Atomic Structure Chapter Notes | Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve PDF Download
Introduction
Everything around us, like air, water, and even our own bodies, is made up of tiny building blocks called atoms. These atoms are so small that we cannot see them with our eyes. Atoms join together to form different types of matter, and they cannot be broken down further by chemical methods. In this chapter, we will learn about what atoms are, how they were discovered, and how they are made up of smaller parts like electrons, protons, and neutrons. We will also understand how these parts are arranged inside an atom and how they help atoms stay stable.
Ancient Views on Atomic Structure
Maharishi Kanada’s View on Atom
- Maharishi Kanada was an Indian thinker who lived around 600 BCE.
- He said that matter is made of very tiny particles called paramanu, which means the smallest particle.
- Paramanu cannot be divided further and is the smallest unit of matter.
- Many paramanu join together to form bigger particles called anu, which is like a molecule.
Democritus and Atoms
- Democritus was a Greek thinker who lived between 460 BCE and 370 BCE.
- He said that everything is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- The word "atom" comes from the Greek word "atomos," which means something that cannot be divided.
Did You Know?
The whole universe is made of five basic elements: earth, water, fire, air, and space. Our body is also made of these five basic elements of nature. We also know these as pancha mahabhutas. The pancha mahabhutas can be felt by our five senses: smell, taste, hearing, touch, and sight.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- John Dalton was a scientist who gave his ideas about atoms in 1808.
- All matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms cannot be broken down, created, or destroyed.
- During chemical reactions, atoms only join together or separate; they do not change.
- All atoms of the same element are the same in size, mass, and other properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different sizes, masses, and properties.
- Atoms of different elements join together in whole numbers to form compounds.
- For example, two hydrogen atoms (H) join with one oxygen atom (O) to form water (H₂O).
Subatomic Particles and Their Discovery
- John Dalton thought atoms could not be broken down into smaller parts.
- Later, scientists found that atoms are made of smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- In 1897, an English scientist named Sir J.J. Thomson proved that atoms can be split into smaller parts.
- Sir J.J. Thomson discovered the electron, which was a big step in understanding the structure of an atom.
Did You Know?
Joseph John Thomson was born on December 18, 1856, in Manchester, England. He studied at Trinity College, a famous college at Cambridge University. In 1906, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the discharge of electricity in gases.
Discovery of Electrons
- In 1879, an English scientist named Sir William Crookes did an experiment to study electricity in gases.
- Gases do not conduct electricity well under normal conditions.
- But when the gas is at a very low pressure (0.01–0.001 mm of mercury) and a very high voltage (more than 10,000 volts) is applied, the gas conducts electricity.
- Crookes made a special glass tube called a discharge tube for his experiment.
- The discharge tube had two metal plates inside, one at each end.
- One plate was connected to the negative terminal (called the cathode) and the other to the positive terminal (called the anode) of a high voltage source.
- A vacuum pump was used to remove most of the air from the tube to create a low pressure inside.
- When a high voltage current was passed through the gas in the tube, a green glow appeared at the end opposite the cathode.
- Crookes saw that rays were coming from the cathode and causing the green glow. These rays were named cathode rays.
- He found that these cathode rays were made of negatively charged particles.
- The direction of these rays could be changed by a magnet.
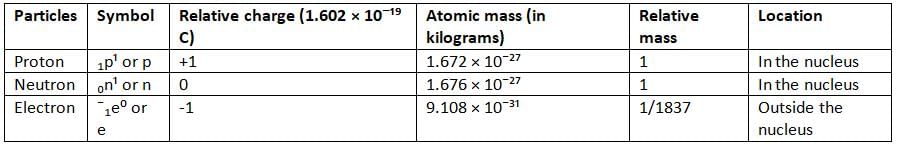
Characteristics of Electrons
- In 1897, J.J. Thomson, a British scientist, proved that cathode rays are made of negatively charged particles called electrons.
- Electrons are present in the atoms of all matter.
- Thomson used his observations to calculate the charge to mass ratio (e/m) of electrons.
- The e/m ratio means the charge of an electron divided by its mass.
- Thomson found the e/m ratio to be 1.78 × 10⁸ C g⁻¹ (coulomb per gram).
- Thomson also found that the e/m ratio does not change based on the type of gas or the material of the electrodes in the discharge tube.
- The mass of an electron was found to be 9.1 × 10⁻³¹ kg.
- This mass is very small, about 1/1837 of the mass of a hydrogen atom.
- Electrons are considered to have very little mass.
- The charge on an electron is one unit of negative charge, which is -1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C (coulomb).
Properties of Cathode Rays
- Cathode rays are produced from the cathode in a discharge tube when an electric current passes through gas at low pressure.
- Cathode rays are made of negatively charged particles.
- When an electric field is applied, the rays get attracted to the positively charged plate or bend toward it.
- Cathode rays are a stream of fast-moving charged particles.
- If a light wheel is placed in the path of cathode rays, the wheel starts to rotate.
- Cathode rays travel in a straight line.
- A shadow is formed on the wall opposite the cathode if an object is placed in the path of the rays.
- This shows that cathode rays travel in a straight line.
Did You Know?
An electron is represented by the symbol -1e⁰. The superscript 0 shows its mass, and the subscript -1 shows its electrical charge.
Discovery of Protons
- If negatively charged electrons are present in an atom, there must also be positively charged particles to balance the charge.
- E. Goldstein, a German scientist, discovered the existence of positively charged particles in an atom.
- In 1886, Goldstein did an experiment using a modified discharge tube with a perforated cathode (a cathode with small holes).
- When a high voltage current was passed through the gas at low pressure, Goldstein saw rays coming from the anode.
- These rays passed through the holes in the cathode and moved in the opposite direction of the cathode rays.
- Since these rays came from the anode, they were called anode rays.
- Anode rays were made of positively charged particles.
Characteristics of Anode Rays
- Anode rays are produced from the anode in a discharge tube when an electric current passes through gas at very low pressure.
- Anode rays are made of positively charged particles.
- When an electric field is applied, the rays get attracted to the negatively charged plate or bend toward it.
- Anode rays are a stream of fast-moving charged particles.
- Anode rays travel in a straight line.
Did You Know?
- Since an atom is electrically neutral, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in that atom.
- A proton is about 1840 times heavier than an electron.
Properties of Protons
- Protons carry a positive electric charge.
- They are a fundamental part of every atom.
- The ratio of a proton’s charge to its mass (e/m) is not constant—it can change.
- This e/m ratio depends on the type of gas used in the discharge tube experiment.
- A proton’s mass is nearly equal to that of a hydrogen atom, about 1.672 × 10⁻²⁴ grams.
- The proton’s charge has the same size as an electron’s charge (1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C), but with the opposite sign.
- Atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons, which keeps them electrically neutral.
Did You Know?
The charge of an electron was found to be 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ coulombs in 1908 by R.A. Millikan.
Thomson’s Model of an Atom
- The discovery of protons and electrons raised a question: how are these particles arranged inside an atom?
- In 1904, J.J. Thomson gave the first model of an atom, called the plum pudding model.
- In this model, an atom is like a sphere (ball) of positive charge with negatively charged electrons spread inside it.
- It looks like a pudding with plums (electrons) scattered in it, where the pudding is the positive charge and the plums are the electrons.
- This model could not explain many experimental observations, so it was not accepted.
Discovery of Nucleus
- In 1911, Ernest Rutherford, a British scientist born in New Zealand, did an experiment to study the arrangement of electrons and protons in an atom.
- He bombarded a very thin sheet of gold (0.00004 cm thick) with fast-moving alpha particles in an evacuated chamber.
- Alpha particles are positively charged particles given off by radioactive substances like uranium or radium.
Rutherford’s Observations
- Most of the alpha particles passed straight through the gold foil without any deflection (change in direction).
- A few alpha particles were deflected at very large angles.
- A very small number of alpha particles were deflected at small angles.
- Some particles even bounced back, which was surprising.
- Out of every 12,000 alpha particles, only one bounced back, showing that the positive charge and mass of the atom were concentrated in a very small area.
Rutherford’s Conclusion
- A lot of space in the atom is empty because most alpha particles passed straight through without any deflection.
- The force that causes large deflections is very strong because small deflections of alpha particles could only happen if there was a center of concentrated positive charge.
- Since some alpha particles bounced back, there must be a heavy center of positive charge in the atom. This heavy center is called the nucleus.
- The particles that hit the nucleus directly bounced back.
Did You Know?
A proton is represented by the symbol ₁p¹. The superscript 1 represents its mass, and the subscript 1 represents its charge.
Rutherford’s Model of an Atom
- In 1911, Rutherford gave his own model of the atom based on his experiment.
- Most of the mass of an atom is concentrated in the center, called the nucleus.
- The nucleus is the densest part of an atom and contains positively charged particles called protons.
- The size of the nucleus is very small compared to the size of the whole atom, so there is a lot of empty space around the nucleus.
- An atom is electrically neutral, which means the number of electrons (negative) is equal to the number of protons (positive).
- Electrons move in circular orbits (shells) around the nucleus.
Did You Know?
A large number of positively charged protons in a small nucleus should lead to repulsion, making the nucleus unstable. But the nucleus is stable. Rutherford explained that protons in the nucleus are held together by an attractive nuclear force that balances the repulsion. Thus, a nucleus is stable.
Bohr’s Atomic Model
- Rutherford’s model could not explain why atoms are stable.
- Positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons should attract each other, causing the atom to collapse. But this does not happen.
- In 1913, Niels Bohr, a Danish scientist, improved Rutherford’s model.
- Electrons move around the nucleus in fixed circular orbits called shells, just like planets move around the sun.
- Each shell has a fixed amount of energy, and the shell nearest to the nucleus has the least energy.
- The energy increases as you go to shells farther from the nucleus.
- Bohr named the shells K, L, M, N, and so on, starting from the innermost shell.
Discovery of Neutron
- Rutherford’s experiment showed that the mass of an atom was mostly in the nucleus due to protons.
- But later experiments found that the mass of the atom is more than just the mass of protons and electrons.
- In 1932, James Chadwick discovered another particle in the nucleus called the neutron.
- The neutron has mass but no electric charge, which means it is electrically neutral.
Properties of Neutrons
- A neutron is an important part of the nucleus of an atom.
- Neutrons and protons together are called nucleons because they are in the nucleus.
- A neutron is represented by the symbol ₀n¹.
- The superscript 1 shows its mass, and the subscript 0 shows its charge (which is zero).
- A neutron is about the same size as a proton.
- A neutron has no charge; it is electrically neutral.
Subatomic Particles
Modern Concept of an Atom
- An atom is made up of three main subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- The atom has two main parts: The nucleus is the central part of the atom, and it contains protons (positively charged) and neutrons (neutral).
- Protons and neutrons are held together in the nucleus by strong nuclear forces.
- The positive charge of the nucleus comes from the protons since electrons have very little mass.
- The extra-nuclear region (outside the nucleus) is the empty space where electrons move.
- Electrons move around the nucleus in fixed orbits or shells.
- Each orbit has a fixed energy level, and the energy increases as you move to outer shells.
- The outward pull (centrifugal force) of the electrons is balanced by the inward attraction between the electrons and protons.
- An atom is electrically neutral because the number of electrons (negative) is equal to the number of protons (positive).
Structural Stability of an Atom
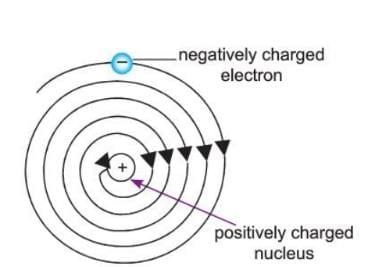
- Electrons (negatively charged) and protons (positively charged) attract each other inside the atom.
- Because of this attraction, the electrons should fall into the nucleus, and the atom should collapse.
- But this does not happen because electrons move in fixed orbits (shells) around the nucleus at very high speeds.
- Each orbit has a fixed amount of energy.
- The electrons in the innermost shells have the least energy, and the energy increases in the outer shells.
- The balance between the inward pull of the nucleus and the outward movement of the electrons keeps the atom stable.
Atomic Number
- The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number.
- It is represented by the letter Z.
- Since the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom, the atomic number also tells us the number of electrons.
- Atomic number (Z) = Number of protons = Number of electrons.
- Each element has a unique atomic number, so no two elements have the same number of protons (or electrons).
Mass Number
- The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the mass number.
- It is represented by the letter A.
- Mass number (A) = Number of protons + Number of neutrons.
- Mass number (A) = Atomic number (Z) + Number of neutrons.
- The symbol of an element X is written as ₓXᴬ, where A is the mass number (superscript) and Z is the atomic number (subscript).
- If we know the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z) of an element, we can find the number of neutrons.
- Number of neutrons = Mass number (A) - Atomic number (Z).
- Number of neutrons = A - Z.
- For example, magnesium has an atomic number (Z) of 12 and a mass number (A) of 24.
- Number of neutrons = A - Z = 24 - 12 = 12.
Atomic Notation and Number of Subatomic Particles of Some Elements
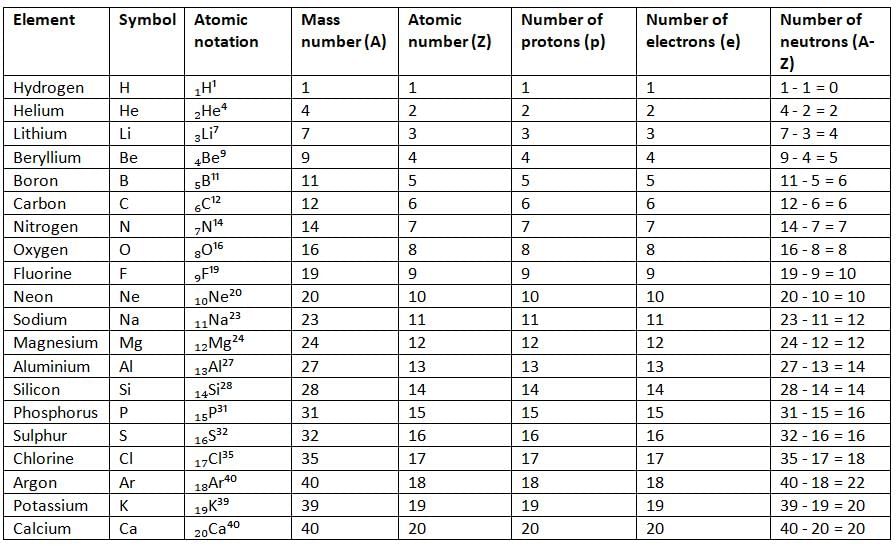
Symbolic Representation of an Element
- The symbol of an element is written as ₓXᴬ, where X is the symbol of the element, Z (subscript) is the atomic number, and A (superscript) is the mass number.
- For example, calcium has an atomic number (Z) of 20 and a mass number (A) of 40, so it is written as ₂₀Ca⁴⁰.
Relative Atomic Mass
- Atoms are very small, so scientists use a standard to measure their weight.
- The standard atom chosen for this is the carbon-12 atom.
- The relative atomic mass of an element is the number of times the average mass of one atom of that element is heavier than 1/12th of the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
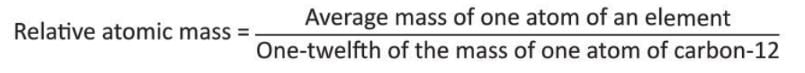
- It is a unitless number (denoted as u).
- For example, the relative atomic mass of hydrogen is 1 u, and oxygen is 16 u.
Did You Know?
The average mass of one atom of an element is used because elements may have atoms of different masses. This is because the number of neutrons in the nucleus may differ from atom to atom of an element.
Isotopes
- Atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- For example, nitrogen has two isotopes: ₇N¹⁴ and ₇N¹⁵.
- The first isotope, ₇N¹⁴, has 7 protons and 7 neutrons (14 - 7 = 7).
- The second isotope, ₇N¹⁵, has 7 protons and 8 neutrons (15 - 7 = 8).
- Both isotopes of nitrogen have the same number of protons and electrons (7), but they have different numbers of neutrons.
- Examples of isotopes of hydrogen are:
- Hydrogen (₁H¹) has 1 proton and 0 neutrons.
- Deuterium (₁H²) has 1 proton and 1 neutron.
- Tritium (₁H³) has 1 proton and 2 neutrons.
- Examples of isotopes of carbon are:
- Carbon-12 (₆C¹²) has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
- Carbon-13 (₆C¹³) has 6 protons and 7 neutrons.
- Carbon-14 (₆C¹⁴) has 6 protons and 8 neutrons.
Properties of Isotopes
- Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number, so the number of electrons and protons is the same.
- Isotopes of an element show the same chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons and protons.
- Properties that depend on mass, like density, melting point, and boiling point, are different for isotopes because their masses are different.
Electronic Configuration
- Electrons are arranged in different orbits or shells around the nucleus of an atom; this arrangement is called the electronic configuration.
- To write the electronic configuration of an element, we need to know:
- The number of electrons in the atom of the element.
- The number of electrons in different shells of the atom.
- Each orbit or shell has a fixed amount of energy.
- The distribution of electrons in different energy shells of an atom is governed by a scheme called the Bohr-Bury scheme.
- The rules of the Bohr-Bury scheme are:
- The amount of energy in the shells increases as you go farther from the nucleus (K < L < M < N…).
- The maximum number of electrons that can be present in any shell is given by the formula 2n², where n is the shell number (K = 1, L = 2, M = 3, N = 4).
- For example:
- Shell K (n = 1): 2(1)² = 2 electrons.
- Shell L (n = 2): 2(2)² = 8 electrons.
- Shell M (n = 3): 2(3)² = 18 electrons.
- Shell N (n = 4): 2(4)² = 32 electrons.
- The outermost shell (also called the valence shell) cannot have more than 8 electrons (octet).
- The second-last shell (K shell) cannot have more than 8 electrons (duplet).
- The reason for this is that having 8 electrons in the outermost shell makes the atom very stable.
- For example, hydrogen has an atomic number of 1, so it has 1 electron, which goes in the K shell (1).
- Lithium has an atomic number of 3, so it has 3 electrons: 2 in the K shell and 1 in the L shell (2, 1).
- Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, so it has 15 electrons: 2 in K, 8 in L, and 5 in M (2, 8, 5).
Number of Electrons Accommodated in Different Shells
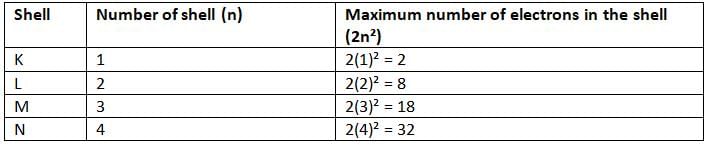
Electronic Configuration of Some Elements
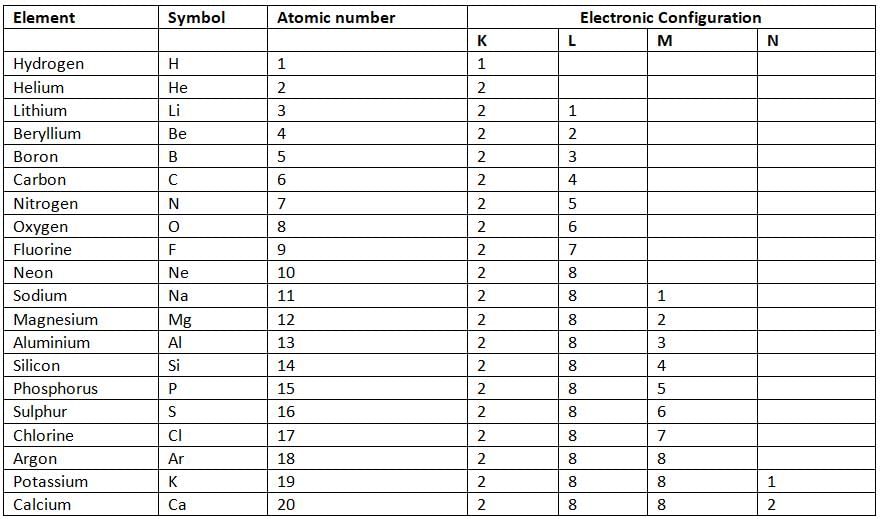
Atomic Structure of the First Twenty Elements
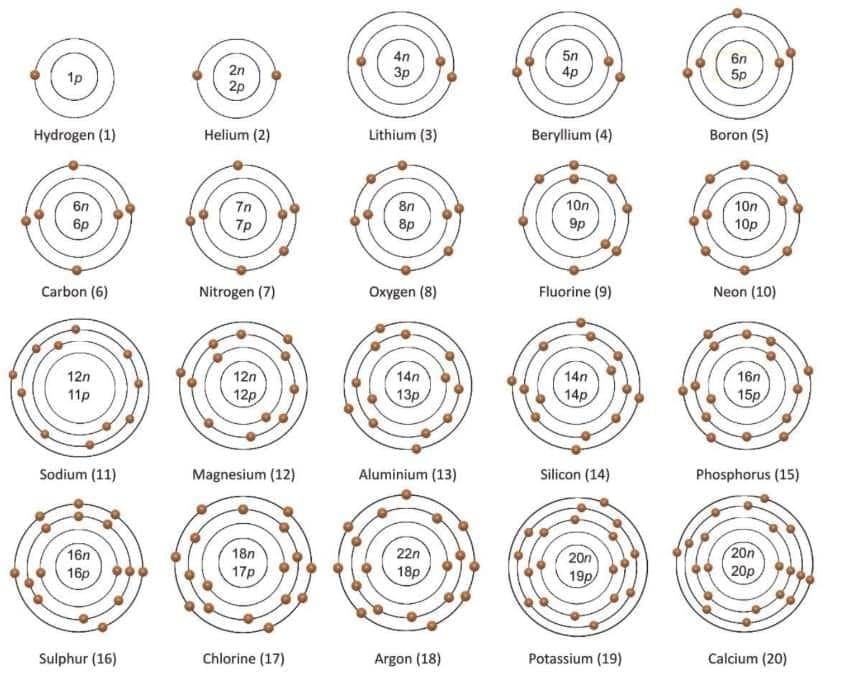
Valency
- The outermost shell of an atom is called the valence shell or valence orbit.
- The electrons in the valence shell are called valence electrons.
- Valence electrons help atoms take part in chemical reactions to form molecules and compounds.
- Electrons in the inner shells of an atom do not take part in chemical reactions.
- Every atom wants to be stable, which means its valence shell should have 8 electrons, except for the first shell, which can hold only 2 electrons.
- Atoms achieve stability by accepting, donating, or sharing electrons to have a complete outer shell with 8 electrons, except the first shell, which needs 2 electrons.
- The number of electrons an atom needs to accept, donate, or share to complete its outer shell (8 electrons, or 2 for the first shell) is called its valency.
- In simple words, valency is the combining capacity of an atom with no charge.
Why Do Atoms of Elements Combine or React?
- Atoms of elements combine or react to become stable and non-reactive in nature.
- A German chemist named Kossel proposed this idea.
- Elements combine in a way that each element gets 8 electrons in its valence shell, except for hydrogen, lithium, and beryllium, which need 2 electrons in their valence shell. This idea is called the octet rule.
In General:
- The valency of metals is the same as the number of electrons in their valence shell.
- For example, sodium has 1 valence electron, so its valency is 1, and magnesium has 2 valence electrons, so its valency is 2.
- The valency of non-metals is found using the formula: 8 minus the number of valence electrons.
- For example, nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, so its valency is 8 - 5 = 3; oxygen has 6 valence electrons, so its valency is 8 - 6 = 2; chlorine has 7 valence electrons, so its valency is 8 - 7 = 1.
- The valency of noble gases like helium, neon, and argon is 0 because they already have 8 electrons in their valence shell and are very stable.
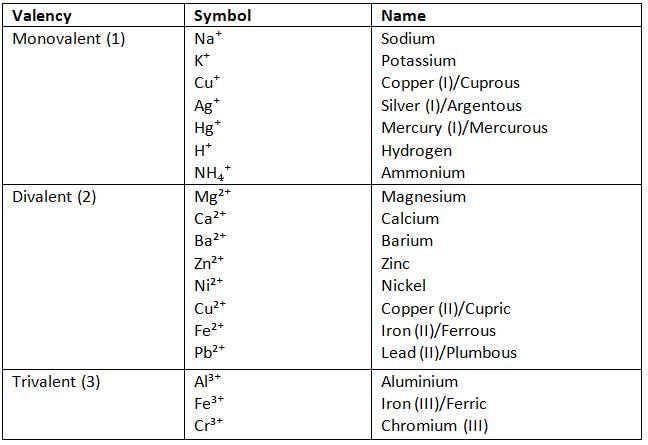
- Elements with valency 1 are called monovalent elements, like sodium and chlorine.
- Elements with valency 2 are called divalent elements, like magnesium and calcium.
- Elements with valency 3 are called trivalent elements, like lithium and phosphorus.
- When an atom gives away electrons to become stable, it becomes a positively charged ion and is called an electropositive ion.
- During chemical reactions, metals give away electrons, which means they have more protons than electrons, so they become positively charged and form cations.
Did You Know?
Kossel was born on 4 January 1888 in Berlin, Germany. In 1916, he put forth his theory of the ionic chemical bond (octet rule). The octet rule was also independently put forth by Gilbert N Lewis in the same year.
Examples of Formation of Electropositive Ions
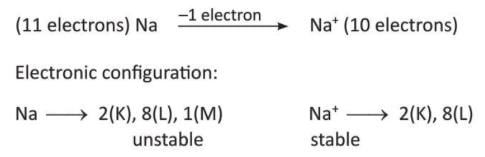
- Sodium (Na) gives 1 electron to become sodium ion (Na⁺).
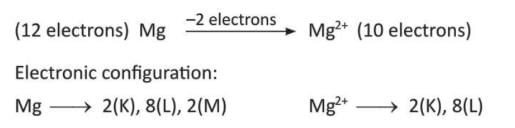
- Magnesium (Mg) gives 2 electrons to become magnesium ion (Mg²⁺).
- Aluminium (Al) gives 3 electrons to become aluminium ion (Al³⁺).
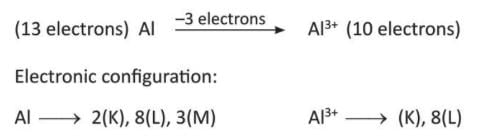
Depending on the number of electrons donated, elements are called monovalent (Na⁺), divalent (Mg²⁺), or trivalent (Al³⁺).
Did You Know?
All metals and hydrogen have positive valency because their valence shells have 1 to 3 electrons.
Valency and Symbol of Some Common Cations
Formation of Electronegative Ions:
- When an atom gains electrons to become stable, it becomes a negatively charged ion called an electronegative ion.
- During chemical reactions, non-metals gain electrons, so they have more electrons than protons and become negatively charged, forming anions.
Examples of Formation of Electronegative Ions
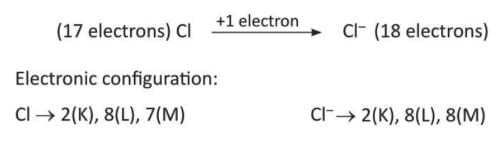
- Chlorine (Cl) gains 1 electron to become chloride ion (Cl⁻1).
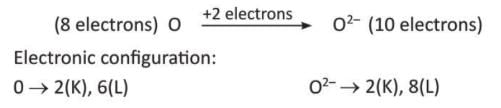
- Oxygen (O) gains 2 electrons to become oxide ion (O²⁻).
- Nitrogen (N) gains 3 electrons to become nitride ion (N³⁻).
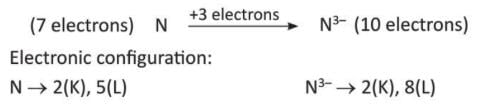
Depending on the number of electrons gained, elements are called monovalent (Cl⁻), divalent (O²⁻), or trivalent (N³⁻).
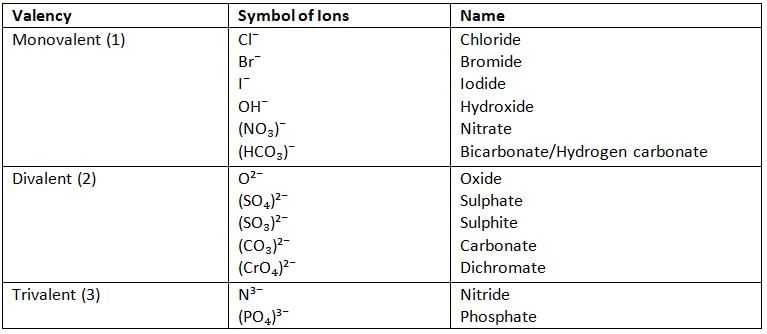
Valency and Symbol of Some Common Anions
Variable Valency
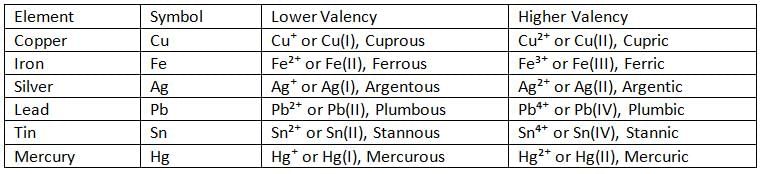
- Some elements can show more than one valency, so they are said to have variable valency.
- For example, copper, iron, silver, lead, and mercury have variable valencies.
Metals with Variable Valency
Radicals
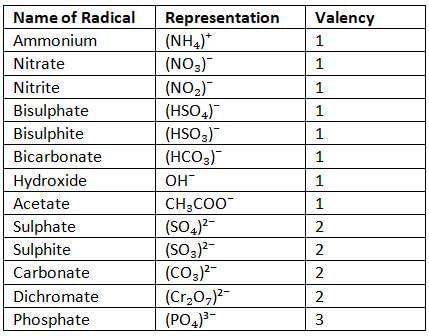
- Two or more non-metals together accept or donate one or more electrons and become negatively or positively charged in the process, and they are called radicals.
- For example, ammonium (NH₄⁺) has valency 1, carbonate (CO₃²⁻) has valency 2, and phosphate (PO₄³⁻) has valency 3.
- Radicals act as a single unit.
Representation of Some Radicals
Chemical Bond
- Atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to become stable.
- The bond formed between two atoms when they combine is called a chemical bond.
- A chemical bond is the force of attraction that holds two or more atoms together in a molecule.
- Atoms can combine either by transferring electrons or by sharing electrons.
Electrovalent Bond
- The chemical bond formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another is called an electrovalent bond or ionic bond.
- The compounds formed this way are called electrovalent or ionic compounds.
- Electrovalent bonds are usually formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal.
- Cations are the particles having a positive charge, and anions are the particles having a negative charge.
- The opposite charges attract each other due to the strong force of electrostatic attraction.
- The formation of the bond happens between an anion and a cation, so it is also called an ionic bond.
Sodium Chloride
- During the formation of sodium chloride, the sodium atom (2, 8, 1) loses 1 electron and becomes a sodium ion (Na⁺), which is a cation.
- The chlorine atom (2, 8, 7) accepts the electron given by sodium and becomes a chloride ion (Cl⁻), which is an anion.
- Since sodium ion and chloride ion are oppositely charged, they attract each other and form sodium chloride (NaCl).
- Equation: Na (2, 8, 1) + Cl (2, 8, 7) → Na⁺ (2, 8) + Cl⁻ (2, 8, 8) → NaCl
Covalent Bond
- The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons is called a covalent bond.
- The compounds formed this way are called covalent compounds.
Oxygen Molecule
- A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between non-metals.
- In an oxygen molecule, one oxygen atom (2, 6) combines with another oxygen atom (2, 6) by sharing two electrons to form an oxygen molecule (O₂).
- Equation: O (2, 6) + O (2, 6) → O₂
Glossary
- Around the turn of the 20th century, it was discovered that an atom was actually a cluster of various subatomic particles (mainly electrons, protons, and neutrons) which can exist separately from each other.
- John Dalton proposed that an atom is a solid, indestructible, and indivisible sphere.
- In 1879, the English scientist William Crookes showed that the rays were emitted from the cathode when a high voltage electric current was passed through the discharge tube.
- In 1897, the English scientist Sir J.J. Thomson proved that an atom can be split into even smaller parts.
- His discovery of the electron was the first step towards a detailed model of the atom.
- J.J. Thomson found that the cathode rays consisted of negatively charged particles called electrons.
- E. Goldstein performed an experiment in the discharge tube with a perforated cathode and found that the anode rays consisted of positively charged particles called protons.
- In 1911, Ernest Rutherford carried out a gold-foil experiment and found that most of the mass of an atom was located in the centre of the atom called the nucleus.
- In 1932, James Chadwick discovered that atoms have neutrons as parts of their structure.
- According to the modern concept of the atom, the three subatomic particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons—form the nucleus, while electrons revolve around the nucleus.
- Electrons are distributed in different energy levels or shells according to the Bohr-Bury scheme of electronic configuration.
- Atoms of an element combine or react to attain the electronic configuration of the nearest noble or inert gas and thus become stable.
- The bond formed between two atoms when they combine is called a chemical bond.
- Atoms can combine either by transferring electrons or by sharing electrons.
- The chemical bond formed by the complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another is called an electrovalent bond or ionic bond.
- The chemical bond formed by the sharing of electrons is called a covalent bond.
Glossary
- Discharge tube: A cylindrical glass tube with sealed electrodes at each end.
- Cathode: A metal plate connected to the negative terminal of the voltage source.
- Anode: A metal plate connected to the positive terminal of the voltage source.
- Cathode rays: A stream of rays originated from the cathode.
- Anode rays: Positively charged particles that are found inside the nucleus.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that are found inside the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Electrically neutral particles that are found inside the nucleus.
- Nucleus: The positively charged central part of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
- Atomic number: The number of protons present inside the nucleus of an atom.
- Mass number: The sum total of the number of protons and the number of neutrons present inside the nucleus of an atom.
- Relative atomic mass: The number of times by which the average mass of one atom of an element is heavier than 1/12th of the mass of a carbon atom.
- Isotopes: Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different mass number.
- Electronic configuration: The arrangement of electrons in different orbits or shells around the nucleus of an atom.
- Valence shell: The outermost shell of an atom.
- Valence electrons: The electrons present in the valence shell of an atom.
- Valency: The number of electrons that an atom needs to accept, donate, or share to form a complete outer octet.
- Electropositive valency: The valency of a positively charged ion.
- Electronegative valency: The valency of a negatively charged ion.
- Monovalent elements: Elements with valency one.
- Divalent elements: Elements with valency two.
- Trivalent elements: Elements with valency three.
- Radicals: Two or more non-metals that collectively accept or donate one or more electrons and become negatively or positively charged.
|
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on Atomic Structure Chapter Notes - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
| 1. What is Dalton’s Atomic Theory and its significance in understanding atomic structure? |  |
| 2. What are subatomic particles and who discovered them? |  |
| 3. How does the modern concept of an atom differ from earlier models? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of atomic number and relative atomic mass? |  |
| 5. What are isotopes and how do they affect the properties of an element? |  |