Landforms Chapter Notes | Geography Class 6 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Endogenic and Exogenic Forces |

|
| Mountains |

|
| Valleys |

|
| Plateaus |

|
| Plains |

|
| Impact of Landforms on Humans |

|
Introduction
Landforms are the natural features that shape the Earth's surface, such as mountains, plateaus, plains, and valleys. This chapter explores how these landforms are formed through natural forces, their types, characteristics, and their importance to humans and the environment. It covers the processes like tectonic movements, erosion, and deposition that create and modify these features, along with their impact on human life and activities.
Landforms are visible features on the Earth's surface, like mountains, plateaus, deserts, and coastal plains.
Endogenic and Exogenic Forces
- Landforms are shaped over time by natural forces acting on the Earth.
- Endogenic forces come from inside the Earth, causing folding, faulting, earthquakes, and volcanic activities.
- Exogenic forces act on the Earth's surface through wind, water, and glaciers, modifying landforms via weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition.
- Exogenic processes create various landforms like mountains, plateaus, and plains.
Mountains
- Mountains are high landmasses rising at least 1,000 feet above their surroundings, with steep slopes, ridges, and a peak or summit.
- A chain of mountains forms a mountain range.
- Mountains can be barren, rocky, or covered with forests, with grasses and shrubs at higher altitudes below the snow line.
- Mountains are classified based on how they are formed.
- Movement at Plate Boundaries: Tectonic plates in the Earth's crust move, creating various landforms.
Fold Mountains
- Fold mountains form when the Earth's crust buckles or folds due to compression from colliding tectonic plates.
- They are usually found at plate edges.
- Fold mountains are divided into young and old types.
Young Fold Mountains
- These are 10 to 25 million years old and still growing.
- Examples include the Himalayas, Alps, Rockies, Andes, and Great Dividing Range.
- Features include faulting, complex folds, volcanic activity, and erosion by wind, ice, or water.
- They often have glacier-capped peaks.
- Mount Everest grows about 2.4 inches per year due to tectonic movement.
Old Fold Mountains
- These are over 200 million years old.
- Examples include the Urals, Appalachians, and Aravallis.
- Features include relic plateaus, sculptured domes, accordant summits, and irregular peaks due to erosion.
Block Mountains
- Formed when one side of a fault in the Earth's crust slides over another, pushing one side up and the other down.
- Also called horsts, with the rift valley formed called a graben.
- Examples include the Vindhya, Satpura, Vosges, Sierra Nevada, and Black Forest Mountains.
Volcanic Mountains
- Formed by molten magma erupting as lava through cracks in the Earth's crust.
- Successive eruptions build a volcanic cone with ash and rocks piling up near the vent.
- Examples include Mt Kilimanjaro and Mt Fuji.
- Formation stages: magma reaches the surface, erupts explosively, lava flows and cools to form a cone, and repeated flows build the mountain.
Importance of Mountains
- Mountains are rich in natural resources like minerals (coal, limestone), timber, lac, and medicinal herbs.
- Perennial rivers from mountains provide water for irrigation and other uses.
- Rivers deposit silt, forming fertile plains like the Indo-Gangetic plains.
- Mountains act as natural political boundaries, like the Himalayas between India and China.
- They block cold winds and influence rainfall, like the Himalayas causing monsoons to ascend.
- Mountains attract tourists due to their pleasant climate and scenic beauty, boosting tourism in places like Shimla, Nainital, and Mussoorie.
Valleys
- Valleys are common landforms carved by water or ice through erosion.
- Found in plains, hills, and mountains, with a sloping floor and valley walls or slopes.
- Rivers and streams in valleys drain land to the ocean, with flood plains along riverbanks.
- Types include river valleys, glacial valleys, and rift valleys.
River Valley
- Formed by water erosion, usually V-shaped with steep walls.
- Deep river valleys are called canyons or gorges, like the Grand Canyon.
Glacial Valley
Carved by glaciers during the Pleistocene Era, with wide, U-shaped contours and flat bottoms.
Rift Valley
- Formed by tectonic plate movements creating faults and depressions.
- Differ from river and glacial valleys as they result from tectonic activity, not erosion.
- Narrow with steep sides and flat floors, often called grabens.
- Formed when outer landmasses move away, causing the middle land to drop, creating a graben.
- Can range from hundreds of feet to many kilometers wide, like the Great Rift Valley (up to 64 km).
- Examples include Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Godavari, and Damodar valleys.
Cenozoic Rift System
- Formed by the collision of European and African plates in the late Cretaceous Period.
- Includes the Bresse Graben and Upper Rhine Graben in Europe.
Narmada Valley
- A rift valley in central India with the Narmada River flowing west between Satpura and Vindhya ranges.
- Other rivers include Damodar and Tapti.
The Great Rift Valley
- Located in eastern Africa, from Lake Malawi to the Dead Sea.
- Contains lakes and the Nile River, originating from Lake Victoria.
Plateaus
- Plateaus are elevated areas with flat or leveled tops and steep slopes on at least one side.
- Found at 600-1,500 meters above sea level, covering about 18% of the Earth's surface.
- Also called high plains or tablelands, they are one of the four major landforms.
- The Deccan Plateau in India is one of the oldest plateaus.
Formation of Plateaus
- Formed by volcanic magma, lava extrusion, running water, and glaciers.
- Magma lifts flat rock areas to form plateaus without breaking through the crust.
- Water erodes rock layers, creating deep channels and steep slopes.
- Wind erosion can shape slopes and plateaus.
- Mountains or other landforms can erode into plateaus, while large plateaus may form smaller mesas or buttes.
Classification of Plateaus
Plateaus are classified into intermontane, piedmont, continental, and dissected types.
Intermontane Plateaus
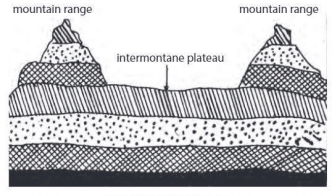
- Located near or within fold mountains, with nearly horizontal rock layers raised high by Earth's movement.
- The Plateau of Tibet is an example, surrounded by the Himalayas, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Tien Shan.
Piedmont Plateaus
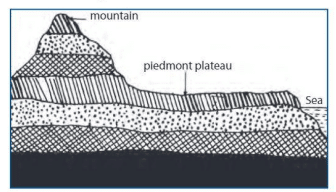
- Found at the foot of mountains, with one side bordered by a sea, plain, or ocean.
- Called plateaus of denudation, as they were once high but eroded down.
- The Malwa Plateau is an example.
Continental Plateaus
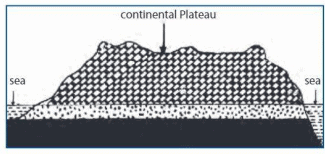
- Bordered by plains or oceans, formed away from mountains.
- Also known as plateaus of accumulation.
- The Plateau of Maharashtra is an example.
Dissected Plateaus
- Intensely eroded plateaus with sharp relief, appearing mountainous or hilly.
- Examples include the Catskill Mountains and Blue Mountains.
Significance of Plateaus
- Rich in minerals like gold, copper, diamond, coal, iron, manganese, and mica.
- River waterfalls at plateau edges are ideal for hydropower generation.
- Elevated areas have a cool climate, even in tropical regions.
- Grasslands support animal rearing, and lava plateaus are fertile for agriculture.
Plains
- Plains are flat, low-lying areas, often rising from sea level to meet higher landforms.
- Can be at high altitudes, with an average height of less than 200 meters.
- Formed by sediment deposition from rivers, wind, ice, or tectonic activity.
Types of Plains
Plains are grouped into structural, depositional, and erosional types.
Structural Plains
- Formed from horizontally bedded rocks with minimal crust disturbance.
- Examples include the Great Plains of the Russian Platform, USA, and Central Lowlands of Australia.
Depositional Plains
- Formed by sediment deposition from rivers, winds, waves, or glaciers.
- Alluvial plains form from river-deposited sediments on floodplains or riverbeds.
- Flood plains are near rivers or lakes, prone to periodic flooding.
- Lacustrine plains form from lake sediment deposits.
- Lava plains result from flowing lava sheets.
- Glacial plains are shaped by glacier movement.
- Abyssal plains are flat areas in deep ocean basins.
Erosional Plains
- Formed when elevated land like mountains or plateaus erodes into a plain.
- Found in northern Canada, northern Europe, and western Africa due to glacial erosion.
Indo-Gangetic Plains
- Large floodplains of the Indus and Ganga-Brahmaputra rivers, running parallel to the Himalayas.
- Stretch from Jammu and Kashmir to Assam, draining northern and eastern India.
Importance of Plains
- Highly populated due to favorable conditions for settlements.
- Flat land supports large industries and robust transport networks.
- Fertile soils from river-deposited silt and alluvium are ideal for agriculture.
- Coastal plains support sea-related industries.
- The Great Plains of North America and Northern Plains of India are key agricultural and industrial regions.
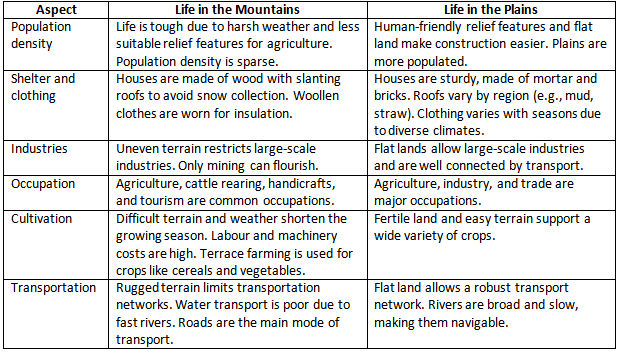
Impact of Landforms on Humans
Landforms like mountains and plains significantly affect human lifestyles.
|
12 videos|44 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Landforms Chapter Notes - Geography Class 6 ICSE
| 1. What are the main types of landforms found on Earth? |  |
| 2. What are endogenic and exogenic forces, and how do they affect landforms? |  |
| 3. How do mountains differ from plateaus? |  |
| 4. What impact do landforms have on human activities? |  |
| 5. Why are valleys important in the study of landforms? |  |




















