The Physical Divisions of India Chapter Notes | Social Studies Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Himalayas |

|
| The Northern Plains |

|
| The Peninsular Plateau |

|
| The Great Indian Desert |

|
| The Coastal Plains |

|
| The Islands |

|
| Major Rivers of India |

|
Introduction
India is a big country with many different types of land. It has tall mountains, flat plains, hot deserts, high plateaus, sea coasts, and beautiful islands. Because of these different lands, we divide India into six parts to learn about them. These parts are called physical divisions. They are the Himalayas, the Northern Plains, the Peninsular Plateau, the Great Indian Desert, the Coastal Plains, and the Islands. Let’s learn about each one in detail!
The Himalayas
The Himalayas are tall mountains in the northern part of India. The word Himalaya means "home of snow" in Sanskrit. The Himalayan mountains are divided into three parallel ranges. They are: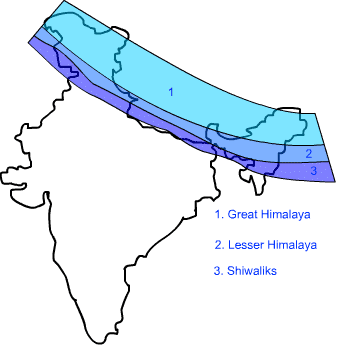
1. The Himadri or the Greater Himalayas
- The Himadri is the highest range in the Himalayas.
- It has many peaks that are more than 6000 meters tall.
- The highest peak in the world, Mount Everest, is in the Himadri range.
- Mount Everest is 8848 meters tall.
- Other tall mountains in this range are Mount K-2 (also called Godwin Austen), Kanchenjunga, and Nanda Devi.
- This area stays covered with snow all year.
- There are big glaciers like Gangotri and Siachen in this region.
- A glacier is a big moving block of snow.
- These glaciers melt and flow down as rivers.
- They give water to northern rivers like the Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra all year.
- Trees and plants cannot grow here because the weather is very harsh.
2. The Himachal or the Lesser Himalayas
- The Himachal range is lower than the Himadri.
- Its height is between 3700 to 4600 meters.
- The Pir Panjal and Dhauladhar ranges are important in this region.
- The Himachal range also has the Kashmir valley in Jammu and Kashmir.
- It has the Kulu and Kangra valleys in Himachal Pradesh.
- This area has many hill stations like Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital, Ranikhet, Almora, Manali, and Darjeeling.
- The mountains here have thick forests of oak, fir, deodar, and pine trees.
3. The Shiwalik or the Outer Himalayas
- The Shiwalik is the southernmost range of the Himalayas.
- It is the lowest range with heights between 900 and 1100 meters.
- It has large flat valleys called Duns.
- Dehra Dun, Kotli Dun, and Patli Dun are some famous Duns.
- This area is covered with thick forests.
- Many tiger reserves and national parks are found here.
- It is home to many wild animals.
- The hill slopes are used for growing fruits.
- Many fruit orchards are found in the Shiwalik region.
The Eastern Himalayas or the Purvachal
- The Eastern Himalayas are also called the Purvachal.
- Purva-east means eastern, and Achal-mountains means mountains.
- These are in northeast India.
- They form low hills between 1500 to 3000 meters tall.
- The Patkai hills, the Naga hills, the Manipur hills, and the Mizo hills together form the Purvachal.
- This area gets heavy rain during the monsoon season.
- It is covered with thick forests.
Importance of the Himalayas
- The Himalayas protect us from the cold winds coming from the north.
- They stop the monsoon winds and help bring rainfall to India.
- The Himalayas act like a natural wall and protect us from foreign invaders.
- Many rivers like the Ganga and Yamuna start from the Himalayas.
- These rivers give us water all year.
- The Himalayan forests give us wood, medicinal plants, and herbs.
- They are also home to many animals.
The Northern Plains
- The Northern Plains are south of the Himalayas.
- They stretch from Punjab in the west to Assam in the east.
- They were made by soil brought by Himalayan rivers.
- The Northern Plains have three basins: the Satluj basin, the Ganga basin, and the Brahmaputra basin.
- A basin is an area watered by a river and its tributaries.
- A tributary is a small river or stream that joins the main river.
Let’s learn about the three basins of the Northern Plains:
1. The Satluj Basin
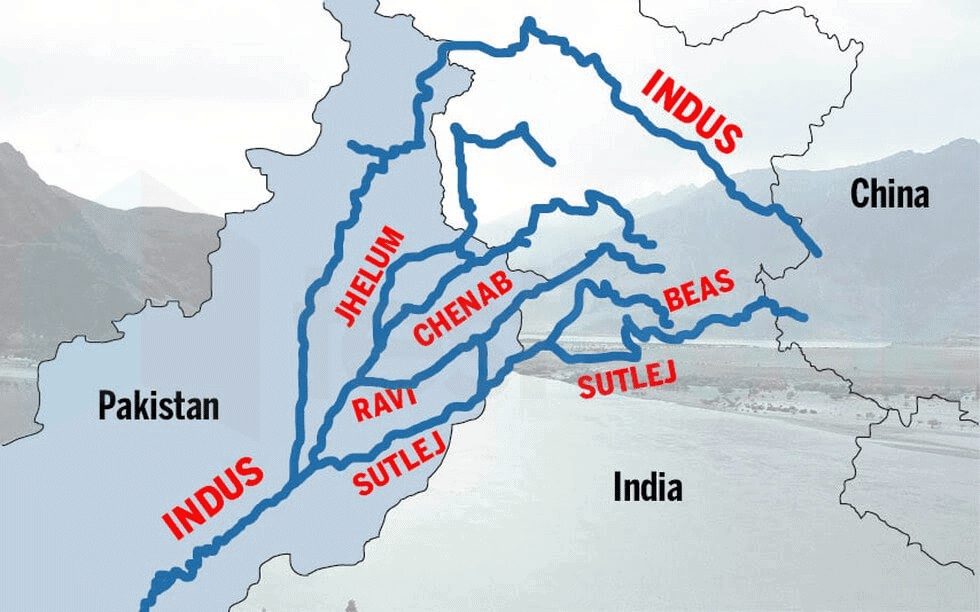
- The western part of the Northern Plains is the Satluj Basin.
- River Satluj and its tributary, Beas, flow here.
- They start in the lowlands of Punjab and Haryana.
- They join the River Indus in Pakistan.
- The main crops grown here are wheat, rice, pulses, cotton, sugarcane, and oilseeds.
- The states of Haryana and Punjab are in this region.
2. The Ganga Basin
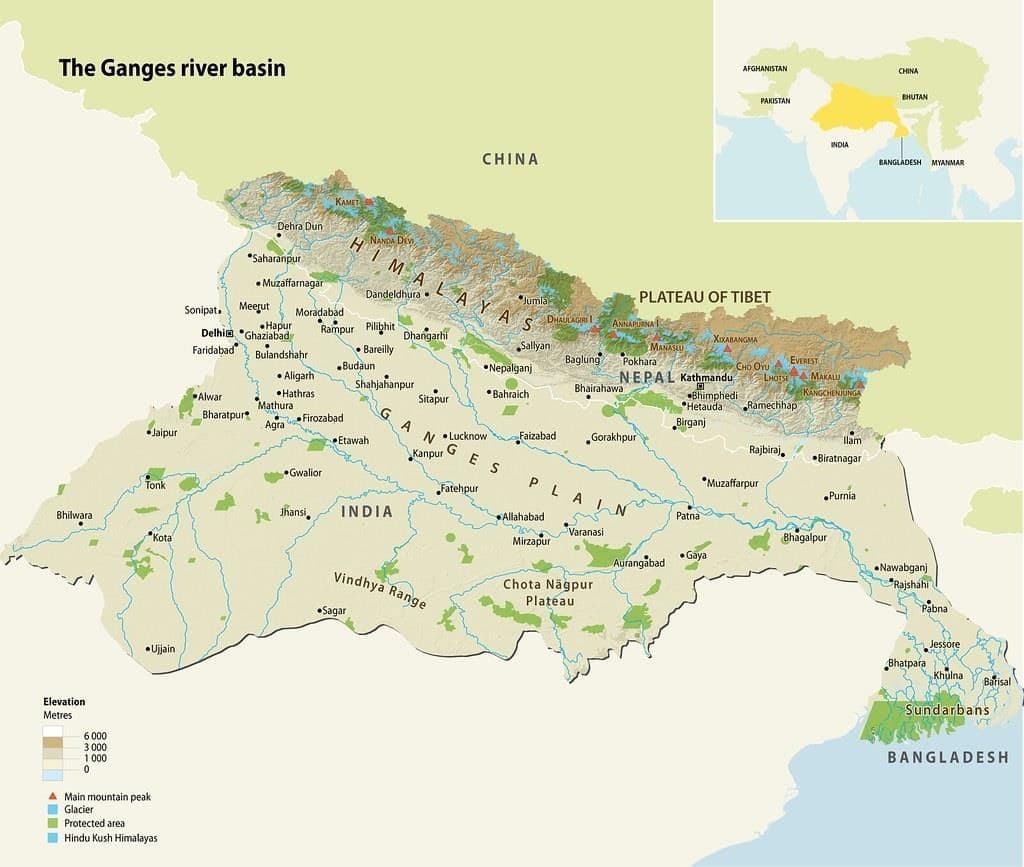
- River Ganga and its tributaries form the Ganga Basin.
- River Ganga enters the plains at Haridwar.
- It flows eastward.
- Yamuna is the main tributary of River Ganga.
- Gomti, Ghaghara, Gandak, and Kosi start in the Himalayas and are other tributaries.
- Rivers from the plateau region, like Chambal and Betwa, are also tributaries.
- River Yamuna meets River Ganga at Prayagraj.
- This meeting point is known as Sangam.
- The states of Uttar Pradesh, Delhi, Bihar, West Bengal, and parts of Madhya Pradesh are in this region.
- Main crops here are rice, wheat, sugarcane, pulses, oilseeds, and jute.
3. The Brahmaputra Basin
- River Brahmaputra and its tributaries form the Brahmaputra Basin.
- This is the eastern part of the Northern Plains.
- The Brahmaputra Basin is very narrow compared to the Ganga Basin.
- River Brahmaputra starts in Tibet, where it is called Tsangpo.
- It flows eastward and enters India in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It then flows through Assam and Meghalaya and enters Bangladesh.
- In Bangladesh, it meets River Ganga.
- Before joining the Bay of Bengal, it branches into many streams and forms the largest delta in the world, called the Sundarbans.
- Rice and jute are the main crops grown here.
Importance of the Northern Plains
- The Northern Plains get enough rainfall.
- They have many rivers, streams, and lakes in this region.
- The soil is fertile and good for agriculture.
- It is also known as the "Food bowl of India."
- The flat land helps in laying roads and railway lines easily.
- It supports a large population.
The Peninsular Plateau
- A plateau is an area of flat land that is higher than the land around it.
- The Peninsular Plateau region is to the south of the Northern Plains.
- It is triangular in shape.
- It is mainly rocky and uneven and tilts towards the east.
- The plateau region has three parts: the Malwa, the Chota Nagpur, and the Deccan Plateau.
- Many rivers like the Narmada and Tapi flow into the Bay of Bengal in the Peninsular Plateau.
Let’s learn about the three parts of the Plateau Plateau:
1. The Malwa Plateau

- The Malwa Plateau is in the northwest part of the Peninsular Plateau.
- It lies between the Vindhya and the Aravalli hills.
- Two important rivers here are the Chambal and the Mahi.
2. The Chota Nagpur Plateau
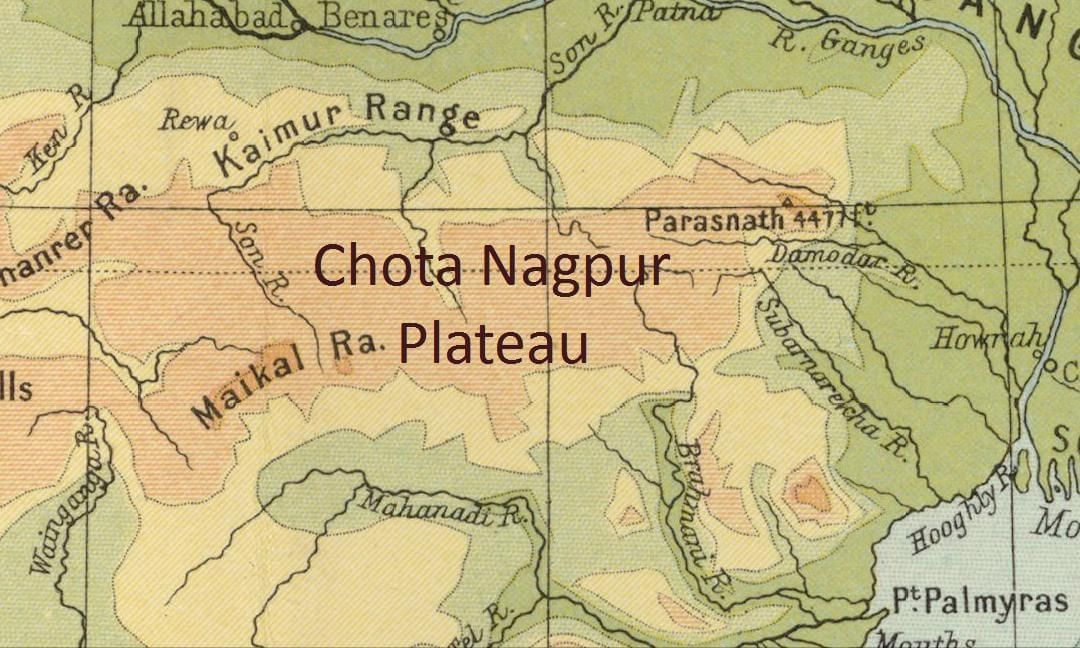
- The eastern part of the Peninsular Plateau is the Chota Nagpur Plateau.
- Two important rivers here are the Damodar and the Subarnarekha.
3. Deccan Plateau
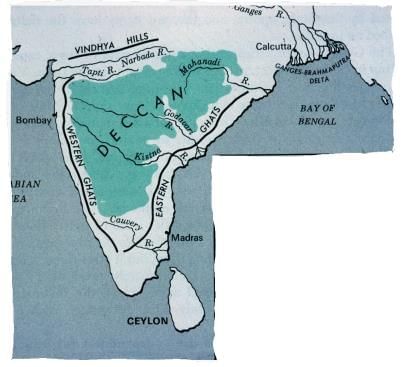
- The Deccan Plateau is a triangular landmass.
- It lies to the south of the Vindhya and the Satpura ranges.
- The Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats lie on the western and eastern edges of the Deccan Plateau.
- The Western Ghats are continuous, but the Eastern Ghats are broken because they are cut by rivers flowing into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Eastern Ghats are lower than the Western Ghats.
- The important rivers here are Krishna, Kaveri, Godavari, Mahanadi, Narmada, and Tapi.
Fun Fact
The peninsula is a piece of land that is surrounded by water on three sides.
Importance of the Peninsular Plateau
- We get minerals like iron, coal, manganese, and bauxite from this region.
- Many steel plants are located in the Chota Nagpur Plateau region.
- The soil of the plateau region is very fertile and good for growing crops like cotton, sugarcane, oilseeds, and rice.
- The forests of the plateau region provide timber and are home to many wild animals.
The Great Indian Desert

- A desert is a stretch of dry land that gets very little or almost no rain.
- The Great Indian Desert is also known as the Thar Desert.
- It is between the Aravalli hills and the Western Coastal Plains.
- It is located in the northwest part of Rajasthan.
- It is a hot and dry desert covered with sandy and thorny bushes.
- Days are very hot, and nights are cold here.
Fun Fact
There are many hills of sand in the desert. They are called sand dunes. When strong winds blow, the sand dunes shift, and their size and shape change.
Importance of the Great Indian Desert
- Marble rocks are found in large scale in this region.
- We get minerals like copper, silver, and limestone from this region.
The Coastal Plains
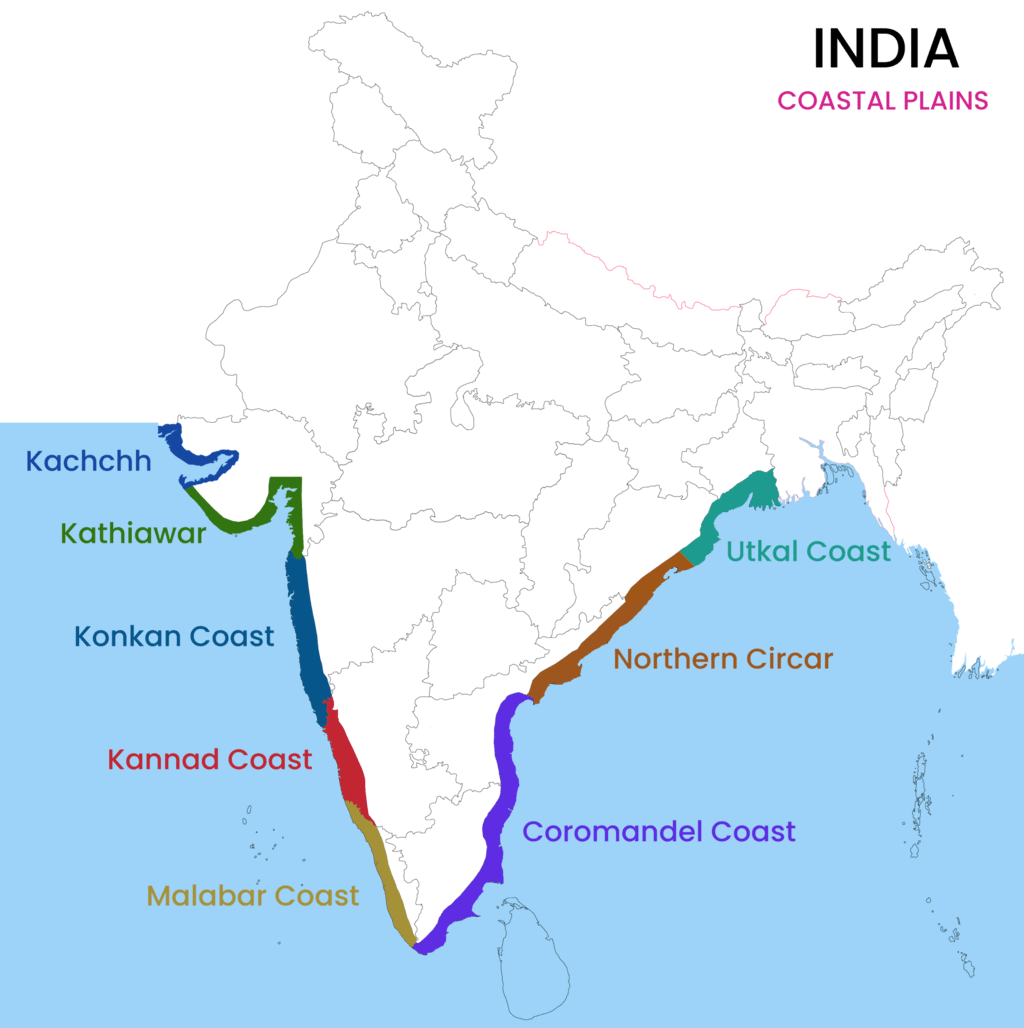
- A coast is a stretch of land along the sea.
- The Coastal Plains of India are located along the Arabian Sea coast in the west.
- They are also along the Bay of Bengal coast in the east.
- The Coastal Plains to the east of the peninsula are called Eastern Coastal Plains.
- Those to the west are called Western Coastal Plains.
- The Western Coastal Plains have three parts.
- The northern part of the Western Coastal Plains is called the Konkan Coast (Mumbai to Goa).
- The central part is called the Kannad Plain.
- The southern part is called the Malabar Coast.
- The Eastern Coastal Plains have two parts.
- The northern part is known as the Northern Circars.
- The southern part is known as the Coromandel Coast.
- The Eastern Coastal Plains are broader than the Western Coastal Plains.
Importance of the Coastal Plains
- Eastern coastal plains have very fertile soil, which is good for agriculture.
- Fishing is the main job of people on the west coast, and they sell fish to other countries.
- The beaches of the coastal plains are places of tourist attraction.
- The seaports like Mumbai, Kandla, and Vishakhapatnam on the coastal plains help in the development of trade with other countries.
The Islands
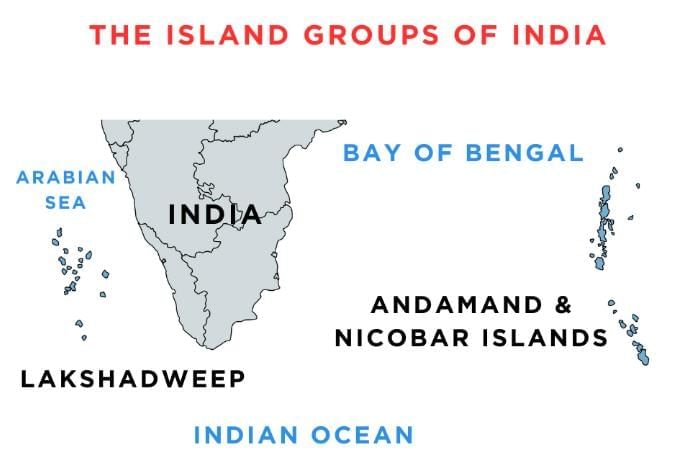
- India has two groups of islands: the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are in the Bay of Bengal.
- Only some of the islands here are lived on by people.
- The Lakshadweep Islands are in the Arabian Sea.
- Minicoy is the largest island here.
- Only some of the islands here are lived on by people.
Fun Fact
The only active volcano in India is found on Barren Island in the Andaman and Nicobar group of islands.
Importance of the Islands
- They support many species of plants and animals.
- They are also places of tourist attraction.
Major Rivers of India
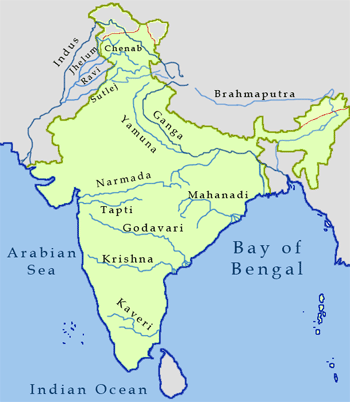
- Water is important for all living beings.
- Rivers are a major source of water needed by living beings.
- The Indian rivers are divided into two groups: Perennial rivers and Non-perennial rivers.
- Perennial rivers have water all year.
- They get water from melted ice (glaciers) from the mountains, so they do not dry even in summers.
- In summers, they also get water from rains.
- River Ganga and Yamuna are examples of perennial rivers.
- River Ganga starts from the Gangotri glacier in the Himalayas.
- Yamuna starts from the Yamunotri glacier in the Himalayas.
- Other perennial rivers of India are Brahmaputra, Satluj, Ghaghara, Gomti, and Kosi.
- Most of the rivers in the northern part of India are perennial.
- Non-perennial rivers do not have water all year.
- They get water from rains only and dry up during summers.
- These are also known as seasonal rivers.
- Non-perennial rivers are found in peninsular India.
- The Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri flow eastward and drain into the Bay of Bengal.
- The Narmada and Tapi flow westward and drain into the Arabian Sea.
Points To Remember
- India is a vast land with various forms of physical divisions.
- It is divided into six distinct regions: the Himalayas, the Northern Plains, the Peninsular Plateau, the Great Indian Desert, the Coastal Plains, and the Islands.
- The Himalayas are a mountain range in the northern part of India.
- The Northern Plains lie to the south of the Himalayas.
- The Northern Plains are divided into three parts: the Satluj, the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra basin.
- The Peninsular Plateau region lies to the south of the Northern Plains.
- It is triangular in shape.
- A desert is a stretch of dry land that receives very less or almost no rain.
- The Coastal Plains of India are located along the Arabian Sea coast in the west and along the Bay of Bengal coast in the east.
- India has two groups of islands—the Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands.
Glossary
- Fertile: Productive
- Inhabited: Occupied for living
- Species: A kind or sort
|
59 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on The Physical Divisions of India Chapter Notes - Social Studies Class 4 ICSE
| 1. What are the major physical divisions of India? |  |
| 2. How do the Himalayas influence the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Northern Plains in India? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of the Great Indian Desert? |  |
| 5. Can you name some major rivers of India and their importance? |  |
















