Western and Central India Chapter Notes | Social Studies Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter tells us about the western and central parts of India. We will learn about the states Rajasthan, Gujarat, and the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu in the west. We will also learn about the states Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand in the central part. We will know about their cities, rivers, plants, crops, and land types.
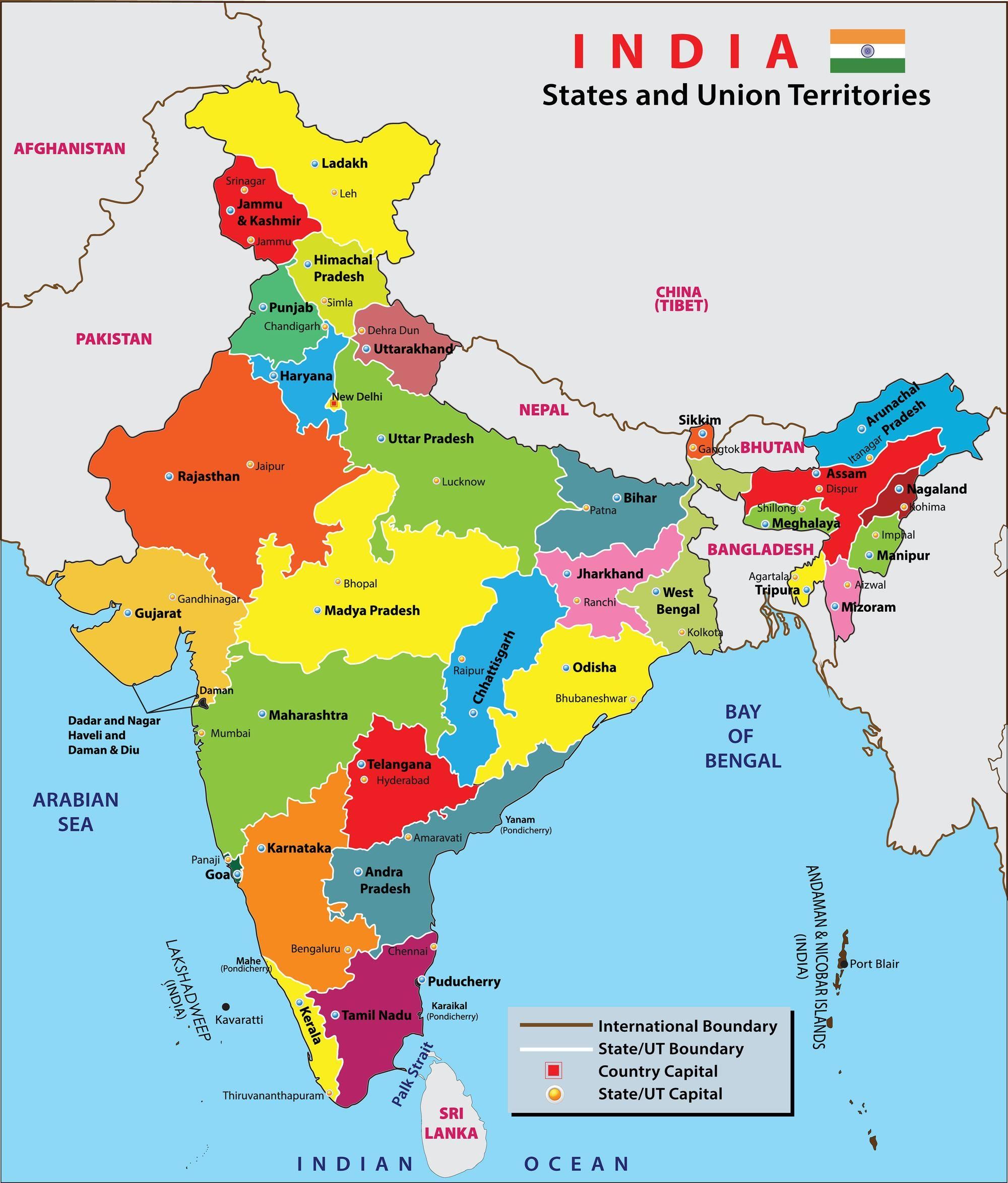
States and Union Territories (UT) of Western India
The states of Rajasthan, Gujarat and the UT of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu are situated in the western part of India.
- Landforms: The western part of India has many types of land like deserts, hills, plains, and coastal areas. The Great Indian Desert, also called the Thar Desert, is in the western part of Rajasthan. Gujarat is near the Thar Desert, so most of its land is dry. Daman and Diu has flat land with sandy beaches. Dadra and Nagar Haveli has some hilly areas.
- Climate: The western states and UT have mild and pleasant winters. The summers are hot and dry. Some areas get good rain, but some areas stay dry.
Rajasthan
Rajasthan is in the north-western part of India. Its neighbouring states are Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Haryana, and Punjab.

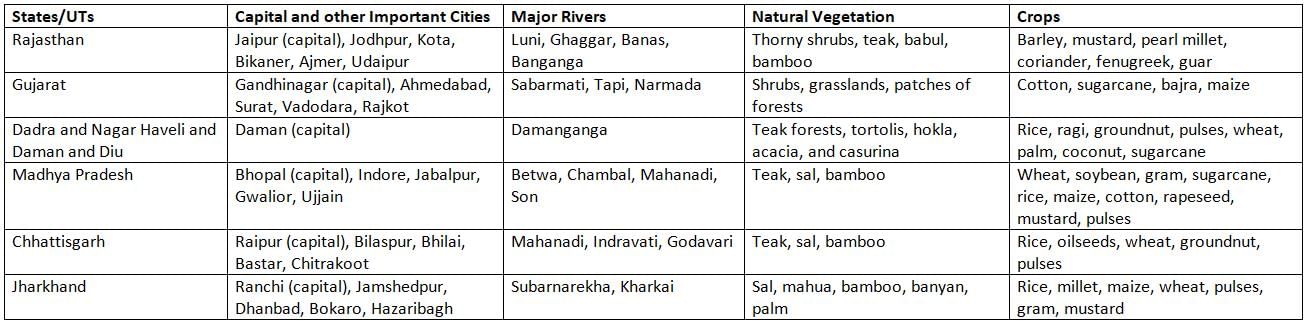
- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of Rajasthan is Jaipur. Jaipur is also called the Pink City because its buildings are painted pink. Jaipur is the biggest city in Rajasthan. Other big cities are Jodhpur, Kota, Bikaner, Ajmer, and Udaipur. Udaipur is called the City of Lakes.
- Rivers: The main rivers in Rajasthan are Luni, Ghaggar, Banas, and Banganga.
- Vegetation: Most of Rajasthan is a desert with little forest. Thorny shrubs and trees like teak, babul, and bamboo grow here.
- Agriculture: The main crops in Rajasthan are barley, mustard, pearl millet, coriander, fenugreek, and guar.
Gujarat
Gujarat is on the western coast of India. It is bordered by Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu. The Arabian Sea is on the western and southern sides of Gujarat.

- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of Gujarat is Gandhinagar. Ahmedabad, Surat, Vadodara, and Rajkot are other important cities.
- Rivers: The main rivers in Gujarat are Sabarmati, Tapi, and Narmada.
- Vegetation: Gujarat has shrubs, grasslands, and some patches of forest land.
- Agriculture: The main crops in Gujarat are cotton, sugarcane, bajra, and maize.
Fun Fact
The Great Rann of Kutch is a salt marsh in the Thar Desert in the Kutch district of Gujarat, India.
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu (UT)
This Union Territory is along the western coast of India. It has three districts i.e. Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman, and Diu. Daman is near the southern coast of Gujarat. Daman and Diu are surrounded by the Arabian Sea and Valsad district of Gujarat state. Dadra and Nagar Haveli is surrounded by Gujarat and Maharashtra.

- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of this Union Territory is Daman.
- Rivers: The main river here is Damanganga.
- Vegetation: The area has teak forests and trees like tortolis, hokla, acacia, and casurina. Thorny scrubs and palm trees are also found.
- Agriculture: The main crops are rice, ragi, groundnut, pulses, wheat, palm, coconut, and sugarcane. Vegetables like tomato, cauliflower, cabbage, and brinjal are grown. Fruits like mango, chikoo, guava, and banana are also grown.
States of Central India
The states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Jharkhand are situated in the central part of India.
- Landforms: The central part of India has hills, mountains, plateaus, and plains.
- Climate: The central states have three seasons: summer, monsoon, and cool winter.
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh is in the central part of India. Its neighbouring states are Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan.

- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of Madhya Pradesh is Bhopal. Other important cities are Indore, Jabalpur, Gwalior, and Ujjain.
- Rivers: The main rivers in Madhya Pradesh are Betwa, Chambal, Mahanadi, and Son.
- Vegetation: Teak, sal, and bamboo forests are important in Madhya Pradesh.
- Agriculture: The main crops are wheat, soybean, gram, sugarcane, rice, maize, cotton, rapeseed, mustard, and pulses.
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh is in the central part of India. Its neighbouring states are Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Jarkhand, and Andhra Pradesh.

- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of Chhattisgarh is Raipur. Other important cities are Bilaspur, Bhilai, Bastar, and Chitrakoot.
- Rivers: The main rivers in Chhattisgarh are Mahanadi, Indravati, and Godavari.
- Vegetation: The state has teak, sal, and bamboo forests.
- Agriculture: The main crops are rice, oilseeds, wheat, groundnut, and pulses. Fruits like guava and banana are also grown.
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is in the central part of India. Its neighbouring states are Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and West Bengal.

- Capital and Important Cities: The capital of Jharkhand is Ranchi. Other important cities are Jamshedpur, Dhanbad, Bokaro, and Hazaribagh.
- Rivers: The main rivers in Jharkhand are Subarnarekha and Kharkai.
- Vegetation: More than one-fourth of Jharkhand’s land has forests. Common trees are sal, mahua, bamboo, banyan, and palm.
- Agriculture: The main crops are rice, millet, maize, wheat, pulses, gram, and mustard.
Summary Table
Glossary
- Desert: A place with very little rain and lots of sand, where not many plants grow. Example: The Thar Desert in Rajasthan.
- Vegetation: All the plants and trees that grow in a place. Example: Teak and bamboo are part of the vegetation in Madhya Pradesh.
- Agriculture: Growing crops and taking care of plants for food. Example: People in Gujarat grow cotton and sugarcane.
- Union Territory (UT): A small area in India that is controlled by the central government, not a state government. Example: Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
- Rivers: Big streams of water that flow through the land. Example: The Narmada River flows in Gujarat.
|
43 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Western and Central India Chapter Notes - Social Studies Class 4 ICSE
| 1. What are the major states and Union Territories in Western India? |  |
| 2. Which states are considered part of Central India? |  |
| 3. What are some key features of Western India? |  |
| 4. How can I summarize the differences between Western and Central India? |  |
| 5. What are some quick revision points for studying Western and Central India? |  |




















