Mnemonics: Locating Places on the Earth | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
1. Types of Maps
Mnemonic: “Physical Hills, Political Borders, Thematic Trends”
- Physical → Physical maps (Show natural features: mountains, rivers, lakes)
- Hills → (Reinforces natural landscapes)
- Political → Political maps (Show boundaries: countries, states, cities)
- Borders → (Reinforces divisions)
- Thematic → Thematic maps (Show specific data: population, climate)
- Trends → (Reinforces focused information)
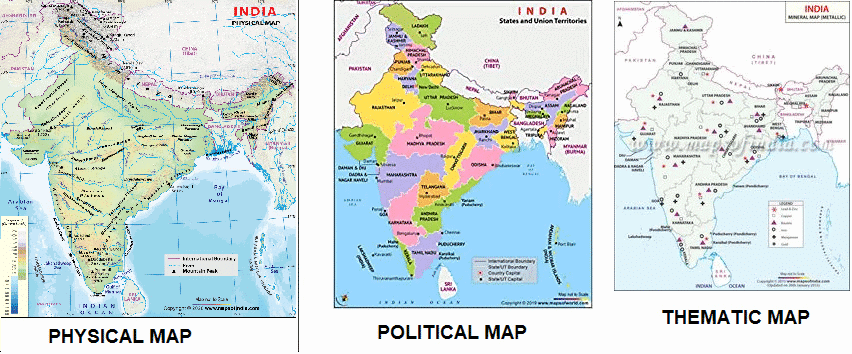
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts physical maps with hills, political maps with borders, and thematic maps showing trends. It covers the three main map types and their purposes, with vivid imagery of their features.
How to Use: Visualize hills on a physical map, borders on a political map, and data trends on a thematic map. Link each word to its map type (e.g., “Physical” = Natural features). Test by recalling: physical (mountains, rivers), political (countries, cities), thematic (population, climate).
2. Components of a Map
Mnemonic: “Scale Shrinks, Arrows Point, Symbols Speak”
- Scale → Distance (Shows map-to-real-world distance, e.g., 1 cm = 500 m)
- Shrinks → (Reinforces scale’s role in reducing distances)
- Arrows → Direction (North, South, East, West; North arrow; intermediate directions)
- Point → (Reinforces directional guidance)
- Symbols → Symbols (Represent features like forests, roads; explained in legend)
- Speak → (Reinforces symbols conveying information)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase shows scale shrinking distances, arrows pointing directions, and symbols speaking through visuals. It covers map components—distance (scale), direction (arrows), symbols (legend)—with a narrative of map readability.
How to Use: Picture a scale shrinking a city, arrows pointing North, and symbols speaking via a legend. Link each word to its component (e.g., “Scale” = Distance). Test by recalling: scale (distance ratio), direction (North/South), symbols (legend, trees, roads).
3. Understanding Coordinates ( Latitudes and Longitudes)
Mnemonic: “Equator Splits, Meridians Meet”
- Equator → Latitudes (0° latitude, divides Earth into hemispheres; parallels measure North/South)
- Splits → (Reinforces hemispheric division)
- Meridians → Longitudes (Prime Meridian at 0°, measure East/West; meet at poles)
- Meet → (Reinforces convergence at poles)
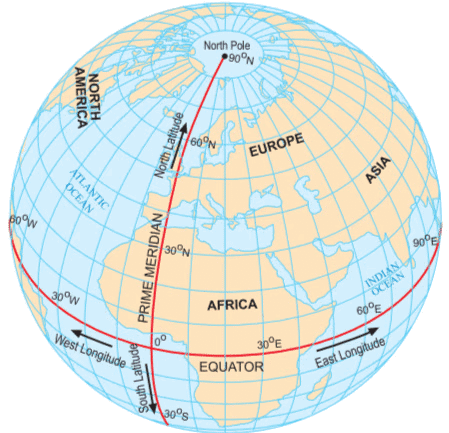
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts the Equator splitting the Earth and meridians meeting at poles. It covers latitudes (Equator, parallels, North/South) and longitudes (Prime Meridian, East/West), with imagery of Earth’s grid system.
How to Use: Visualize the Equator splitting the globe and meridians meeting at poles. Link each word to its coordinate (e.g., “Equator” = Latitudes). Test by recalling: latitudes (Equator, 0°, North/South), longitudes (Prime Meridian, East/West).
4. Climate Zones
Mnemonic: “Torrid Heats, Temperate Balances, Frigid Freezes”
- Torrid → Torrid zone (Near Equator, hot climate)
- Heats → (Reinforces high temperatures)
- Temperate → Temperate zones (Between tropics and polar circles, moderate climate)
- Balances → (Reinforces moderate conditions)
- Frigid → Frigid zones (Near poles, very cold)
- Freezes → (Reinforces icy conditions)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase shows torrid zones heating, temperate zones balancing, and frigid zones freezing. It covers the three climate zones based on latitude, with a narrative of temperature extremes.
How to Use: Picture the Equator heating, mid-latitudes balancing, and poles freezing. Link each word to its zone (e.g., “Torrid” = Hot). Test by recalling: torrid (Equator, hot), temperate (moderate), frigid (poles, cold).
5. Time Zones and Prime Meridian
Mnemonic: “Greenwich Starts, Hours Shift”
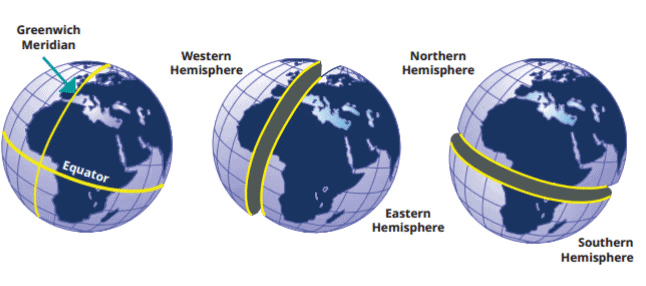
- Greenwich → Prime Meridian (0° longitude, Greenwich; divides Eastern/Western hemispheres)
- Starts → (Reinforces time reference)
- Hours → Time zones (15° = 1 hour; add/subtract time East/West)
- Shift → (Reinforces time changes)
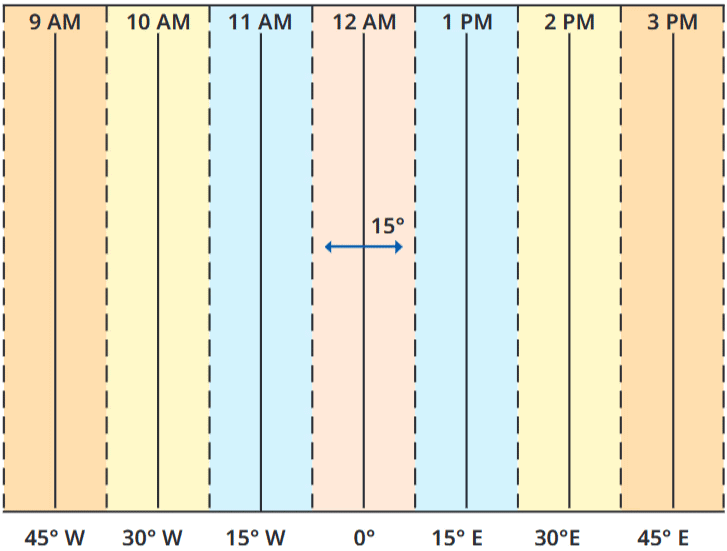
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts Greenwich starting time and hours shifting across zones. It covers the Prime Meridian (0°, time base) and time zones (15° per hour, East +1 hr, West -1 hr), with imagery of global timekeeping.
How to Use: Visualize Greenwich as the starting line and hours shifting across the globe. Link each word to its concept (e.g., “Greenwich” = Prime Meridian). Test by recalling: Prime Meridian (0°, Greenwich), time zones (15°, hour shifts).
6. International Date Line
Mnemonic: “Date Flips, Line Wiggles”
- Date → International Date Line (Near 180° longitude, changes date)
- Flips → (Reinforces adding/subtracting a day)
- Line → Approximate 180° (Deviates to avoid splitting countries)
- Wiggles → (Reinforces irregular path)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase shows the date flipping at a wiggling line. It covers the International Date Line’s role (date change at ~180°) and its deviations (avoids country splits), with imagery of time travel.
How to Use: Picture a line wiggling at 180°, flipping the date when crossed. Link each word to its concept (e.g., “Date” = Change). Test by recalling: Date Line (~180°, add/subtract day), deviations (avoids countries).
7. Ancient Indian Ujjayinī Meridian
Mnemonic: “Ujjain Guides, Stars Align”
- Ujjain → Ujjayinī meridian (Madhya rekhā, ancient Indian prime meridian)
- Guides → (Reinforces navigation role)
- Stars → Astronomy (Used by astronomers like Varāhamihira, 1,500 years ago)
- Align → (Reinforces celestial calculations)
Mnemonic Explanation: This phrase depicts Ujjain guiding via its meridian, with stars aligning for astronomers. It covers the Ujjayinī meridian (ancient Indian 0° longitude) and its astronomical use, with a narrative of historical navigation.
How to Use: Visualize Ujjain’s meridian guiding astronomers under aligned stars. Link each word to its concept (e.g., “Ujjain” = Meridian). Test by recalling: Ujjayinī (madhya rekhā, Ujjain), astronomy (Varāhamihira, calculations).
|
66 videos|344 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Locating Places on the Earth - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What are the different types of maps and their uses? |  |
| 2. What are the key components of a map? |  |
| 3. How do latitudes and longitudes work for locating places on Earth? |  |
| 4. What are climate zones and how do they differ? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the International Date Line? |  |

















