Map Based Questions: Geographical Diversity of India | Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q.1: Identifying Landforms: Locate and mark the Himalayan Mountain Range on the physical map of India.
Ans: The Himalayan Mountain Range is located in the northern part of India, stretching across the northern border from Jammu and Kashmir in the west to Arunachal Pradesh in the east. (Mark this range on the map along the northern boundary.)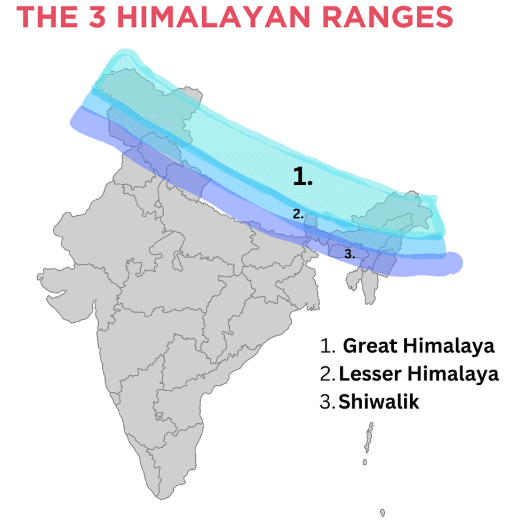
Q.2: Rivers and Their Flow:
a) Trace the path of the Ganga River from its origin to where it meets the Bay of Bengal on the physical map.
b) Identify and name two states through which the Ganga flows, using the political map.
Ans:
a) The Ganga River originates at Gaumukh in the Gangotri Glacier (Uttarakhand) and flows southeast through the Gangetic Plains, passing through Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal before meeting the Bay of Bengal at the Sundarbans delta. (Trace this path on the map.)
b) Two states through which the Ganga flows are Uttar Pradesh and Bihar.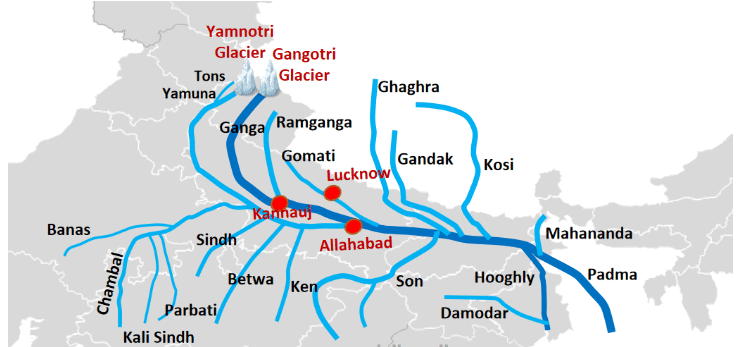
Q.3: The Thar Desert:
a) On the physical map, locate and shade the Thar Desert.
b) Mark the location of Jaisalmer in the Thar Desert and indicate why it is called the "Golden City."
Ans:
a) The Thar Desert is located in the northwestern part of India, primarily in western Rajasthan, extending into parts of Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana. (Shade this yellowish area on the physical map.)
b) Jaisalmer is located in the heart of the Thar Desert in Rajasthan. It is called the "Golden City" because its fort and buildings are made of yellow sandstone, which glows golden in the sunlight. (Mark Jaisalmer in western Rajasthan.)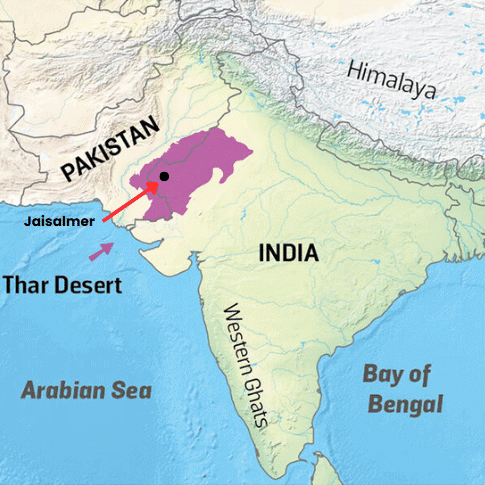
Q.4: The Peninsular Plateau
a) On the physical map, locate and outline the Peninsular Plateau.
b) Name one river that originates in the Peninsular Plateau and flows into the Bay of Bengal.
c) Locate and mark the Lakshadweep Islands and Andaman and Nicobar Islands on the physical map.
Ans:
a) The Peninsular Plateau is located in central and southern India, forming a triangular shape bordered by the Western Ghats, Eastern Ghats, and northern plains. (Outline this central region on the physical map.)
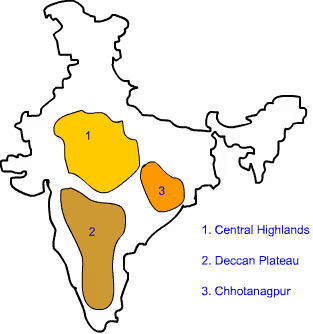
b) The Godavari River originates in the Peninsular Plateau (in Maharashtra) and flows eastward into the Bay of Bengal. (Mark its path from central Maharashtra through Andhra Pradesh to the Bay of Bengal.)
c) Marking of the Lakshadweep Islands and Andaman and Nicobar Islands on the physical map is as follows: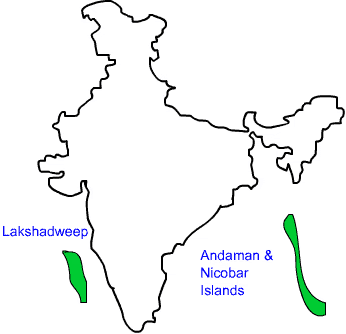
Q.5: Coastal Features: On the physical map, locate and label the West Coast and East Coast of India.
Ans: The West Coast stretches along the Arabian Sea from Gujarat to Kerala, and the East Coast lies along the Bay of Bengal from West Bengal to Tamil Nadu. 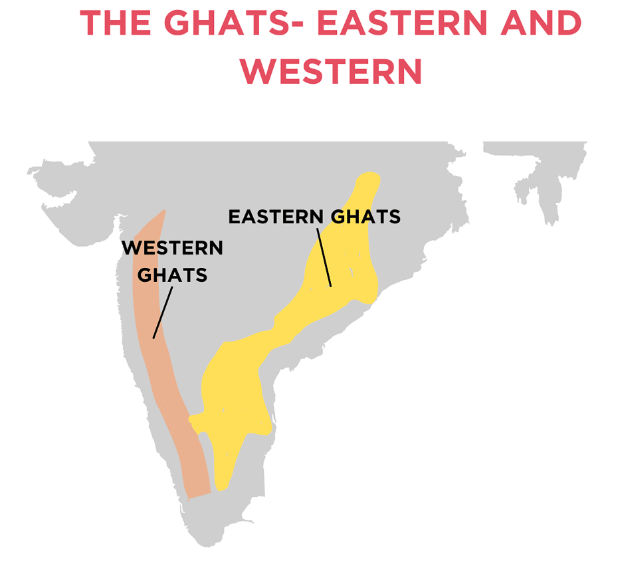
Q.6: The Aravalli Hills
a) Locate and outline the Aravalli Hills on the physical map.
b) Name two states that the Aravalli Hills span, using the political map.
c) Name the highest peak of the Aravallis.
Ans:
a) The Aravalli Hills are located in northwestern India, stretching from Gujarat through Rajasthan to Haryana and Delhi. (Outline this range on the physical map.)
b) Two states that the Aravalli Hills span are Rajasthan and Haryana.
c) Mount Abu, the highest peak of the Aravallis, is located in Rajasthan.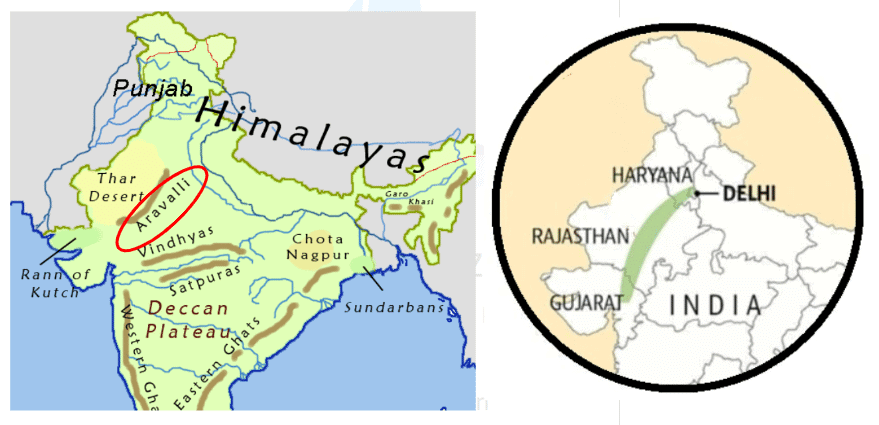
Q.7: The Sundarbans
a) On the physical map, locate and mark the Sundarbans in the delta region of West Bengal.
b) Name the two major rivers that contribute to the formation of the Sundarbans delta.
Ans:
a) The Sundarbans is located in the delta region of southern West Bengal, near the Bay of Bengal. (Mark this area on the physical map.)
b) The two major rivers that contribute to the Sundarbans delta are the Ganga and Brahmaputra.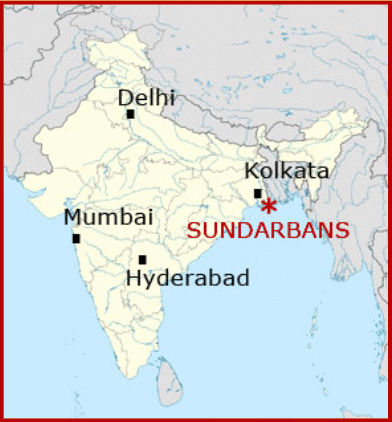
|
28 videos|204 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Map Based Questions: Geographical Diversity of India - Social Science Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main geographical features of India that contribute to its diversity? |  |
| 2. How does the geographical diversity of India affect its climate? |  |
| 3. What role do rivers play in the geographical diversity of India? |  |
| 4. How do mountains influence the lifestyle of people in India? |  |
| 5. In what ways do coastal regions contribute to the geographical diversity of India? |  |

















