermediate.
Arginine
- Characteristics: Glucogenic, semiessential.
- Metabolic Pathway: L-glutamate semialdehyde → α-ketoglutarate.
- Functions:
- Nitric oxide synthesis.
- Agmatine synthesis (decarboxylation, neurotransmitter, antihypertensive).
- Urea cycle (arginine → ornithine + urea).
- Creatine synthesis.
- Nitric Oxide (NO):
- Properties: Uncharged, free radical, short half-life (0.1 s), gaseous, cGMP second messenger.
- Functions:
- Vasodilator.
- Penile erection.
- Neurotransmitter.
- Inhibits platelet adhesion/activation.
- Low NO linked to pylorospasm in hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
- Therapeutic Uses:
- Inhaled NO for pulmonary hypertension.
- Sildenafil (cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitor) for impotence.
- Glyceryl nitrite for angina pectoris.
- Synthesis: By nitric oxide synthase (NOS, cytosolic monooxygenase).
- Cofactors: NADPH, FAD, FMN, heme, tetrahydrobiopterin.
- Isoforms:
- nNOS: Neuronal, Ca²⁺-activated, deficiency causes pyloric stenosis, aggressive sexual behavior.
- iNOS: Macrophage, Ca²⁺-independent, deficiency increases infection susceptibility.
- eNOS: Endothelial, Ca²⁺-activated, deficiency causes elevated blood pressure.
- Mechanism: Ca²⁺ activates NOS → NO release → activates guanylyl cyclase → cGMP → smooth muscle relaxation.
Histidine
- Characteristics: Semiessential, contains imidazole ring, maximum buffering at physiological pH.
- Metabolism:
- Derivatives: Urocanate, FIGLU (formimino glutamic acid).
- Folic Acid Deficiency: FIGLU excretion in urine (histidine load test).
- Biologically Important Compounds:
- Histamine: From decarboxylation (PLP coenzyme).
- Functions:
- H1 Receptor: Smooth muscle contraction, vascular permeability.
- H2 Receptor: Gastric HCl secretion.
- H3 Receptor: Histamine synthesis/release in brain.
- Carnosine (β-alanyl histidine), anserine (methyl carnosine), homocarnosine, ergothionine.
- Functions:
- Metabolic Disorder: Histidinemia (histidase deficiency).
Acidic Amino Acids
Glutamic Acid (Glutamate)
- Characteristics: Nonessential, glucogenic, central role in amino acid metabolism.
- Biosynthesis: Reductive amidation of α-ketoglutarate by glutamate dehydrogenase.
- Functions:
- Concentrates amino groups from all amino acids via transamination.
- Synthesis of N-acetyl glutamate (regulates urea cycle).
- Glutathione synthesis.
- Gamma-amino butyric acid (GABA) synthesis (decarboxylation, PLP coenzyme).
Glutamine
- Biosynthesis: From glutamic acid by glutamine synthetase.
- Functions:
- Traps inorganic ammonium ions (first-line ammonia trapping).
- Transports amino groups from brain/other tissues.
- Contributes N3, N9 (purine), N3 (pyrimidine).
- Source of ammonia for guanine, cytosine.
- Conjugating agent.
- Ammonia excretion in kidney (acid-base balance).
Aspartic Acid (Aspartate)
- Characteristics: Nonessential, glucogenic.
- Biosynthesis: Transamination of oxaloacetate.
- Functions:
- Contributes amino group to urea synthesis.
- Purine and pyrimidine synthesis.
- Metabolic Disorder: Canavan Disease.
- Inheritance: Autosomal recessive, prevalent in Ashkenazi Jews.
- Biochemical Defect: Aspartoacylase deficiency.
- Accumulation of N-acetylaspartic acid (possible acetate reservoir for myelin).
- Features: Leukodystrophy, excessive N-acetylaspartic acid excretion.
- Diagnosis: Aspartoacylase deficiency in fibroblasts, urinary N-acetylaspartic acid.
Asparagine
- Biosynthesis: From aspartate by asparagine synthetase (uses glutamine, not ammonium ions).
- Catabolism:
- Glutamate, glutamine → α-ketoglutarate.
- Aspartate, asparagine → oxaloacetate.
Amino Acids and TCA Cycle
- To α-Ketoglutarate: Arginine, histidine, glutamine, proline (via glutamate).
- To Succinyl CoA: Valine, isoleucine, methionine, threonine.
- To Fumarate: Tyrosine, phenylalanine, aspartate.
- To Oxaloacetate: Asparagine (via aspartate).
Quick Review Points
- UV Light Absorption: Tryptophan, phenylalanine, tyrosine.
- No Asymmetric Carbon: Glycine.
- β-Alanine Source: Uracil, cytosine.
- Isoelectric pH: Amino acid has no net charge.
- Oxidative Deamination: Glutamate.
- Transamination Coenzyme: PLP.
- Ammonia Transport:
- Glutamine: Brain, most organs.
- Alanine: Skeletal muscle.
- Urea Nitrogen: Ammonia, aspartate.
- Urea Cycle Rate-Limiting Step: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I.
- Common Urea Cycle Disorder: Hyperammonemia Type II (ornithine transcarbamoylase defect).
- Polyamine Precursors: Ornithine, methionine, lysine.
- Cahill Cycle: Alanine.
- Gluconeogenic in Starvation: Alanine.
- Carnitine Precursors: Lysine, methionine.
- Selenocysteine Precursor: Serine.
- Glutamic Acid Products: GABA, α-ketoglutarate.
- Folate Trap: THFA as methyl derivative.
Metabolic Disorders and Biochemical Defects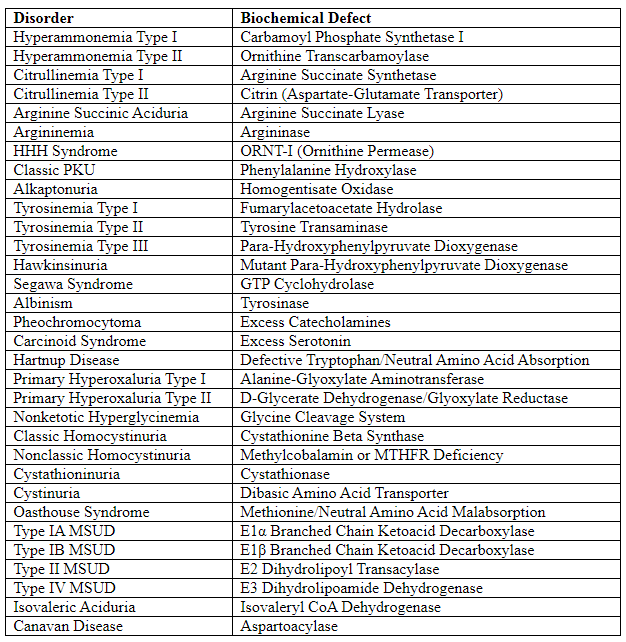
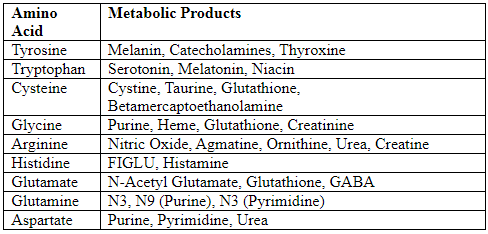
Specialized Products from Amino Acids
Peculiar Odors in Amino Acidurias
|
48 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Chemistry and Metabolism of Amino Acids - 2 - Biochemistry - NEET PG
| 1. What is the role of phenylalanine in the synthesis of catecholamines? |  |
| 2. How are catecholamines degraded in the body? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) in metabolism? |  |
| 4. How is melanin synthesized in the body? |  |
| 5. What are the clinical implications of abnormalities in tyrosine metabolism? |  |





















