Mnemonics: Climate | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| 1. Definition of Climate and Weather |

|
| 2. Climatic Controls |

|
| 3. Factors Affecting India’s Climate |

|
| 4. Four Seasons of India |

|
| 5. Characteristics of the Monsoon |

|
| 6. Distribution of Rainfall |

|
1. Definition of Climate and Weather
Mnemonic: “Climate Lasts, Weather Shifts”
- Climate → Long-term conditions (Sum of weather over 30+ years, large area)
- Lasts → (Reinforces climate’s long duration)
- Weather → Short-term state (Atmosphere at a specific time, fluctuates daily)
- Shifts → (Reinforces weather’s variability)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase contrasts climate’s lasting nature with weather’s shifting state. It covers the definitions of climate (long-term, large-scale) and weather (short-term, variable), with elements like temperature, humidity, and precipitation implied, using a clear, memorable contrast.
How to Use: Visualize climate as a steady, lasting pattern and weather as a shifting daily mood. Link each word to its concept (e.g., “Climate” = Long-term). Test by recalling: climate (30+ years, large area), weather (daily, variable, same elements).
2. Climatic Controls
Mnemonic: “Latitude Alters, Altitude Cools, Winds Push, Sea Moderates, Currents Warm, Relief Blocks”
- Latitude → Solar energy variation (Less energy toward poles, affects temperature)
- Alters → (Reinforces latitude’s impact)
- Altitude → Temperature decrease (Higher altitudes are cooler, less dense air)
- Cools → (Reinforces altitude’s cooling effect)
- Winds → Pressure and wind systems (Influence temperature, rainfall via latitude/altitude)
- Push → (Reinforces wind movement)
- Sea → Distance from sea (Continentality: inland areas have extreme weather)
- Moderates → (Reinforces sea’s moderating effect)
- Currents → Ocean currents (Warm/cold currents affect coastal climate)
- Warm → (Reinforces currents’ warming/cooling)
- Relief → Relief features (Mountains block winds, cause precipitation)
- Blocks → (Reinforces relief’s barrier role)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase sequences the six climatic controls—latitude, altitude, winds, sea distance, currents, relief—with actions (alters, cools, push, moderates, warm, blocks) to depict their effects. It covers how each factor shapes climate, with vivid imagery for recall.
How to Use: Picture latitude altering heat, mountains cooling, winds pushing rain, seas moderating, currents warming coasts, and relief blocking winds. Link each word to its control (e.g., “Latitude” = Solar energy). Test by recalling: latitude (equator to poles), altitude (cooler heights), winds (pressure systems), sea (continentality), currents (coastal climate), relief (mountain barriers).
3. Factors Affecting India’s Climate
Mnemonic: “Tropic Splits, Himalayas Shield, Monsoons Blow”
- Tropic → Latitude (Tropic of Cancer splits India: south tropical, north subtropical)
- Splits → (Reinforces latitudinal division)
- Himalayas → Altitude (6,000m mountains block cold Central Asian winds, milder winters)
- Shield → (Reinforces Himalayas’ protective role)
- Monsoons → Pressure and winds (Northeast winds in winter, southwest monsoon in summer; cyclonic disturbances, tropical cyclones)
- Blow → (Reinforces wind reversals)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase highlights India’s climate shaped by the Tropic splitting regions, Himalayas shielding cold, and monsoons blowing rain. It covers latitude (tropical/subtropical), altitude (Himalayas’ role), and pressure/winds (monsoon dynamics), with a narrative of regional influence.
How to Use: Visualize the Tropic splitting India, Himalayas shielding it, and monsoons blowing in. Link each word to its factor (e.g., “Tropic” = Latitude). Test by recalling: latitude (Tropic of Cancer), altitude (Himalayas, 6,000m), pressure/winds (monsoon, cyclones).
4. Four Seasons of India
Mnemonic: “Winter Chills, Summer Sizzles, Monsoon Soaks, Transition Heats”
- Winter → Cold weather season (Mid-November to February, 10–15°C northern plains, mahawat rains)
- Chills → (Reinforces cold nights, frost, snowfall in Himalayas)
- Summer → Hot weather season (March to May, 38–45°C, loo winds, mango showers)
- Sizzles → (Reinforces heat, dust storms)
- Monsoon → Advancing monsoon (June to September, southwest monsoon, 250+ cm Western Ghats)
- Soaks → (Reinforces heavy rainfall, breaks in monsoon)
- Transition → Retreating monsoon (October–November, October heat, cyclones on eastern coast)
- Heats → (Reinforces high day temperatures, oppressive humidity)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase sequences India’s seasons—winter chilling, summer sizzling, monsoon soaking, and transition heating. It covers the cold season (winter, mahawat), hot season (summer, loo), advancing monsoon (rainy), and retreating monsoon (transition, cyclones), with vivid seasonal imagery.
How to Use: Picture winter chilling north India, summer sizzling deserts, monsoon soaking coasts, and transition heating with cyclones. Link each word to its season (e.g., “Winter” = Cold season). Test by recalling: winter (November–February, 10–15°C), summer (March–May, 45°C), advancing monsoon (June–September), retreating monsoon (October–November).
5. Characteristics of the Monsoon
Mnemonic: “Sudden Rains, Breaks Vary, Floods Droughts”
- Sudden → Rapid onset (Southwest monsoon arrives early June, covers India in a month)
- Rains → (Reinforces heavy rainfall, 30 km/h winds)
- Breaks → Wet/dry spells (Monsoon has breaks due to trough movement, wet plains or dry Himalayas)
- Vary → Uncertainty (Irregular arrival/retreat, variable intensity)
- Floods → Floods in heavy rain areas (Himalayan rivers, high rainfall zones)
- Droughts → Droughts in low rain areas (Rajasthan, Gujarat, due to variability)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts monsoons with sudden rains, varying breaks, and causing floods or droughts. It covers rapid onset, wet/dry spells, uncertainty, and extreme outcomes (floods, droughts), with a narrative of unpredictability.
How to Use: Visualize sudden monsoon rains, breaks varying, and floods or droughts striking. Link each word to its characteristic (e.g., “Sudden” = Rapid onset). Test by recalling: onset (June), breaks (trough movement), uncertainty (irregular), floods (high rainfall), droughts (low rainfall).
6. Distribution of Rainfall
Mnemonic: “Northeast Soaks, West Dries, Himalayas Snow”
- Northeast → High rainfall (Over 400 cm in Mawsynram, Meghalaya, Western Ghats)
- Soaks → (Reinforces heavy rain in northeast, coastal areas)
- West → Low rainfall (Less than 60 cm in western Rajasthan, Gujarat, Leh)
- Dries → (Reinforces drought-prone west)
- Himalayas → Snowfall (Snow in Himalayan regions, moderate rain elsewhere)
- Snow → (Reinforces Himalayan snowfall)
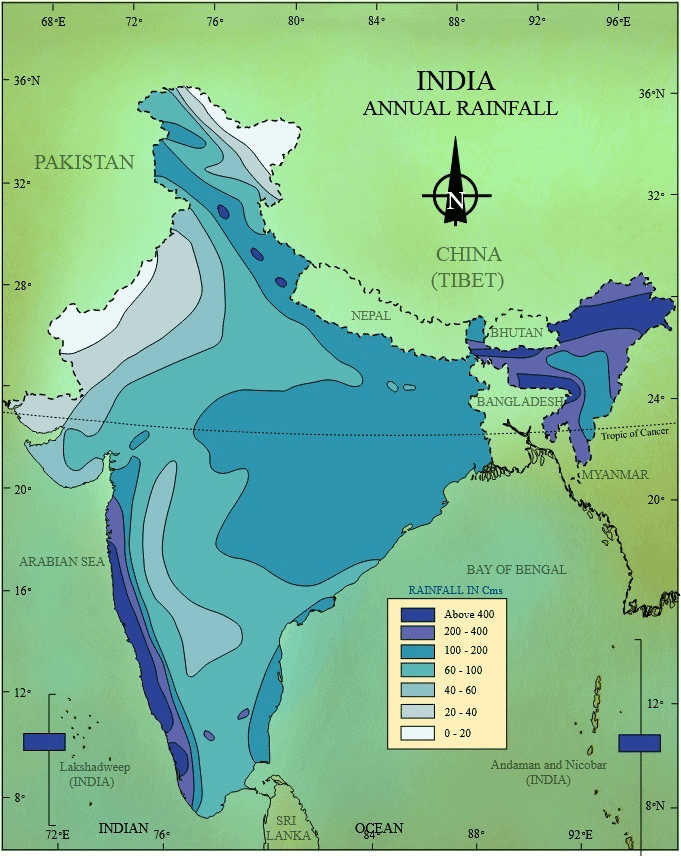
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase shows the northeast soaking with rain, west drying out, and Himalayas getting snow. It covers high rainfall (northeast, coasts), low rainfall (west, interior Deccan), and snowfall (Himalayas), with a clear regional contrast.
How to Use: Picture the northeast soaked, western deserts dry, and Himalayas snowy. Link each word to its region (e.g., “Northeast” = High rainfall). Test by recalling: high rainfall (400 cm, Mawsynram), low rainfall (60 cm, Rajasthan), snowfall (Himalayas).
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Climate - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What is the difference between climate and weather? |  |
| 2. What are the main climatic controls that affect weather patterns? |  |
| 3. What factors specifically affect India's climate? |  |
| 4. What are the four main seasons in India? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of the monsoon season in India? |  |















