Arun Sharma Summary: Profit , Loss & Discount | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
Introduction
Profit and Loss is one of the most practical topics in Arithmetic, forming the base for many real-life and exam questions. It deals with the difference between the Cost Price (CP) — the price at which an item is purchased, and the Selling Price (SP) , the price at which it is sold. This topic also introduces related terms like Marked Price (MP), Discount, and Profit/Loss Percentage, which are widely used in business, trade, and exams like CAT, XAT, SNAP, and NMAT.
Understanding these basics allows you to solve not only simple profit–loss questions but also advanced problems involving successive discounts, false weights, overhead costs, and break-even analysis.

Key Terms & Standard Language in Profit & Loss
1. Cost Price (CP)- The amount a seller pays to acquire or produce an item.
2. Selling Price (SP)
- The amount at which the seller sells the item to a buyer.
3. Profit (Gain)
- Occurs when the selling price is greater than the cost price.
- Formula: Profit = Selling Price - Cost Price.
- Example:
Selling price = ₹250,
Cost price = ₹200,
So ,Profit = ₹250 − ₹200 = ₹50.
4. Loss
- Occurs when the selling price is less than the cost price.
- Formula: Loss = Cost Price - Selling Price.
- Example:
Selling price = ₹180,
Cost price = ₹200, so
Loss = ₹200 − ₹180 = ₹20.
5. Profit Percentage
- The profit is expressed as a percentage of the cost price.
- Formula:
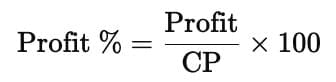
- Example:
Profit = ₹50 on Cost price = ₹200,
so Profit Percentage = (50 ÷ 200) × 100 = 25%.
6. Loss Percentage
- The loss is expressed as a percentage of the cost price.
- Formula:
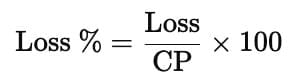
- Example:
Loss = ₹20 on Cost price = ₹200,
so Loss Percentage = (20 ÷ 200) × 100 = 10%.
7. Marked Price (MP) or List Price
- The labelled price printed on an item before any discount.
8. Discount
- Reduction allowed from the marked price when selling.
- Formula: Discount = Marked Price - Selling Price.
- Example: Marked price = ₹300, Selling price after discount = ₹270, Discount = ₹300 − ₹270 = ₹30.
9. Discount Percentage
- The discount is expressed as a percentage of the marked price.
- Formula:
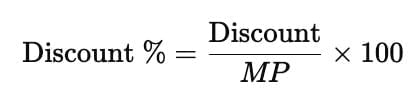
- Example:
Marked price = ₹300,
Discount = ₹30,
Discount Percentage = (30 ÷ 300) × 100 = 10%.
Profit & Loss( In Case of an Individual)
Profit: SP > CP,
Profit = SP - CP.
Loss: SP < CP,
Loss = CP - SP.
Percentage Profit/Loss:
- Percentage Profit =
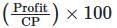
- Percentage Loss =
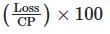
Example: For an item with CP ₹100 and SP ₹120, profit = ₹20, percentage profit = 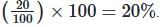
Profit & Loss as Applied to Commercial Transactions
1. Profit in Multiple Units of Products are Being Bought or Sold:
Total CP = CP per unit × number of units,
Total SP = SP per unit × number of units.
Profit = Total SP - Total CP
2. Loss in Multiple Units of Products are Being Bought or Sold:
If SP < CP per unit,
Loss = total CP - total SP.
Types of Costs
1. Direct Costs (Variable Costs)
- Variable costs (e.g., transportation) are proportional to the number of units. Total CP includes these costs.
- Example: For 10 pens at CP ₹5 each, variable cost ₹1 per pen,
Total CP = (₹5 + ₹1) × 10 = ₹60.
2. Indirect Costs (Overhead Costs or Fixed Costs)
- Fixed costs (e.g., rent) remain constant regardless of units sold. They are added to the total CP.
- Example: For 100 pens at CP ₹10 each, fixed cost ₹100,
Total CP = 100 x₹10 + ₹100 = ₹1100.
SP = ₹12 each,
Total SP = ₹1200,
Profit = ₹100.
3. Semi-Variable Costs
- Semi-variable costs combine fixed and variable components, increasing with sales volume.
- Example: A fixed rent of ₹500 plus ₹1 per unit transport for 100 units adds ₹100 variable cost,
Total CP = base CP + ₹500 + ₹100.
The Concept of the Break-Even Point
The break-even point occurs when total SP = total CP, resulting in no profit or loss.
Break-Even Sales: Total SP = Total CP.
Break-Even Units: Number of units sold where total revenue equals total cost.
Example: For 100 pens, CP = ₹8 each, total CP = ₹800. To break even at SP ₹10 each, sell 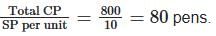
Profit Calculation based on Equating the Amount Spent and the Amount Earned
- Profit is determined by equating total CP (amount spent) and total SP (amount earned).
- Formula: Profit = Total SP - Total CP.
- Example:
For 100 pens, CP = ₹8 each,
SP = ₹10 each,
total CP = ₹800,
total SP = ₹1000,
Profit = ₹200,
Percentage Profit =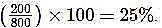
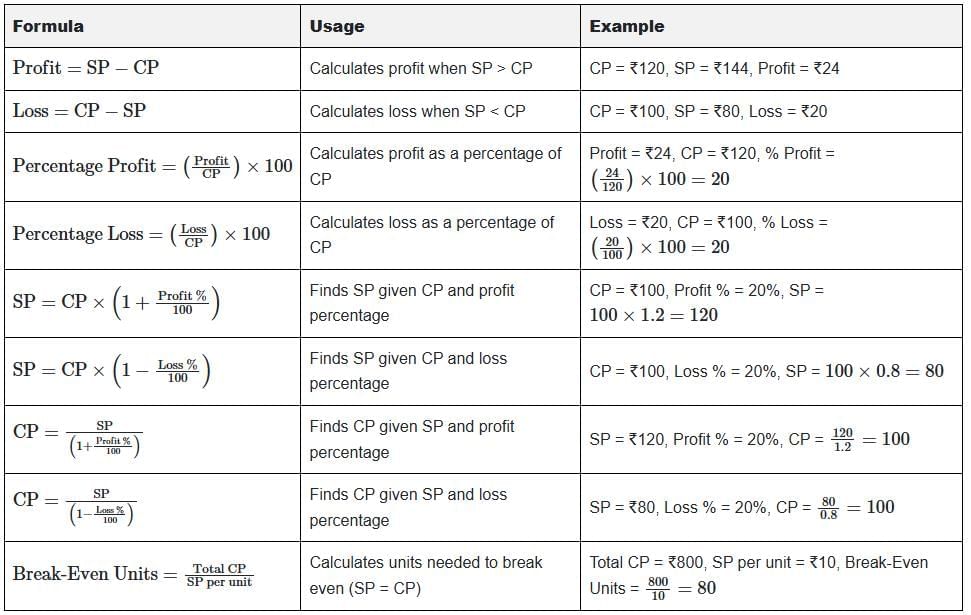
Table: Summary of Key Formulas and Examples
|
167 videos|238 docs|95 tests
|
FAQs on Arun Sharma Summary: Profit , Loss & Discount - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. What is the difference between direct costs and indirect costs in profit and loss calculations? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the break-even point in a business? |  |
| 3. What are semi-variable costs and how do they affect profit calculations? |  |
| 4. How can profit be calculated by equating the amount spent and the amount earned? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding profit and loss important for businesses? |  |
















