Mnemonics & Strategies: Para Summary | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
Introduction
In the Para Summary section, you’re given a short paragraph (typically 100–150 words) and asked to choose the best summary from 3 or 4 options. Your goal is to:
Understand the central idea
Identify the author’s intent
Choose the option that captures the essence without adding or missing key points.
What Makes a Good Summary?
A good summary is:
Concise – Shorter than the original
Complete – Covers all main points, not minor details
Accurate – Doesn't distort, exaggerate, or add assumptions
Neutral – Matches the tone of the original paragraph
The 4 Golden Mnemonics for Para Summary
1. GIST – Find the Core Message
G – Group ideas that repeat or support each other
I – Ignore examples, stats, and fluff
S – Spot the main argument or stance
T – Tone check: Is the author critical, supportive, or neutral?
Why use it? Helps you boil the paragraph down to its core.
2. MAIN – What Makes a Summary Right
Check if the option has:
M – Main idea covered
A – Author’s viewpoint preserved
I – Important points included
N – No extra ideas or assumptions
Why use it? Helps eliminate close but flawed options.
3. TRAPS – Spot the Wrong Choices
Avoid options with:
T – Twisted meaning
R – Repetition or too much detail
A – Assumptions not in the original
P – Partial coverage of the idea
S – Stray facts or examples as the focus
Why use it? Most wrong options fall into these traps.
4. CUTS – Strategy to Cut the Paragraph
Break the paragraph using:
C – Contrast words (but, however, although)
U – Unifying idea that links all lines
T – Transition words (thus, therefore, hence)
S – Shift in tone or direction
Why use it? To map the structure and locate the core.
Step-by-Step Summary Approach (5 Steps)
Read the paragraph quickly once to understand the essence of the passage.
Apply GIST – Get the core message in one line mentally.
Skim options and eliminate using TRAPS.
Verify remaining options with MAIN.
Choose the one that best preserves the essence and the tone.
Example Question
Paragraph:
Despite technological advances, online education struggles with low completion rates. Many students sign up enthusiastically but fail to finish. A major reason is a lack of motivation and structure. In physical classrooms, peer interaction and real-time feedback keep students engaged. Online settings lack these, and platforms must find ways to address the engagement gap.
Options:
A. Technological progress has made online education accessible to all.
B. Despite being accessible, online education faces challenges in student motivation and completion.
C. Students prefer classroom learning over online education due to peer interaction.
D. Online education is failing because students lack discipline.
Analysis using GIST:
Central idea: Online education is widespread but struggles with completion due to a lack of engagement.
Eliminate A (too broad), C (focus shifts to preference), and D (oversimplified blame).
Answer: B
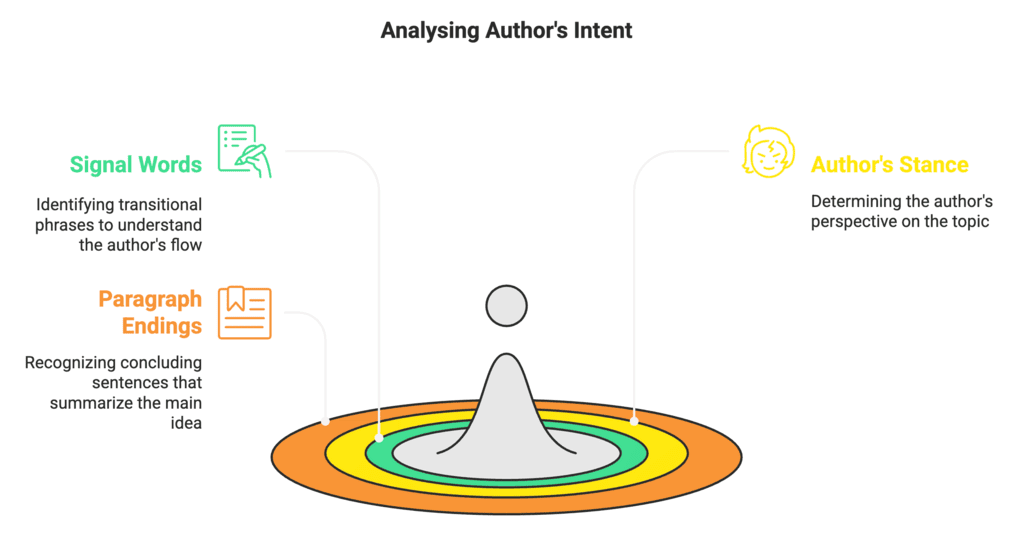
Bonus Tip – Author’s Intent Clues
Look for:
Signal words like "however," "therefore," "despite"
Author’s stance – is it critical, supportive, warning, or neutral?
End of paragraph – often wraps the idea
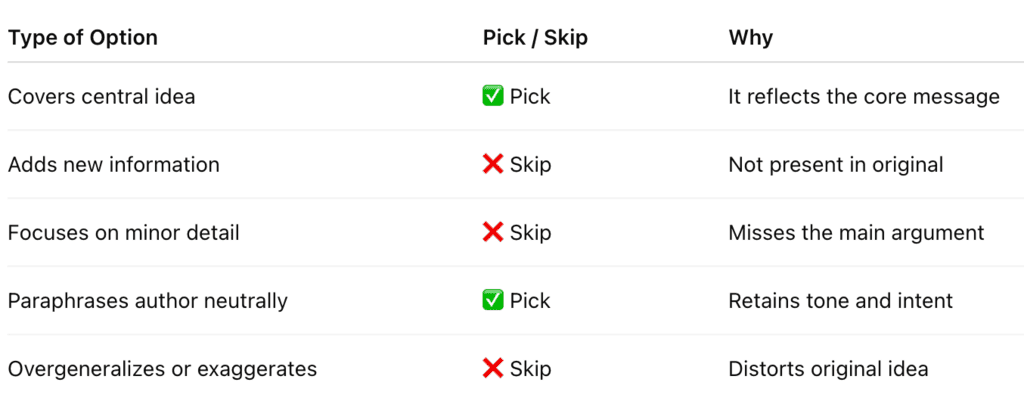
Check List: What to Pick and What to Skip
|
111 videos|452 docs|90 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics & Strategies: Para Summary - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What are the key components that make a good summary? |  |
| 2. How can the 4 Golden Mnemonics help in creating an effective summary? |  |
| 3. What is the step-by-step approach to summarizing a text? |  |
| 4. What role does the author's intent play in summarizing? |  |
| 5. What should be included in a checklist for effective summarization? |  |





















