Important Formulae and Points to Remember: Expressions Using Letter - Numbers | Mathematics (Ganita Prakash) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
1. Concept of Letter-Numbers
Letter-numbers are letters used to represent unknown or variable values (e.g.,
a,n,x).Algebraic expressions are combinations of numbers and letter-numbers, joined by operations (+, –, ×, ÷).
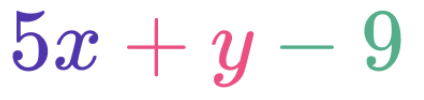
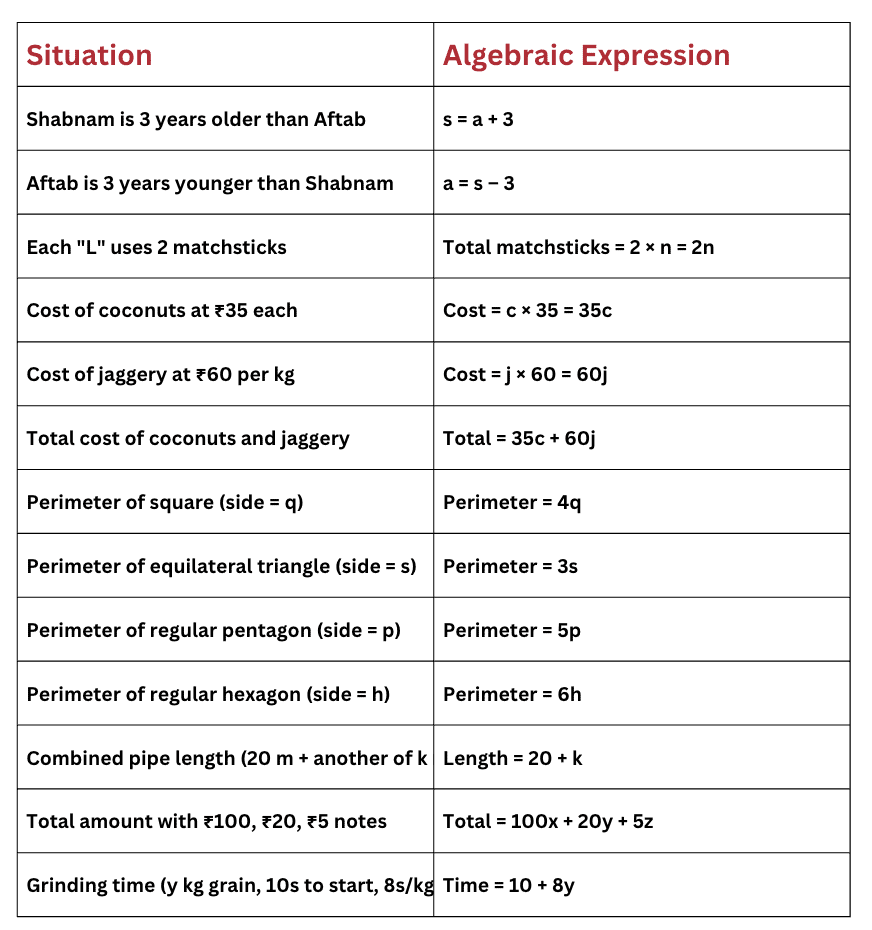
2. Writing Expressions from Situations
3. Common Arithmetic Expression Properties
Swapping (Commutative Property): Order of addition doesn't affect the result:
a + b = b + aGrouping (Associative Property): Regrouping terms doesn’t change the sum:
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)Distributive Property:
a × (b + c) = ab + ac
4. Evaluating Expressions
Replace letter-numbers with given values.
Follow BODMAS (Brackets, Orders, Division/Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction).
Example:
If a = 23, then a + 3 = 23 + 3 = 26.
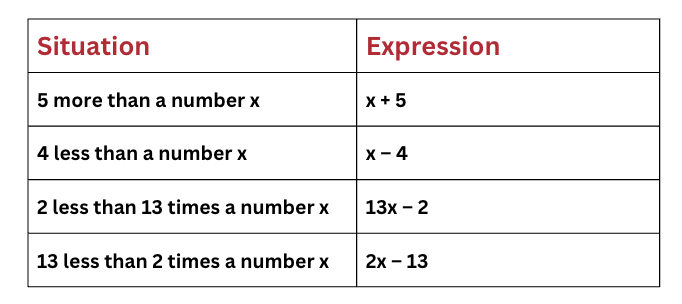
5. Writing Your Own Expressions
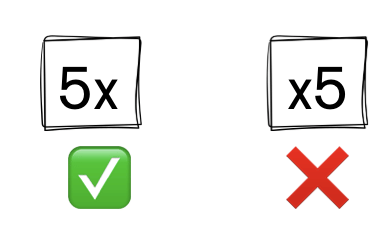
6. Omitting Multiplication Sign
- 4 × n is written as 4n
- Always write the number before the letter:
7. Sequences and nth Term Formula
What is a Sequence?
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers that follow a specific pattern or rule. Each number in the sequence is called a term.
Example Sequence:
4, 8, 12, 16, ...
This sequence increases by 4 each time, so it's called an arithmetic sequence (a sequence where each term increases or decreases by the same fixed number).
For a sequence like: 4, 8, 12, 16... (multiples of 4)
nth term = 4n
8. Perimeter of a Rectangle
Expression:
p = l + b + l + b
p = 2l + 2b
(where l = length, b = breadth)
9. Like and Unlike Terms
Like Terms: Same letter-numbers (e.g., 5c, 3c)
Unlike Terms: Different letter-numbers (e.g., 5c, 11d)
Rule: Only like terms can be added or subtracted.
10. Distributive Property in Use
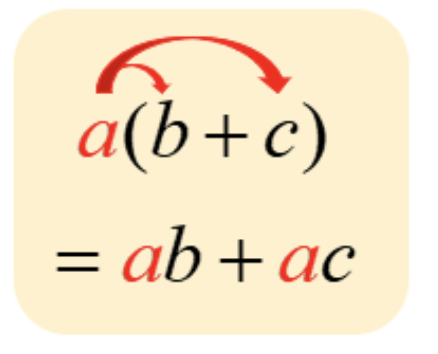
Example: 4 (x+y) −y
= 4x + 4y − y
= 4x+3y
11. Non-equivalent Expressions
Sometimes, two expressions look similar but are not equal because they follow different mathematical rules or structures.
To check if two expressions are equivalent, we can:
Simplify both expressions, or
Substitute a value into each and compare the results
Exmaple: Check whether 5u and 5 + u are equal or not
These two expressions look alike, but they're not the same.
Let's substitute u = 2:
5u = 5 × 2 = 10
5 + u = 5 + 2 = 7
Since 10 ≠ 7,
5u and 5 + u are not equivalent.
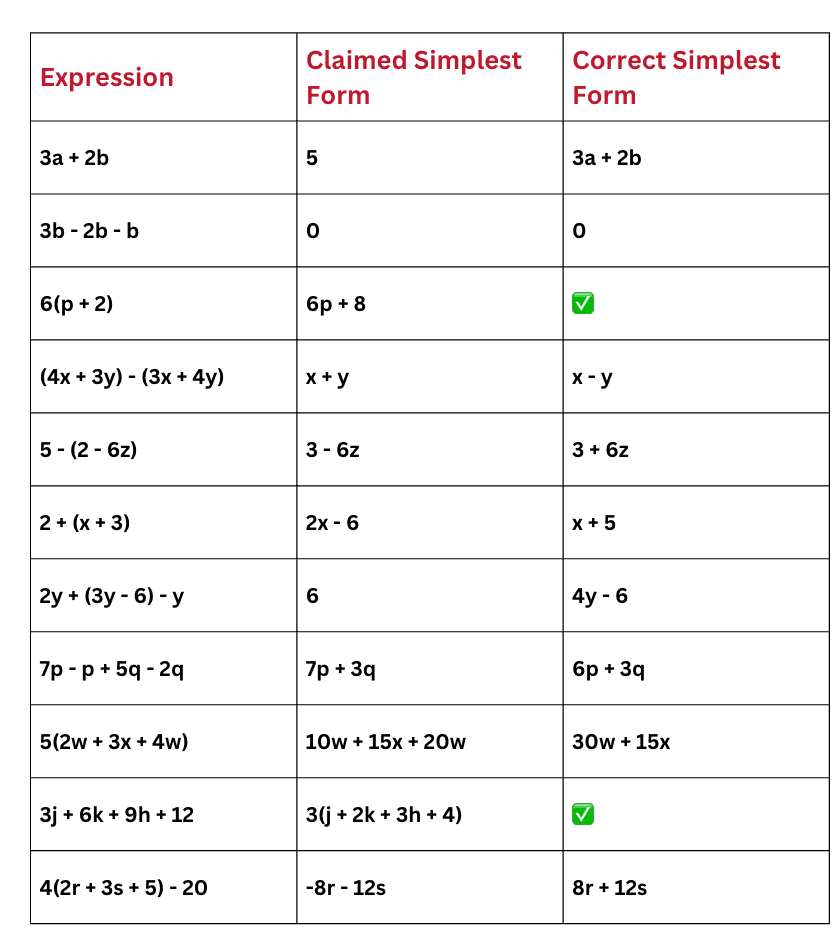
12. Common Mistakes in Simplification
13. Number Machines (Input-Output Rules)
A formula or expression represents the operation performed on two inputs.
Example:
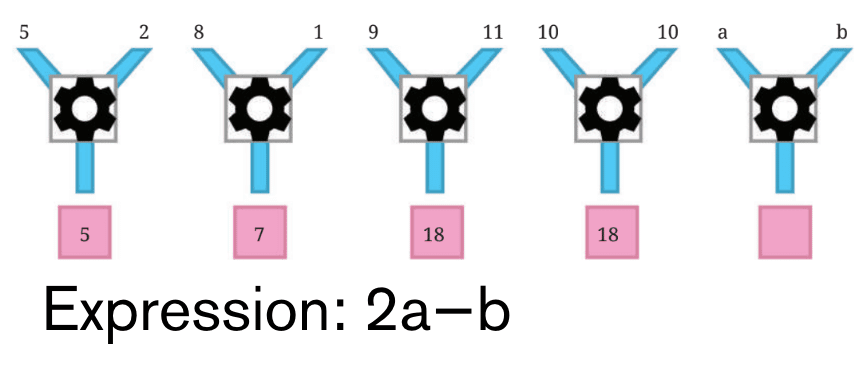 If the machine uses inputs
If the machine uses inputs aandb, and performs2a - b, then:
Output=2a−bPractice finding formulas for different number machines.
14. Patterns in a Calendar (2 × 2 Squares)
In any 2 × 2 block on a calendar: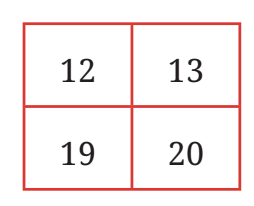
Top-left number = a
Other positions:
Top-right: a + 1
Bottom-left: a + 7
Bottom-right: a + 8
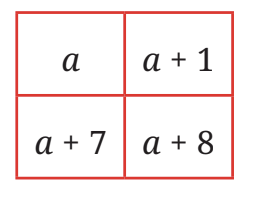
Diagonal Sums:
a + (a + 8) = (a + 1) + (a + 7) = 2a + 8
15. Matchstick Patterns
Pattern of Triangles using Matchsticks: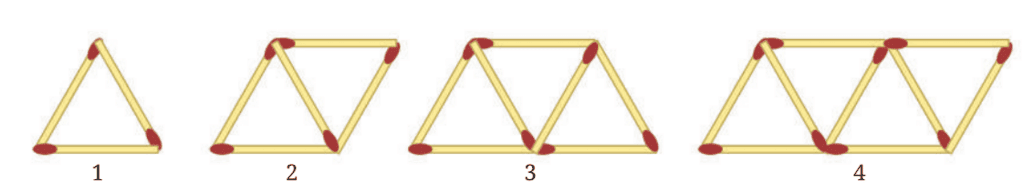
Step 1: 3 matchsticks
Each new triangle shares 1 side with the previous triangle, so you only add 2 new matchsticks each time.
To find the number of matchsticks needed for any step y, use the formula:
Matchsticks at Step y = 2y + 1
|
41 videos|251 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulae and Points to Remember: Expressions Using Letter - Numbers - Mathematics (Ganita Prakash) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are letter-numbers and how are they used in expressions? |  |
| 2. How do you write an expression from a word problem? |  |
| 3. What are some common properties of arithmetic expressions? |  |
| 4. How can you evaluate an expression with a variable? |  |
| 5. What is the distributive property and how is it used in expressions? |  |






















