Diagram Based Questions: Methods of Separation in Everyday Life | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Q.1: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What method of separation is shown in diagram?
(ii) Why is handpicking suitable for separating black peppers from pulao?
(iii) What property of black peppers makes them easy to identify in the diagram?
(iv) How does the quantity of black peppers affect the use of handpicking in diagram?
(v) Why is handpicking not used for separating fine impurities like sand from pulao?
Ans:
(i) Handpicking.
(ii) Black peppers differ in size, color, and shape from rice, making them easy to pick out.
(iii) Black peppers are larger and darker than rice grains, as shown in diagram.
(iv) Handpicking is effective for small quantities of black peppers, as it is time-consuming for large amounts.
(v) Fine impurities like sand are too small and numerous to pick by hand, unlike the distinct peppers in diagram.
Q.2: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: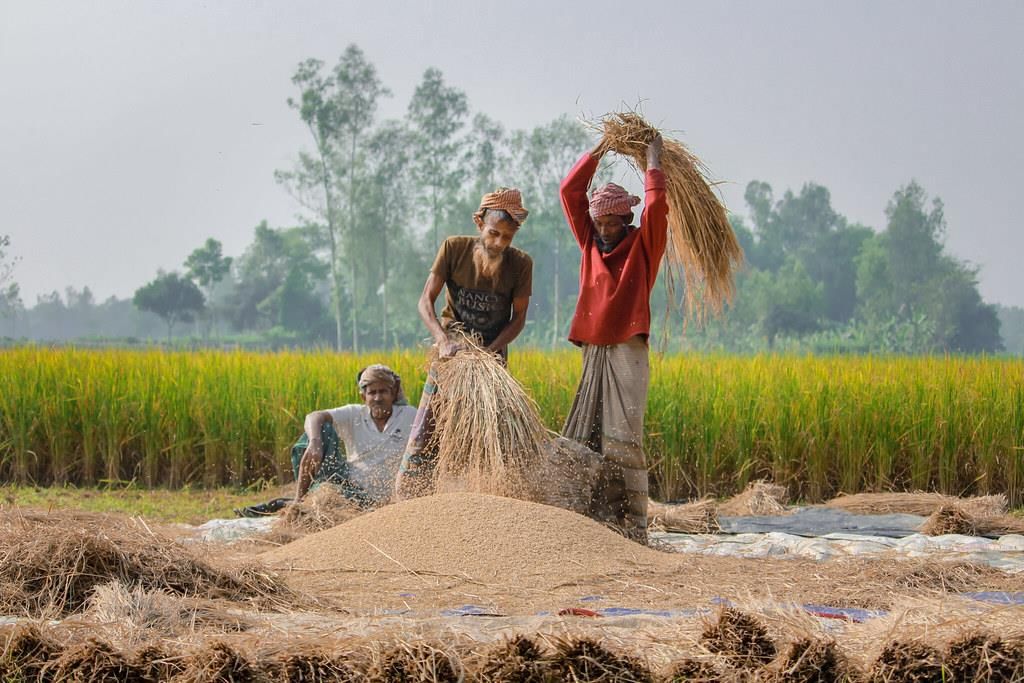
(i) What process is depicted in diagram?
(ii) What is the main purpose of the action shown in the diagram?
(iii) Why are the wheat stalks beaten on a wooden log in diagram?
(iv) How does drying the stalks before threshing, as mentioned in process shown?
(v) Why is threshing necessary before winnowing in the separation process?
Ans:
(i) Threshing.
(ii) To separate grains from wheat stalks.
(iii) Beating breaks the stalks, releasing the grains, as shown in diagram.
(iv) Drying makes stalks brittle, allowing grains to separate easily when beaten.
(v) Threshing frees grains from stalks, enabling winnowing to separate grains from husk.
Q.3: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What separation method is shown in the diagram?
(ii) What is the main difference in the behavior of wheat grains and husk in the diagram?
(iii) Why is the farmer standing on a raised platform in diagram?
(iv) How does wind contribute to the separation process shown in the diagram?
(v) Why does winnowing fail in a closed room?
Ans:
(i) Winnowing.
(ii) Husk is blown away by wind; wheat grains fall closer due to their weight.
(iii) The raised platform in diagram allows better wind flow to carry husk away.
(iv) Wind blows lighter husk away while heavier grains fall, as shown in diagram.
(v) Winnowing requires air movement, absent in a closed room, to separate components.
Q.4: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: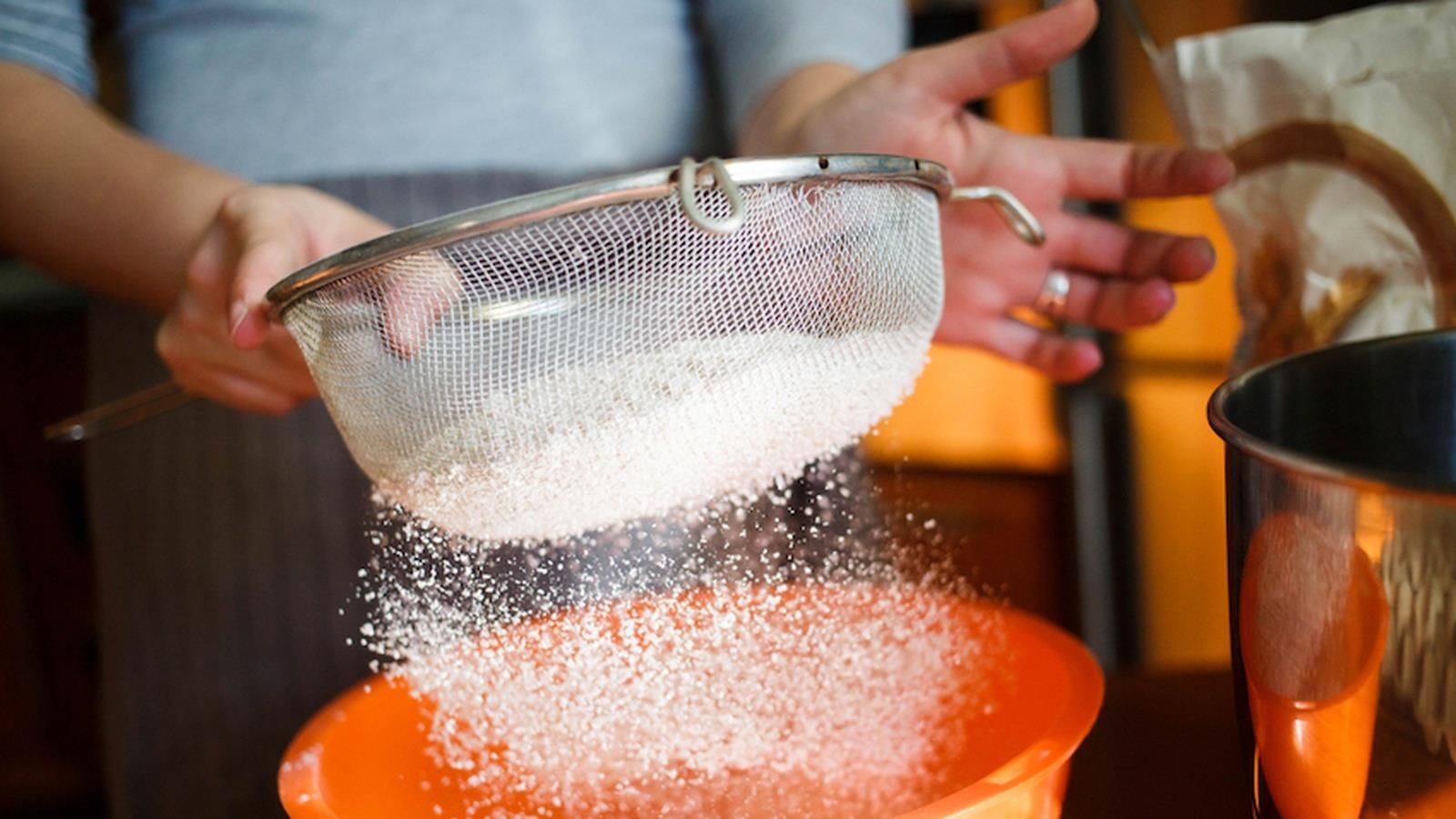
(i) What process is illustrated in diagram?
(ii) What is the main difference between the particles that pass through and those that remain on the sieve?
(iii) Why do bran and stones remain on the sieve in diagram?
(iv) How does the sieve’s hole size affect the separation process shown in the diagram?
(v) Why is sieving used at construction sites?
Ans:
(i) Sieving.
(ii) Fine flour passes through; larger bran and stones remain on the sieve.
(iii) Bran and stones are larger than the sieve’s holes.
(iv) Holes allow smaller particles to pass while retaining larger ones, enabling separation.
(v) Sieving separates larger pebbles from finer sand, similar to bran from flour.
Q.5: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What separation method is depicted in diagram?
(ii) What is the main difference between the components left in the pits and those removed?
(iii) Why are shallow pits used in diagram for this process?
(iv) How does sunlight contribute to the separation shown in the diagram?
(v) Why is further purification needed after the process shown in diagram?
Ans:
(i) Evaporation.
(ii) Solid salt remains; water evaporates as vapor.
(iii) Shallow pits increase surface area for faster evaporation, as shown in diagram.
(iv) Sunlight heats seawater, causing water to evaporate and leave salt behind.
(v) The solid mixture contains impurities, requiring purification to obtain pure salt.
Q.6: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What process is depicted in diagram?
(ii) What is the main difference between the tea leaves and the liquid tea in the diagram?
(iii) Why are tea leaves left at the bottom in diagram?
(iv) How does sedimentation contribute to the process shown in the diagram?
(v) Why does decantation not fully separate tea leaves, as noted in diagram?
Ans:
(i) Decantation.
(ii) Tea leaves are heavier and insoluble; liquid tea is lighter and pourable.
(iii) Tea leaves settle at the bottom due to sedimentation, as shown in diagram.
(iv) Sedimentation allows heavier tea leaves to settle, enabling liquid to be poured off.
(v) Some fine tea leaves may remain suspended, not fully settling during decantation.
Q.7: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below: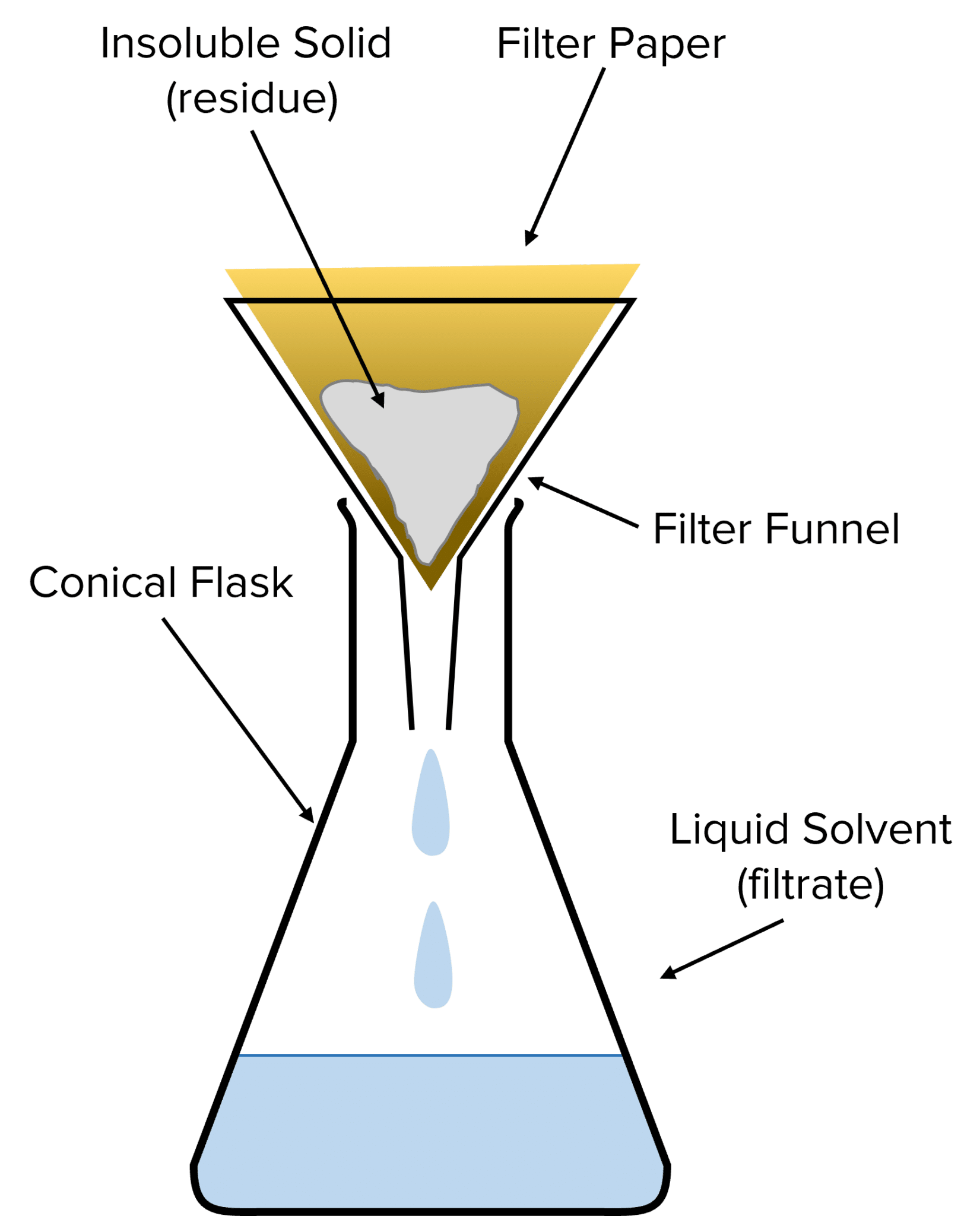
(i) What separation method is shown in diagram?
(ii) What is the main difference between the water in the funnel and the water in the conical flask?
(iii) Why do mud particles remain on the filter paper in diagram?
(iv) How does the filter paper’s pore size affect the process shown in the diagram?
(v) Why is filtration more effective than decantation for muddy water in diagram?
Ans:
(i) Filtration.
(ii) Water in the funnel is muddy; water in the flask is clear.
(iii) Mud particles are larger than the filter paper’s pores, as shown in diagram.
(iv) Small pores trap mud while allowing water to pass through.
(v) Filtration traps all mud particles; decantation may leave some suspended particles.
Q.8: Answer the following questions based on the diagram given below:
(i) What separation method is depicted in image above?
(ii) What is the main difference between iron nails and sawdust in the diagram?
(iii) Why are iron nails attracted to the magnet in image?
(iv) How does the process in diagram benefit industrial recycling?
(v) Why is magnetic separation not suitable for separating sand from sawdust?
Ans:
(i) Magnetic separation.
(ii) Iron nails are magnetic; sawdust is non-magnetic.
(iii) Iron nails are attracted due to their magnetic properties, as shown in diagram.
(iv) It efficiently separates iron from waste, allowing recycling of scrap iron.
(v) Neither sand nor sawdust is magnetic, so a magnet cannot separate them.
|
69 videos|289 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Diagram Based Questions: Methods of Separation in Everyday Life - Science for Class 6
| 1. What are some common methods of separation used in everyday life? |  |
| 2. How does filtration work as a method of separation? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between evaporation and condensation in the context of separation? |  |
| 4. Can you explain sedimentation and how it is used in daily life? |  |
| 5. What role does magnetic separation play in separating materials? |  |
















