Mnemonics: Atoms and Molecules | Science Class 9 PDF Download
1. Historical Milestones of Atomic Theory
Mnemonic: "Kanad’s Kat Demo Look Lavoisier Proves"
- Kanad’s Kat → Kanad & Katyayama (Suggested matter divides into Parmanu)
- Demo Look → Democritus & Leucippus (Proposed indivisible atoms)
- Lavoisier→ Lavoisier (late 18th century) (Established laws of chemical combination)
- Proves → Proust (Conducted experiments to support chemical combination laws)
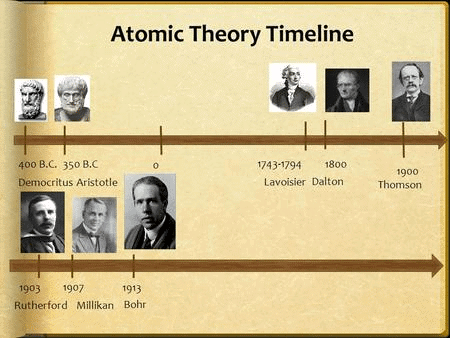
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase imagines Kanad’s philosophical ideas leaping forward with Lavoisier and Proust proving them through experiments. It covers the key historical figures and their contributions to atomic theory, from early philosophical ideas to experimental validation.
- Maharishi Kanad and Pakudha Katyayama in India suggested that matter can be divided into smaller particles called Parmanu.
- Democritus and Leucippus in Greece proposed that matter can be divided until it reaches indivisible particles called atoms.
- These ideas were based on philosophical considerations and lacked experimental validation until the eighteenth century.
- In the late 18th century, Antoine L. Lavoisier laid the foundation of chemical sciences by establishing two important laws of chemical combination.
- Lavoisier and Joseph L. Proust conducted numerous experiments to establish the laws of chemical combinations.
- These laws of chemical combination became crucial in understanding the combination and behavior of elements and compounds.
2. Law of Conservation of Mass
Mnemonic: “Mass is a Guest—Never Leaves, Never Arrives”
Mnemonic Explanation: In any reaction, the total mass stays the same—no gain, no loss.
Law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
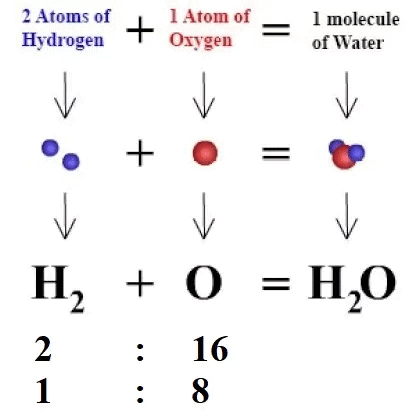
3. Law of Constant Proportion
Mnemonic: “Every Water Drop is an H:O = 1:8 Shop”
Mnemonic Explanation: No matter the source of water, H and O are always in a 1:8 mass ratio.
The law states that in a chemical substance, the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
4. John Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Key Postulates)
Mnemonic: “SIMPLE”
S – Smallest particle (atom)
I – Indivisible
M – Mass is same for same element
P – Properties same for same element
L – Locked ratios form compounds
E – Elements don’t change during reactions
Mnemonic Explanation:
- All matter consists of atoms participating in chemical reactions.
- Atoms are indivisible and remain unchanged in reactions.
- Atoms of the same element are identical in mass and properties.
- Atoms of different elements have distinct masses and properties.
- Atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds.
- The composition of atoms in a compound is constant.
5. Modern Symbols of Elements
Mnemonic for symbol rules: “First Big, Next Small”
Mnemonic Explanation: The first letter is capital (e.g., H), and if there is a second, it’s lowercase (e.g., He, Na, Cl).
Examples (for tricky ones):
Fe – Ferrum (Iron)
Na – Natrium (Sodium)
K – Kalium (Potassium)
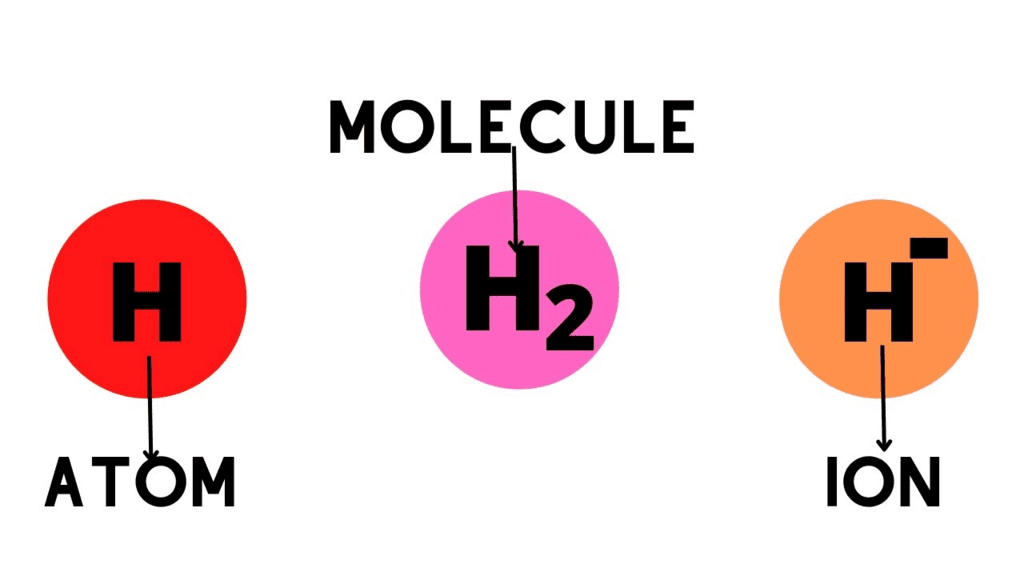
6. Difference Between Atom, Molecule, and Ion
Mnemonic: “Atom single netural and molecule group neutral with always Charged Ion”
Mnemonic Explanation:
Atom: Single neutral particle
Molecule: Neutral group of atoms bonded
Ion: Charged atom or group
7.Writing Chemical Formula (Crossover Method)
Mnemonic: “Swap and Drop”
Mnemonic Explanation: Swap the valencies and drop them as subscripts.
Example: 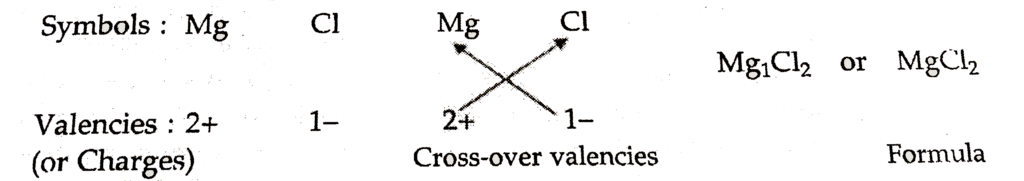
8. Molecular Mass
Mnemonic: “Add All Atomic Masses”
Mnemonic Explanation: H2O = 2H + 1O = 2×1 + 16 = 18u
9. Formula Unit Mass
Mnemonic: “Ionic Version of Molecular Mass”
Mnemonic Explanation: Just like molecular mass, but for ionic compounds like NaCl, CaCl2.
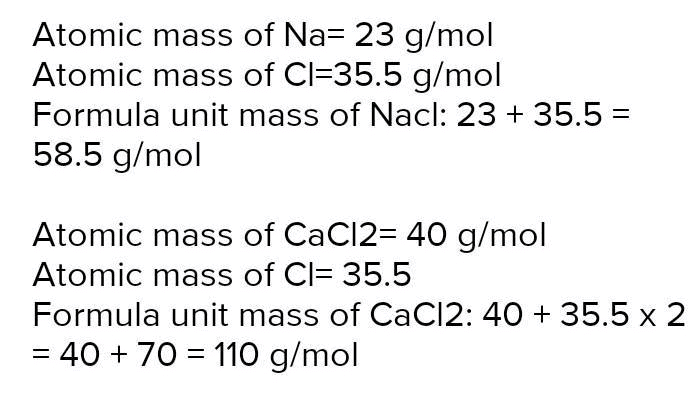
10. Difference Between Atomic Mass and Molecular Mass
Mnemonic: “Atom = 1, Molecule = Many”
Mnenomic Explanation:
Atomic Mass = mass of a single atom.
Molecular Mass = sum of all atoms in the molecule.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Atoms and Molecules - Science Class 9
| 1. What are the historical milestones of atomic theory? |  |
| 2. What is the Law of Conservation of Mass? |  |
| 3. What is the Law of Constant Proportion? |  |
| 4. What are the key postulates of John Dalton’s Atomic Theory? |  |
| 5. What is the difference between atomic mass and molecular mass? |  |





















