Diagram Based Questions: Diversity in the Living World | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Q.1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 
(i) Identify the type of plant (tree, shrub, or herb) for each of the three plants shown in the diagram.
(ii) What is the main difference in the stem structure of the mango tree compared to the tomato plant?
(iii) Why are the branches of the rose plant shown starting close to the ground?
(iv) How does the height of the mango tree help it in its environment?
(v) Why is it important to observe the stem’s color and texture when classifying plants?
Ans: (i) Mango: Tree; Rose: Shrub; Tomato: Herb.
(ii) Mango tree has a thick, brown, woody stem; tomato plant has a green, tender, thin stem.
(iii) Rose is a shrub, characterized by multiple stems branching close to the ground.
(iv) The height of the mango tree allows it to access sunlight in dense forests and provide shade/shelter.
(v) Stem color and texture (e.g., woody vs. tender) indicate plant type (tree, shrub, herb) and strength.
Q.2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 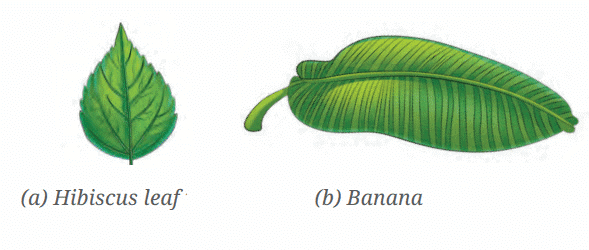
(i) Identify the type of venation in the hibiscus leaf and the banana leaf.
(ii) What is the main difference between reticulate and parallel venation shown in the diagram?
(iii) How does the venation pattern help classify plants into groups?
(iv) Why might the hibiscus leaf’s venation be suited for its environment?
(v) Why is it important to observe leaf venation without damaging the plant?
Ans: (i) Hibiscus: Reticulate venation; Banana: Parallel venation.
(ii) Reticulate has a net-like vein pattern; parallel has veins running side by side.
(iii) Reticulate venation indicates dicot plants; parallel venation indicates monocot plants.
(iv) Reticulate venation supports efficient nutrient transport in broad leaves, suitable for sunlight-rich environments.
(v) Observing without damaging preserves the plant’s ability to photosynthesize and survive.
Q.3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 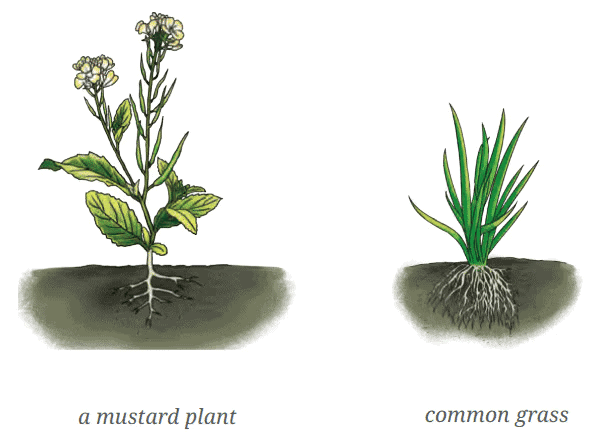 (i) Identify the type of root system in the mustard plant and the grass.
(i) Identify the type of root system in the mustard plant and the grass.
(ii) What is the main difference between the taproot and fibrous root systems shown?
(iii) Name one other plant that has a root system similar to the mustard plant.
(iv) How does the fibrous root system help grass survive in its environment?
(v) Why should you replant herbs after observing their roots, as shown in the diagram?
Ans: (i) Mustard: Taproot; Grass: Fibrous roots.
(ii) Taproot has one main root with side branches; fibrous roots are a cluster of thin roots.
(iii) Hibiscus or chickpea (taproot).
(iv) Fibrous roots spread widely to absorb water and prevent soil erosion, suitable for grassy areas.
(v) Replanting ensures the plant continues to grow and thrive after observation.
Q.4: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: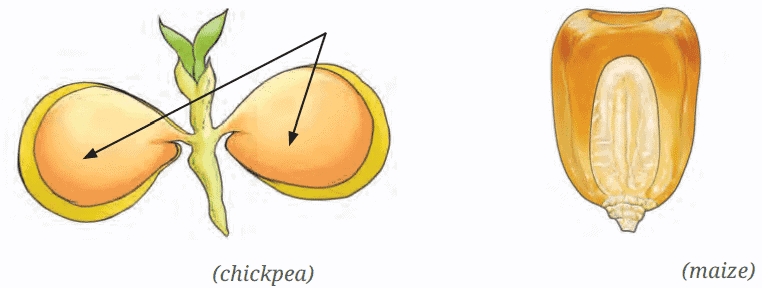 (i) Classify the chickpea and maize seeds as dicot or monocot based on the diagram. (ii) What is the difference in the number of cotyledons between the two seeds?
(i) Classify the chickpea and maize seeds as dicot or monocot based on the diagram. (ii) What is the difference in the number of cotyledons between the two seeds?
(iii) How does the seed structure relate to the plant’s root system?
(iv) Why is the cotyledon important for the seed shown in the diagram?
(v) Why should seeds be soaked before observing their structure, as described in the activity?
Ans: (i) Chickpea: Dicot; Maize: Monocot.
(ii) Chickpea has two cotyledons; maize has one cotyledon.
(iii) Dicots (chickpea) have taproots; monocots (maize) have fibrous roots.
(iv) Cotyledons provide nutrients to the growing embryo until it can photosynthesize.
(v) Soaking softens the seed coat, making it easier to observe internal structures without damage.
Q.5: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 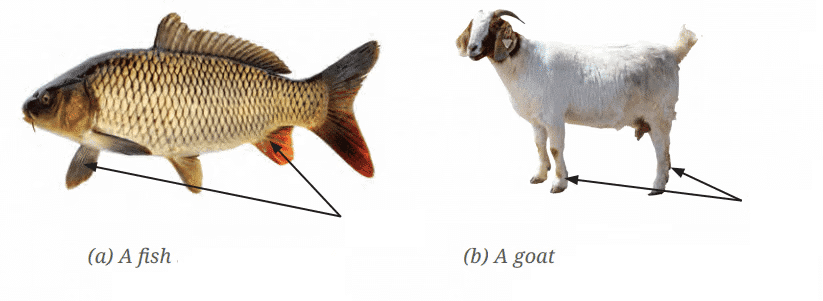
(i) Identify the type of movement performed by the fish and the goat shown in the diagram.
(ii) What body parts are used by the fish for movement, as shown in the diagram?
(iii) How do the goat’s legs help it move in its habitat?
(iv) Why is the habitat of the fish different from that of the goat, as depicted in the diagram?
(v) Why is it important to observe the movement of animals like the fish and goat without disturbing them?
Ans: (i) Fish: Swims; Goat: Walks and jumps.
(ii) Fish: Uses dorsal, pectoral, and tail fins for movement.
(iii) Goat’s legs: Strong legs with hooves allow walking and jumping on grassy or rocky terrain, providing stability and agility in terrestrial habitats.
(iv) Habitat difference: Fish lives in an aquatic habitat (water, e.g., rivers or oceans) requiring fins for swimming; goat lives in a terrestrial habitat (land, e.g., grasslands or mountains) requiring legs for walking/jumping.
(v) Observing without disturbing: Prevents stress or harm to animals, maintains their natural behavior, and preserves their habitat.
Q.6: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 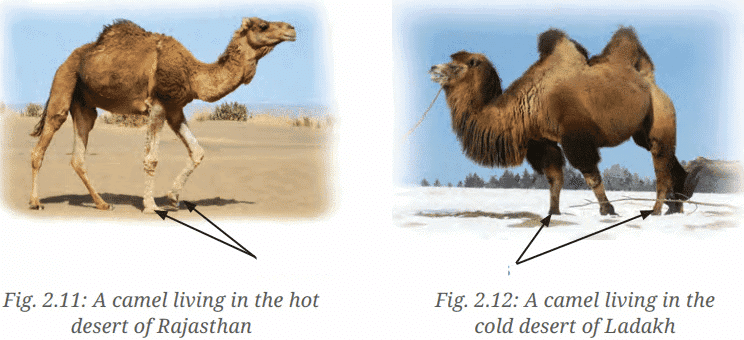 (i) How many humps does each camel in the diagram have?
(i) How many humps does each camel in the diagram have?
(ii) What is the difference in leg structure between the two camels?
(iii) How does the long hair of the cold desert camel help it survive?
(iv) Why are the wide hooves of the hot desert camel important for its habitat?
(v) Why is it important to compare adaptations of animals in different regions, as shown?
Ans: (i) Hot desert camel: One hump; Cold desert camel: Two humps.
(ii) Hot desert camel has long legs; cold desert camel has shorter legs.
(iii) Long hair protects the cold desert camel from cold winters in Ladakh.
(iv) Wide hooves prevent the hot desert camel from sinking into sandy deserts.
(v) Comparing adaptations helps understand how animals survive in specific environments.
Q.7: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: 
(i) What type of feet does the duck have in the diagram?
(ii) How do the duck’s feet differ from the pigeon’s feet?
(iii) What activity can the duck perform using its webbed feet?
(iv) Why is the pigeon’s foot structure suited for its habitat?
(v) Why should we observe animal features like feet without capturing the animal?
Ans: (i) Duck has webbed feet.
(ii) Duck’s feet have skin connecting toes; pigeon’s feet have separate, clawed toes.
(iii) Duck uses webbed feet to swim in water.
(iv) Pigeon’s clawed feet help it perch on branches and walk on land in terrestrial habitats.
(v) Observing without capturing prevents stress or harm to the animal.
|
67 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Diagram Based Questions: Diversity in the Living World - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is biodiversity and why is it important in the living world? |  |
| 2. How do we classify living organisms? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of different types of ecosystems? |  |
| 4. How do human activities impact biodiversity? |  |
| 5. What steps can be taken to protect biodiversity? |  |

















