Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Mathematics Class 4 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Multiplication
Multiplication Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Multiplication is like a magic trick in mathematics that helps us combine groups of numbers quickly! Imagine you have several boxes, each containing the same number of candies. Instead of counting each candy one by one, multiplication allows us to find the total number of candies in a snap. This chapter will take you on an exciting journey through multiplication tables, grids, and methods like lattice multiplication, making it easy to solve real-world problems, such as calculating the total number of items in multiple groups. Get ready to discover how multiplication makes math fun and efficient!

Constructing Tables
- Multiplication tables can be built using different methods like repeated addition, skip counting, or adding numbers from 1 to 10.
- Repeated addition involves adding a number to itself multiple times to find the product.
- Skip counting means counting by a specific number to create the table.
- Adding 1 to 10 involves using the table of a previous number and adding the next numbers to get the new table.
Example: Construct the table of 7 using repeated addition
- Add 1 seven times: 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 7, so 7 × 1 = 7
- Add 2 seven times: 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 14, so 7 × 2 = 14
- Add 3 seven times: 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 21, so 7 × 3 = 21
- Add 4 seven times: 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 28, so 7 × 4 = 28
- Add 5 seven times: 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 35, so 7 × 5 = 35
- Add 6 seven times: 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 + 6 = 42, so 7 × 6 = 42
- Add 7 seven times: 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 + 7 = 49, so 7 × 7 = 49
- Add 8 seven times: 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 = 56, so 7 × 8 = 56
- Add 9 seven times: 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 = 63, so 7 × 9 = 63
- Add 10 seven times: 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 70, so 7 × 10 = 70
Construct the table of 8 using skip counting.

Construct the table of 9 by adding 1 to 10.
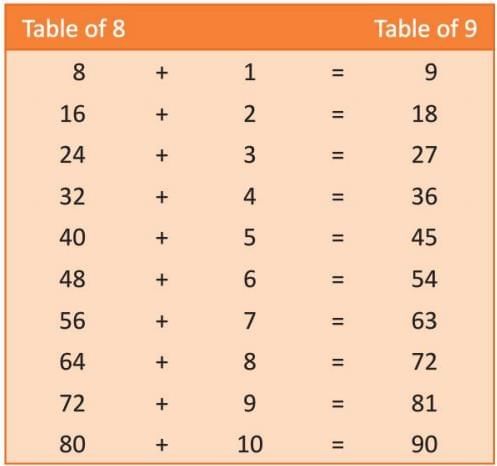
Multiplication Tables in a Grid
- A multiplication grid helps find the product of two numbers by locating their intersection.
- Numbers from 1 to 10 are written horizontally (top row) and vertically (first column).
- Steps to fill the grid:
- Step 1: Take the multiplier from the first column and the multiplicand from the first row, multiply, and write the product where they intersect.
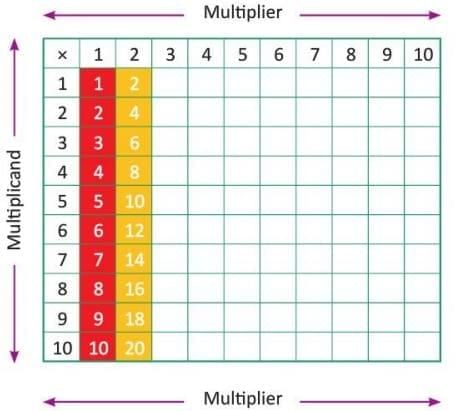
- Step 2: Repeat for the next multiplier and multiplicands to fill the next column.
- Step 3: Continue until all columns are filled by multiplying each pair of numbers.
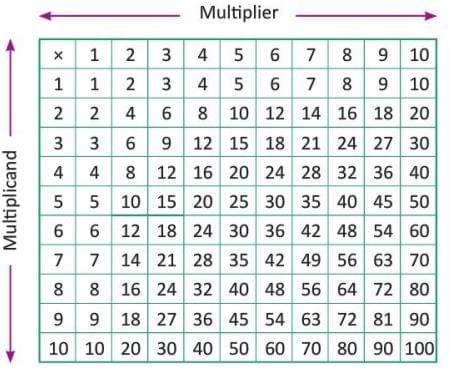
- The product of any two numbers (1 to 10) can be found at their intersection point.
Example: Filling a multiplication grid
- Take 1 as the multiplier (first column) and 1 as the multiplicand (first row): 1 × 1 = 1, write 1 at their intersection.
- Take 1 as the multiplier and 2 as the multiplicand: 2 × 1 = 2, write 2 at their intersection.
- Continue for multiplier 1 and all multiplicands to complete the second column.
- Take 2 as the multiplier and 1 as the multiplicand: 1 × 2 = 2, write 2 at their intersection.
- Repeat for multiplier 2 and all multiplicands to complete the third column.
- Continue this process to fill the entire grid.
- To find 3 × 8, locate the intersection of the third row and eighth column, which gives 24.
Multiplication Facts
- Numbers can be multiplied in any order, and the product remains the same (commutative property).
- Multiplying any number by 0 gives 0.
- Multiplying any number by 1 gives the number itself.
Example: Applying multiplication facts
- 52 × 9 = 468 and 9 × 52 = 468, showing order doesn’t change the product.
- 13 × 0 = 0 and 423 × 0 = 0, showing multiplication by 0 results in 0.
- 18 × 1 = 18 and 204 × 1 = 204, showing multiplication by 1 gives the same number.
Multiplication by Numbers Ending with Zero
Multiplication by a Number Ending with One Zero
- To multiply by 10, add one zero to the multiplicand.
- For numbers like 20, 30, 40, etc., add a zero to the multiplicand, then multiply by the non-zero digit(s) and place the result before the zero.
Example: Multiply 64 by 20
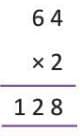
- 64 × 20: First, multiply 64 × 2 = 128, then add a zero, so 64 × 20 = 1,280.
Multiplication by a Number Ending with Two or Three Zeros
- To multiply by 100, add two zeros to the multiplicand.
- For numbers like 200, 300, 400, etc., add two zeros, then multiply by the non-zero digit(s) and place the result before the zeros.
Example: Multiply 96 by 100 and 47 by 5,000
- 96 × 100 = 9,600 (add two zeros to 96).
- 47 × 5,000: First, multiply 47 × 5 = 235, then add three zeros, so 47 × 5,000 = 235,000.
Multiplication of Numbers (without carry over)
Steps to multiply without carry over
- Step 1: Multiply the multiplicand by the ones digit of the multiplier.
- Step 2: Multiply the multiplicand by the tens digit of the multiplier, adding a zero to the result.
- Step 3: Add the products from steps 1 and 2 to get the final result.
Example: Multiply 24 by 12
- Step 1: 24 × 2 (ones) = 48.
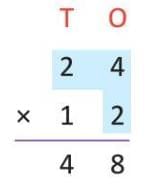
- Step 2: 24 × 1 (tens) = 24 × 10 = 240.
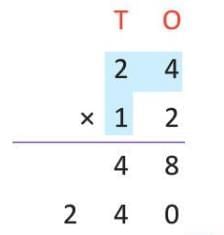
- Step 3: Add 48 + 240 = 288.
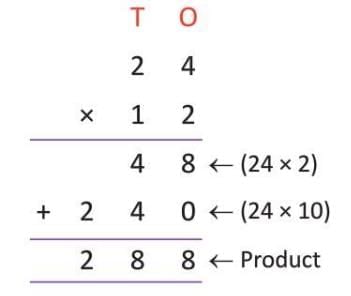
- So, 24 × 12 = 288.
Multiplication of Numbers (with carry over)
- Multiplication with carry over involves handling digits that exceed 9 in a place value, carrying over the excess to the next place.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Multiply the multiplicand by the ones digit of the multiplier, carrying over any tens to the next place value.
- Step 2: Multiply the multiplicand by the tens digit of the multiplier, adding a zero to the result, and carry over any tens as needed.
- Step 3: Add the products from steps 1 and 2 to get the final result.
Example: Multiply 76 by 37
- Step 1: 76 × 7 (ones) = 532 (carry over may occur in intermediate steps).
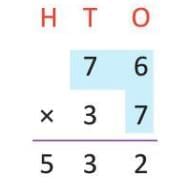
- Step 2: 76 × 3 (tens) = 76 × 30 = 2,280.
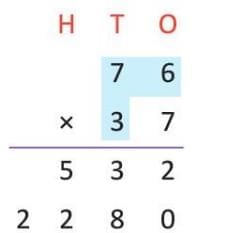
- Step 3: Add 532 + 2,280 = 2,812.
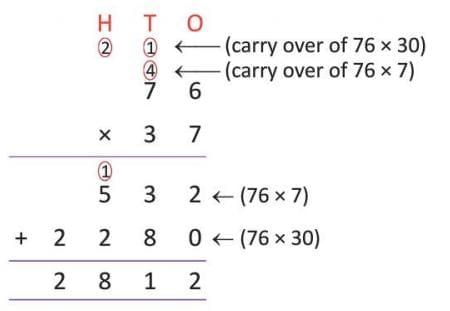
- So, 76 × 37 = 2,812.
Lattice Multiplication
- Lattice multiplication uses a grid to break multiplication into smaller steps.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Draw a grid based on the number of digits in the multiplicand and multiplier.
- Step 2: Write the multiplicand on top and the multiplier on the right side of the grid.
- Step 3: Multiply each digit of the multiplicand by each digit of the multiplier, placing the tens digit above and the ones digit below the diagonal in each cell.
- Step 4: Add the numbers diagonally, carrying over tens to the next diagonal if needed.
- Step 5: Read the sum from left to right to get the final product.
Example: Multiply 345 by 15 using lattice multiplication
- Step 1: Create a 3×2 grid (3 digits in 345, 2 digits in 15).
- Step 2: Write 345 on top and 15 on the right side.
- Step 3: Multiply each digit (e.g., 3 × 1, 3 × 5, 4 × 1, etc.), placing tens above and ones below the diagonal in each cell.
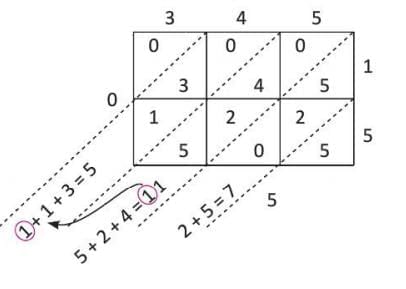
- Step 4: Add diagonally, carrying over tens to the next diagonal.
- Step 5: Read the result from left to right: 5,175.
- So, 345 × 15 = 5,175.
Solving Word Problems
- Word problems involve translating real-life situations into multiplication problems.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Identify the numbers to multiply (e.g., quantity per group and number of groups).
- Step 2: Multiply the numbers to find the total.
- Step 3: Write the final answer with proper units.
Example: A pet store has 15 tanks of tadpoles, each with 46 tadpoles
- Step 1: Identify numbers: 46 tadpoles per tank, 15 tanks.
- Step 2: Multiply 46 × 15 = 690.
- Step 3: The pet store has 690 tadpoles.
Framing Word Problems
- Create word problems by describing a situation that involves multiplication.
- Include the numbers to be multiplied and a context that makes sense for the calculation.
Example: Frame two word problems for 3,432 × 6
- Problem 1: A baker sells 3,432 loaves of bread in a week. How many loaves does he sell in 6 weeks? (3,432 × 6 = 20,592 loaves).
- Problem 2: A machine fills 3,432 cans in a day. How many cans does it fill in 6 days? (3,432 × 6 = 20,592 cans).
Mixed Problems
- Mixed problems combine multiplication with other operations like subtraction to solve real-life scenarios.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Identify the total quantity and the part that involves multiplication.
- Step 2: Perform the multiplication to find the partial quantity.
- Step 3: Subtract the partial quantity from the total to find the remaining amount.
Example: A factory has 1,563 workers, 80 vans, with 8 workers per van
- Step 1: Total workers = 1,563, vans = 80, workers per van = 8.
- Step 2: Multiply 80 × 8 = 640 workers in vans.
- Step 3: Subtract 1,563 - 640 = 923 workers travel by other means.
Multiplication by Expanded Form
- Expanded form breaks a number into its place values (e.g., hundreds, tens, ones) before multiplying.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Write the multiplicand in expanded form.
- Step 2: Multiply each part by the multiplier.
- Step 3: Add the products to get the final result.
Example: Multiply 325 by 9 using expanded form
- Step 1: Write 325 as 300 + 20 + 5.
- Step 2: Multiply: (300 × 9) + (20 × 9) + (5 × 9) = 2,700 + 180 + 45.
- Step 3: Add: 2,700 + 180 + 45 = 2,925.
- So, 325 × 9 = 2,925.
Estimating Product of Two Numbers
- Estimation involves rounding numbers to the nearest 10, 100, or 1,000 to find an approximate product.
- Steps:
- Step 1: Round both numbers to the nearest 10, 100, or 1,000.
- Step 2: Multiply the rounded numbers to get the estimated product.
- Step 3: Compare with the actual product for verification.
Example: Estimate the product of 48 and 72
- Step 1: Round 48 to 50 and 72 to 70.
- Step 2: Multiply 50 × 70 = 3,500.
- Step 3: Actual product: 48 × 72 = 3,456, which is close to 3,500.
The document Multiplication Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE is a part of the Class 4 Course Mathematics Class 4 ICSE.
All you need of Class 4 at this link: Class 4
|
98 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Multiplication Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 4 ICSE
| 1. What are multiplication tables and why are they important in learning math? |  |
Ans.Multiplication tables are charts that display the results of multiplying numbers together. They are important because they help students memorize multiplication facts, which are essential for more advanced math concepts. Being familiar with multiplication tables allows students to perform calculations more quickly and accurately.
| 2. How can I construct a multiplication table in a grid format? |  |
Ans.To construct a multiplication table in a grid format, start by drawing a large square or rectangle. Divide it into smaller squares based on the range of numbers you want to multiply (e.g., 1 to 10). Label the top row and the left column with numbers. Then, fill in each square with the product of the corresponding row and column numbers.
| 3. What is lattice multiplication and how does it work? |  |
Ans.Lattice multiplication is a method of multiplying numbers using a grid. To use this method, draw a lattice grid, split each cell diagonally, and write the digits of the numbers being multiplied along the top and side. Multiply each pair of digits and place the results in the corresponding cells, then sum the diagonals to find the final product. This method can be particularly helpful for visual learners.
| 4. How do I solve word problems that involve multiplication? |  |
Ans.To solve word problems involving multiplication, first read the problem carefully and identify the key information. Look for keywords that indicate multiplication, such as "each," "total," or "groups of." Then, write a multiplication equation based on the information provided. Finally, calculate the answer and make sure it answers the question posed in the problem.
| 5. What are some strategies for multiplying numbers that end with zero? |  |
Ans.When multiplying numbers that end with zero, a helpful strategy is to ignore the zeros initially, multiply the other digits, and then add the same number of zeros to the end of the product. For example, to multiply 30 and 20, you can first multiply 3 and 2 to get 6, and then add two zeros to get the final answer of 600. This makes the calculations simpler and quicker.
Related Searches















