Diagram Based Questions: Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Q.1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram below (change in cooking tools over time):

(i) Identify the modern cooking tools shown in the diagram.
(ii) What is the primary difference in the operation of the chulha compared to the modern gas stove?
(iii) Why is the electrical grinder a more advanced tool than the sil-batta?
(iv) How does the design of the modern gas stove contribute to safer cooking practices?
(v) Why is it important to understand the evolution of tools like those shown in the diagram when studying changes in culinary practices?
Ans:
(i) The modern cooking tools shown are the modern gas stove and the electrical grinder.
(ii) The chulha operates by burning solid fuels like wood or coal, producing smoke and ash, while the modern gas stove uses gas for cleaner, controlled combustion.
(iii) The electrical grinder is automated, using electricity to grind ingredients quickly, whereas the sil-batta requires manual effort, making it slower and more labor-intensive.
(iv) The modern gas stove has features like precise flame control and enclosed burners, reducing the risk of fire hazards and smoke inhalation compared to the open-flame chulha.
(v) Understanding the evolution of tools shows how technological advancements have improved efficiency, safety, and convenience in cooking, reflecting changes in lifestyle and resources.
Q.2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram below ( Some sources of carbohydrates):

(i) Identify three food items shown in the diagram that are sources of carbohydrates.
(ii) What is the main difference between the carbohydrate sources, like rice and fruits like bananas in terms of their form?
(iii) Why are cereals like wheat and maize prominently featured in the diagram?
(iv) How does the inclusion of vegetables like potatoes in the diagram contribute to a balanced diet?
(v) Why is it important to recognize the variety of carbohydrate sources shown in the diagram for dietary planning?
Ans:
(i) Three food items shown are rice, wheat, and bananas.
(ii) Rice is a cereal grain, consumed as a staple after cooking, while bananas are fruits, eaten raw or processed, offering quicker energy.
(iii) Cereals like wheat and maize are featured because they are primary carbohydrate sources, providing energy for daily activities in many diets.
(iv) Potatoes provide carbohydrates for energy, along with fiber and vitamins, contributing to a balanced diet when consumed in moderation.
(v) Recognizing the variety ensures diverse energy sources, preventing nutrient deficiencies and supporting dietary preferences across cultures and regions.
Q.3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram below:
(i) Identify two plant sources and two animal sources of proteins shown in the diagram.
(ii) What is the main difference between plant sources like pulses and animal sources like fish in terms of protein content?
(iii) Why is paneer highlighted as an animal-based protein source in the diagram?
(iv) How do plant-based protein sources like beans contribute to the diet of vegetarians as shown in the diagram?
(v) Why is it important to include both plant and animal protein sources in the diet, as depicted in the diagram?
Ans:
(i) Plant sources: pulses, beans; animal sources: fish, paneer.
(ii) Pulses provide protein along with fiber but in smaller amounts, while fish gives richer and easier-to-use protein for the body
(iii) Paneer is highlighted because it is a versatile, protein-rich dairy product widely used in Indian cuisine for muscle growth.
(iv) Beans provide vegetarians with essential proteins, fiber, and nutrients, supporting growth and repair without animal products.
(v) Including both ensures a complete amino acid profile and diverse nutrients, catering to varied dietary needs and health goals.
Q.4: Answer the following questions based on diagram below ( Some sources of different vitamins):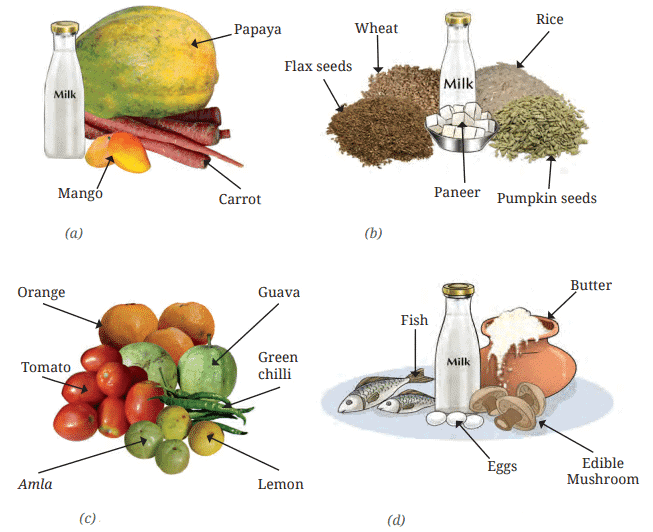
(i) Identify one food source shown for each of Vitamin A, Vitamin B1, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D in the diagram.
(ii) What is the main difference between the sources of Vitamin C and Vitamin D shown in the diagram?
(iii) Why is exposure to sunlight included as a source of Vitamin D in the diagram?
(iv) How do sources like amla for Vitamin C in the diagram help in preventing deficiency diseases?
(v) Why is it important to include a variety of vitamin sources as shown in the diagram in daily meals?
Ans:
(i) Vitamin A: carrot; Vitamin B1: rice; Vitamin C: amla; Vitamin D: fish.
(ii) Vitamin C sources (e.g., amla, oranges) are plant-based and consumed raw or cooked, while Vitamin D sources include sunlight and animal products (e.g., fish).
(iii) Sunlight is included because it triggers Vitamin D synthesis in the skin, essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
(iv) Amla, rich in Vitamin C, prevents scurvy by supporting immunity and healing, countering bleeding gums and slow wound recovery.
(v) A variety of vitamin sources ensures adequate intake of protective nutrients, preventing deficiency diseases and promoting overall health.
Q.5: Answer the following questions based on the figure mentioned below (Testing for the presence of starch in various food items):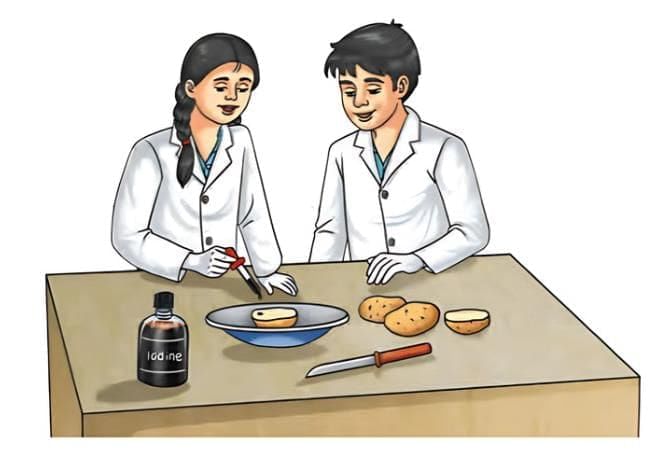
(i) Identify food items shown in the diagram that are tested for starch.
(ii) What is the main difference in the appearance of food items before and after the iodine test in the diagram?
(iii) Why is the iodine solution used in the diagram to test for starch?
(iv) How does the blue-black color change in the diagram indicate the presence of starch in food items?
(v) Why is it important to test multiple food items as shown in the diagram to understand their nutritional content?
Ans:
(i) The food items shown in the diagram are potatoes and bread.
(ii) Before the iodine test, food items retain their natural color; after, starch-containing items turn blue-black.
(iii) Iodine solution is used because it reacts with starch to produce a distinct blue-black color, confirming its presence.
(iv) The blue-black color results from iodine binding with starch molecules, indicating carbohydrates that provide energy.
(v) Testing multiple food items helps identify carbohydrate-rich foods, aiding in dietary planning for balanced energy intake.
Q.6: Answer the following questions based on the figure mentioned below (Testing for the presence of protein in various food items):
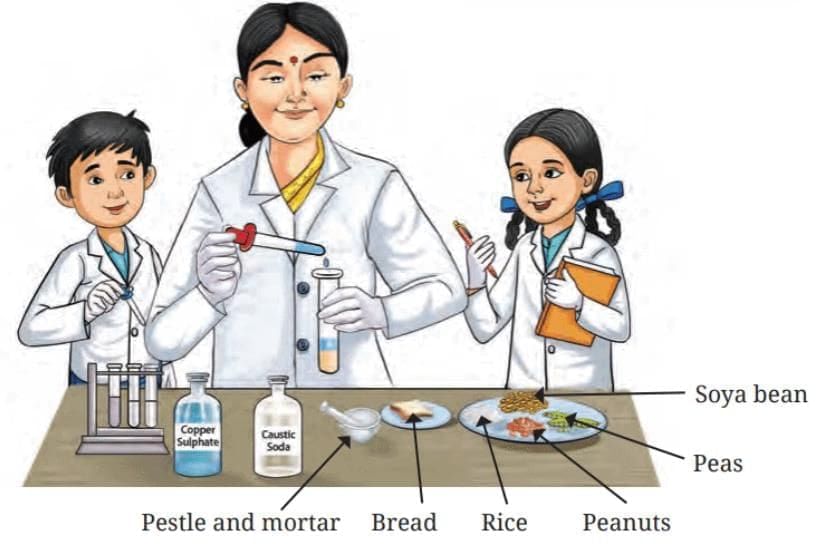
(i) Identify the chemicals used in the diagram to test for proteins in food items.
(ii) What is the main difference in the appearance of food samples before and after the protein test in the diagram?
(iii) Why is the pestle and mortar used to prepare food samples in the diagram?
(iv) How does the violet color change in the diagram confirm the presence of proteins?
(v) Why is it important to follow safety precautions when conducting the protein test shown in the diagram?
Ans:
(i) The chemicals used are copper sulphate solution and caustic soda solution.
(ii) Before the test, food samples retain their natural color, but after the test, protein-containing samples turn violet.
(iii) The pestle and mortar is used to grind food into a paste or powder, ensuring uniform mixing with test chemicals.
(iv) The violet color results from the reaction of proteins with copper sulphate and caustic soda, confirming their presence.
(v) Safety precautions are important because caustic soda and copper sulphate are harmful, requiring careful handling to avoid skin or ingestion risks.
Q.6: Answer the following questions based on the diagram (From farm to plate) given below:
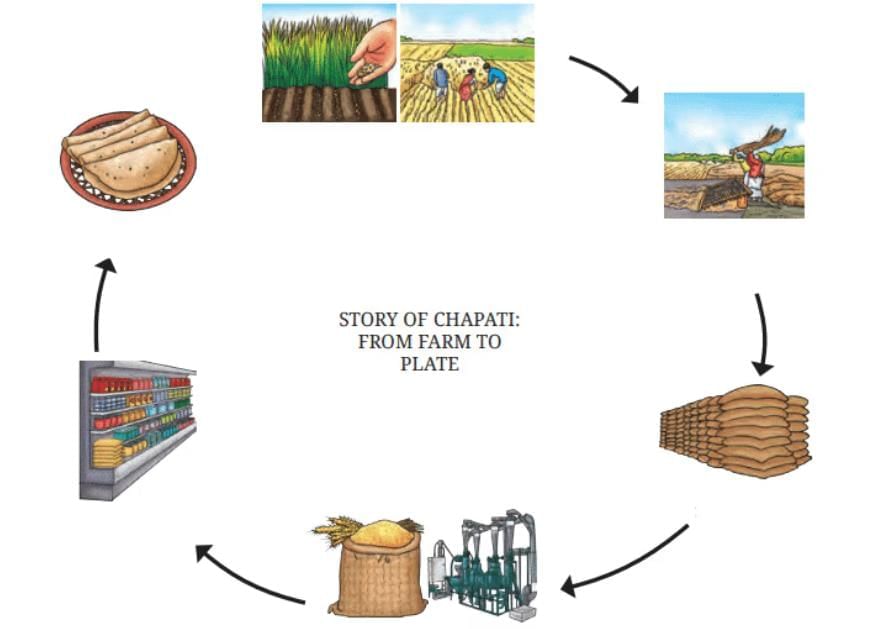
(i) Identify the stage in the diagram where wheat is processed into a usable form for cooking.
(ii) What is the key difference between the "harvesting" and "transport to retail shop" stages?
(iii) Why is the "sowing of seed grains" stage foundational for the entire process shown?
(iv) How does the "food on our plate" stage depend on the earlier stages in the diagram?
(v) Why is it important to reduce food miles as illustrated by the stages in the diagram?
Ans:
(i) The stage where wheat is processed into a usable form is "grinding of grains and packing."
(ii) Harvesting involves collecting mature wheat from fields, while transport to retail shop involves moving processed flour to stores for consumer purchase.
(iii) The "sowing of seed grains" stage is foundational because it initiates the growth of wheat, which is necessary for all subsequent stages leading to chapati production.
(iv) The "food on our plate" stage depends on earlier stages for growing, harvesting, processing, and transporting wheat, as each step ensures the availability of flour for cooking.
(v) Reducing food miles, as shown by the stages, minimizes transportation-related pollution, supports local economies, and ensures fresher, healthier food for consumers.
|
69 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Diagram Based Questions: Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is mindful eating? |  |
| 2. How can mindful eating help in maintaining a healthy body? |  |
| 3. What are some techniques to practice mindful eating? |  |
| 4. Can mindful eating benefit mental health as well? |  |
| 5. Is mindful eating suitable for children? |  |

















