Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Chapter Notes: India - Human Resources
India - Human Resources Chapter Notes - Class 8 PDF Download
Introduction
Human resources refer to the people who contribute to a country's growth and development through their skills and abilities. This chapter explores the concept of human resources, their importance, and how they are managed in India. It covers population distribution, rural-urban and geographical factors, sex ratio, the role of health and education, and the significance of skilled and unskilled human resources. The chapter also highlights efforts by the government and corporations to enhance skills and improve the economic contribution of India's large populatio
India - Human Resources
- Human resources are people who use their skills and abilities to benefit a country.
- Managing people is known as human resource management.
- Humans are a resource because they help improve and make things convenient for society.
- They contribute to the growth of a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) through productive work.
- Humans, with proper knowledge, skills, and technology, can turn physical materials into valuable resources.
- India is rich in human resources due to its large population, with 65% aged between 25 and 35.
- Investing in education, vocational training, and medical care turns a population into a valuable resource.
- Human resources are more powerful than other resources because people can be educated, healthy, and determined.
- Like natural resources, human resources are not evenly distributed across the world.
- Human resources hold unique and irreplaceable value for a country.
Population Distribution
- Population is the total number of people living in a specific area at a specific time.
- People are not evenly spread across the Earth due to physical and human factors.
- Relief, soil, and climate affect population density.
- Low, flat lands with a temperate climate attract dense populations.
- Areas with extreme heat, cold, mountains, deserts, or hostile environments have fewer people.
Population Distribution in India
- India’s demography is diverse, with over 2,000 ethnic groups.
- Factors like income, education, sex ratio, geography, and rural-urban divide add to this complexity.
Rural-urban Distribution
- India is largely an agrarian society, with more than three-fourths of people living in rural areas.
- Most rural people depend on agriculture and related jobs for their livelihood.
- Agriculture remains a key part of India’s economy in the 21st century.
- Urban areas have 75% of people working in non-agricultural jobs like IT or marketing.
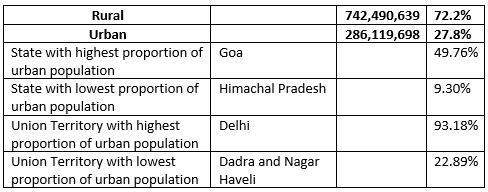
- About 27.8% of India’s population lives in urban areas, according to a recent census.
- Cities like Kolkata, Chennai, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Delhi, Chandigarh, Pune, Bengaluru, Ahmedabad, and Kanpur are highly urbanized.
- The average density in these urban centers is around 6,888 persons per square kilometer.
- Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Tamil Nadu are the most urbanized states in terms of economy and development.
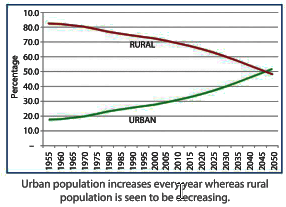
- Large-scale migration from rural to urban areas is happening due to urbanization.
- Over the last 50 years, rural population growth has been slow, while urban population has grown significantly.
Table Showing the Distribution of Rural-urban Population
Migration Effect
- Rural areas face issues like limited job opportunities, low income, and lack of education and medical facilities.
- To escape these problems and seek better opportunities, people migrate to urban areas.
- This migration increases the urban population and changes population distribution.
Benefits of Urban Life
- Urban areas offer better education, medical, and health facilities.
- They provide more job opportunities, better transport, and recreation options.
- These benefits attract rural people to settle in towns and cities.
- The National Sample Survey Organisation notes that rural men migrate for jobs, while women often move for marriage.
- Urban population grows yearly, while rural population decreases.
Geographical Features
- Geographical features and location influence population density and distribution.
- Fertile agricultural land, good soil, and water availability attract large agrarian populations.
- The northern plains, especially the Ganga Plain, have the highest population concentration.
- India’s diverse geography and weather affect population patterns.
- Coastal areas and cities near large water bodies draw people due to favorable climates.
- The Thar Desert in western India is sparsely populated due to its harsh climate.
- Plains support modern development, better infrastructure, and transport like roadways and railways.
- Cities like Srinagar Valley, Delhi, Pune, and Nasik benefit from good connectivity.
- Some areas are ideal for industries due to connectivity and raw material availability, leading to population growth.
Sex Ratio
- The number of females per 1,000 males is the indicator of the sex ratio in any country.
- This composition is a very significant and important indicator of the quality of population of a country.
- It also indicates the status of women in a country.
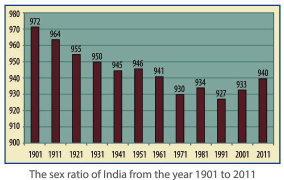
- In the last two decades, there has been a considerable improvement in the Indian sex ratio.
- Sex ratio in India, as per the recent census, is 940 which is largely comparable to the best performance (941 in 1961) in the last fifty years.
- The sex ratio directly reflects the status and position of women in a society.
- In the regions with rampant gender discrimination, the sex ratio tends to bend towards males.
- Areas where such discrimination occurs usually have many cases of female foeticide, female infanticide and domestic violence against women.
Sex ratio is calculated as follows:
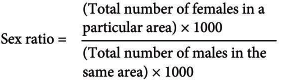
Suppose in a district, the total number of females is 11,500 and the total number of males is 14,000. Thus,
Sex ratio = (11500/14000) x 1000
= 822 females per thousand males.
Role of Health and Education
- Health and education are vital for developing a country’s human resources.
- Education indirectly supports health and connects individuals, families, and society.
- It shapes present actions and future plans, helping people understand the world.
- Education and literacy indicate a society’s development level.
- At the end of British rule, India’s literacy rate was only 12%.
- In the 1950s, it rose to 18.33%, reaching 65.37% by 2001 and 74.04% by 2011.
- Kerala has the highest literacy rate at 94%, followed by Mizoram (91.33%) and Lakshadweep (91.85%).
- Female literacy is lower at 65.46%, compared to 80% for males.
Education Helps People Become Better Citizens
- Education raises awareness of socioeconomic issues in one’s own and other countries.
- Educated people contribute to progress by conserving water or using public transport to save fuel.
- Uneducated people often lack awareness of their surroundings, rights, and duties.
Education Shows the Importance of Rights and Duties
- Educated people understand actions that benefit themselves and their country.
- They know their duties and vote for leaders who can improve the economy.
- This raises their standard of living and supports national growth.
Education Helps in Getting Jobs
- Uneducated people struggle to find good jobs, and unemployment slows economic growth.
- Education exposes people to new ideas, economics, politics, and science.
- It helps them engage globally and perform their duties effectively.
- The Government of India passed the Right to Education Act 2009 on August 4, 2009.
- This act ensures free and compulsory education for children up to age 14.
- Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan also aims to universalize education in a time-bound manner.
- Education boosts productivity and speeds up technological advancements.
- It leads to healthier, more productive children and promotes economic development.
- Education empowers people to build a better society.
Skilled and Unskilled Human Resources
Human resources are also referred to as manpower. There are three types of human resources—skilled, semi-skilled and unskilled. In this section, we shall learn about skilled and unskilled human resources.Skilled Human Resources
- Skilled labor, with specialized training or skill sets, drives economic growth.
- These workers can be blue-collar (manual, technical labor) or white-collar (office, administrative work).
- They have the knowledge and aptitude to perform specific tasks well.
- A skilled workforce ensures business success, even with limited resources.
- Businesses with skilled workers help the country’s economy grow.
- Skilled people work efficiently and are dedicated to their fields.
- Examples include teachers, doctors, and engineers.
Unskilled Human Resources
- Unskilled labor involves jobs that don’t require special skills or training.
- These workers perform manual tasks without using reasoning or intellectual skills.
- Examples include packagers, assemblers, apprentices, and farm workers.
- Unskilled jobs need little formal education and can be done by most people.
- Technology and societal changes are reducing unskilled jobs.
- Manual tasks are now often done by computers, requiring workers to learn new skills.
- Remaining unskilled jobs include farm laborers, grocery clerks, hotel maids, and cleaners.
Unskilled Human Resources in India
- India has a large population, but only 5% are trained and skilled.
- Most people lack formal training or specialized skills.
- Investing in vocational education and training can benefit the country.
- With a changing economy, improving the skills of young people is essential.
Various Programmes Run by Some Corporations in the Country
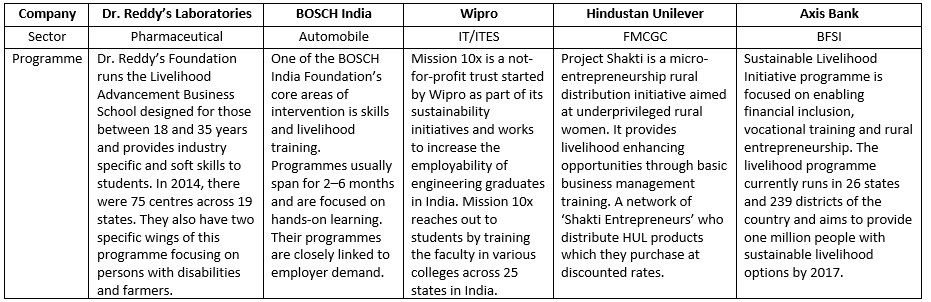
Increasing Skilled Human Resources in India
- The Government of India created a Skills Ministry to promote innovative skill development ideas.
- This ministry supports youth in skilling and entrepreneurial activities.
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) identified 24 high-growth sectors needing skilled workers.
- Key sectors include manufacturing, textile, construction, automotives, retail, healthcare, and transportation.
- Companies can gain by investing in skill development programs for these sectors.
- The Skill India Mission encourages companies to bridge the skill gap.
- Private sector involvement, alongside government and agencies, is vital for widespread impact.
- Training programs can skill the large unskilled population, benefiting industries and the country.
Impact of Skilled Human Resources on the Development of a Country
- Human beings are everywhere, but only skilled ones are true human resources.
- Human resources are the active age group contributing to economic growth.
- Their value in a country grows daily due to their impact.
Agricultural Development
- Agriculture is a priority in agrarian countries like India and requires skilled labor.
- Skilled workers use scientific tools, new ideas, and methods to boost agriculture.
- Transforming agriculture from subsistence to a business needs skilled human resources.
- Development in agriculture also strengthens the economy.
Optimum Use of Resources
- Skilled human resources use a country’s resources carefully and efficiently.
- Progress depends on sustainable use of water, forests, and minerals.
- Active human initiatives ensure resources are used wisely.
Development of Industries
- Skilled human resources drive industrial growth.
- Industries need modern technology, new ideas, machinery, raw materials, and energy.
- These essentials rely on skilled and trained workers.
Large-scale Production
- Human resources are active factors in production, using land, capital, and organization.
- With optimum resource use, large-scale production is possible.
Economic Development
- Skilled human resources are key to economic development.
- Other infrastructure development relies on active, skilled people.
- They act as agents of change for a better life and progress.
Agent of Foreign Trade
- Skilled human resources excel in foreign trade.
- They understand how to expand trade and maximize benefits.
- They also help minimize losses in international trade.
FAQs on India - Human Resources Chapter Notes - Class 8
| 1. What is population distribution and why is it important? |  |
Ans.Population distribution refers to how people are spread across a particular area or region. It is important because it helps governments and organizations understand where resources are needed, plan for infrastructure, and address issues like housing, transportation, and healthcare. Understanding population distribution can also highlight areas that may require more investment or support.
| 2. How does the sex ratio impact the population dynamics in India? |  |
Ans.The sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. In India, the sex ratio has been a concern due to a historical preference for male children. A skewed sex ratio can lead to various social issues, including gender imbalance, increased crime rates, and difficulties in marriage patterns. Addressing the sex ratio is crucial for ensuring gender equality and sustainable population development.
| 3. What role do health and education play in enhancing human resources? |  |
Ans.Health and education are critical components in developing human resources. A healthy population is more productive and able to contribute effectively to the workforce. Education equips individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform various jobs efficiently. Together, they enhance the quality of the workforce, leading to economic growth and improved living standards.
| 4. How is India working to increase its skilled human resources? |  |
Ans.India is implementing various initiatives to boost skilled human resources, such as the Skill India Mission, which aims to provide training and certification in various trades. Additionally, vocational training programs, partnerships with industries, and educational reforms are being introduced to align skills with market needs. This focus on skill development is essential for enhancing employability and driving economic progress.
| 5. What is the impact of skilled human resources on a country's development? |  |
Ans.Skilled human resources significantly impact a country's development by driving innovation, increasing productivity, and fostering economic growth. A well-trained workforce can adapt to technological changes and improve efficiency in various sectors. Moreover, skilled individuals contribute to higher income levels, better standards of living, and overall social progress, making them vital for the sustainable development of any nation.
Related Searches




















