Fractions Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Fractions are like slicing a pizza or sharing a chocolate bar with friends—it's all about dividing something into equal parts! Imagine you have a whole cake, and you want to share it equally among your buddies. Fractions help us understand how much each person gets. In this chapter, we’ll dive into what fractions are, how to represent them, and even how to add or subtract them when they’re similar. Get ready to explore the world of parts and wholes in a fun and simple way!

Numerator and Denominator
- A fraction is a way to show a part of a whole, written as one number over another.
- The number on top is called the numerator. It shows how many parts we have.
- The number on the bottom is called the denominator. It shows how many equal parts the whole is divided into.
- To name a fraction, say the numerator first, then the denominator as an ordinal number (like "third" for 3 or "eighth" for 8).
- Example: In the fraction 1/3, 1 is the numerator, and 3 is the denominator. It’s read as "one-third."
- Shruti bought a pizza and cut it into 4 equal slices. She gave 1 slice to Kriti. Shruti’s share is 3 out of 4 slices, so her fraction is 3/4. Kriti’s share is 1 out of 4 slices, so her fraction is 1/4.
Some Common Fractions
- Common fractions describe specific parts of a whole, like half, one-third, one-fourth, or three-fourths.
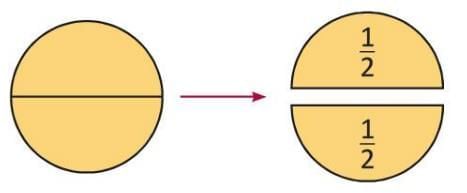
Half
- When a whole is divided into 2 equal parts, each part is called a half.
- It is written as 1/2.
- Two halves make one whole.
- Arnabh and Shashwat share a chocolate by dividing it into 2 equal pieces.
- Each gets one piece, so each has 1/2 of the chocolate.
One-third
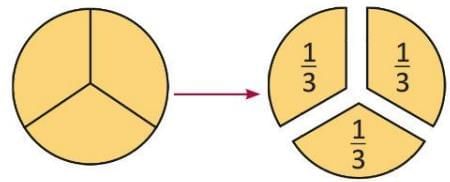
- When a whole is divided into 3 equal parts, each part is called one-third.
- It is written as 1/3.
- Three one-thirds make one whole.
- John and his two friends divide a pie into 3 equal slices.
- Each friend gets one slice, so each has 1/3 of the pie.
One-fourth
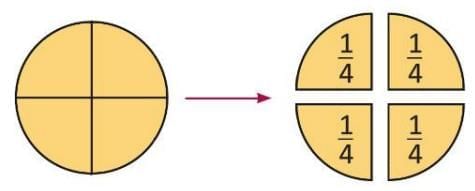
- When a whole is divided into 4 equal parts, each part is called one-fourth.
- It is written as 1/4.
- Four one-fourths make one whole.
- Aarohi cuts a cake into 4 equal parts to share with three friends.
- Each friend gets one part, so each has 1/4 of the cake.
Three-fourths
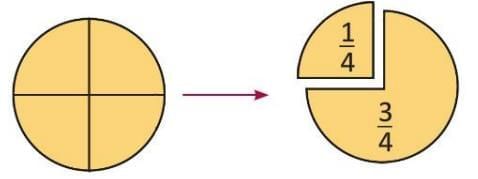
- When a whole is divided into 4 equal parts, and you take 3 parts, it’s called three-fourths.
- It is written as 3/4.
- Zainab divides a pizza into 4 equal parts and takes 1 part.
- The remaining pizza is 3 out of 4 parts, so it’s 3/4 of the whole pizza.
Fraction of a Collection
- A fraction can also show parts of a group or collection of items.
- The numerator shows how many items are chosen, and the denominator shows the total number of items in the collection.
- There are 3 flowers: 1 red and 2 yellow. The fraction of red flowers is 1/3, and the fraction of yellow flowers is 2/3.

Types of Fractions
Fractions come in different types based on their numerators and denominators.
Like Fractions
- Fractions with the same denominator are called like fractions.
- Fractions like 1/8, 2/8, 5/8, and 7/8 are like fractions because they all have the denominator 8.
Unlike Fractions
- Fractions with different denominators are called unlike fractions.
- Fractions like 2/5, 3/6, 5/9, and 8/15 are unlike fractions because their denominators are different.
Unit Fractions
- Fractions with a numerator of 1 are called unit fractions.
- Fractions like 1/1, 1/2, 1/3, 1/9, and 1/17 are unit fractions because their numerator is 1.
Equivalent Fractions
- Fractions that show the same part of a whole, even with different numerators and denominators, are called equivalent fractions.
- Fractions like 1/2, 2/4, 3/6, and 4/8 are equivalent because they represent the same part of a whole.
Visual Idea of Equivalent Fractions
- Dividing a whole in different ways can show the same part using different fractions.
- Visualizing with shapes (like rectangles) helps see that different fractions can represent the same amount.
- A rectangle divided into 2 parts with 1 colored shows 1/2.
- The same rectangle divided into 4 parts with 2 colored shows 2/4. Both represent half, so 1/2 = 2/4.
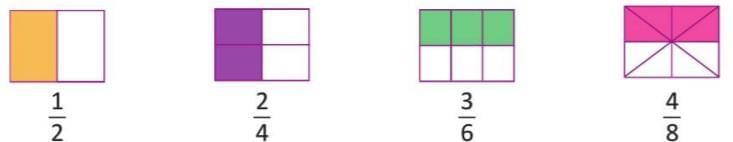
Showing Equivalence of Fractions
- To check if two fractions are equivalent, multiply the numerator of the first fraction by the denominator of the second, and the denominator of the first by the numerator of the second.
- If the products are equal, the fractions are equivalent.
- To check if 2/4 and 4/8 are equivalent: 2 × 8 = 16 and 4 × 4 = 16. Since 16 = 16, the fractions 2/4 and 4/8 are equivalent.
Addition of Like Fractions
- To add like fractions, add the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
- For 2/8 + 3/8, add the numerators: 2 + 3 = 5.
- Keep the denominator: 8. So, 2/8 + 3/8 = 5/8.
Properties of Addition of Fractions
- Like fractions can be added in any order, and the result stays the same.
- Adding 0 to a fraction gives the same fraction.
- For 1/4 + 2/4 = 3/4 and 2/4 + 1/4 = 3/4, the result is the same.
- Also, 7/11 + 0 = 7/11.
Subtraction of Like Fractions
- To subtract like fractions, subtract the numerators and keep the denominator the same.
- For 5/7 − 3/7, subtract the numerators: 5 − 3 = 2.
- Keep the denominator: 7. So, 5/7 − 3/7 = 2/7.
Properties of Subtraction of Fractions
- Subtracting 0 from a fraction gives the same fraction.
- Subtracting a fraction from itself gives 0.
- For 8/15 − 0 = 8/15, and 3/11 − 3/11 = 0.
Word Problems
- Word problems use fractions to solve real-life situations like sharing or comparing amounts.
- We use addition or subtraction of like fractions to find the answers.
- Always simplify the fraction to its lowest form if needed.
Problem 1: Adding Like Fractions
Question: Mrs. Jha bought 1/2 kg of sugar, and Mrs. Dua bought 3/2 kg of sugar. Find the total amount of sugar bought by them. Write the fraction in the lowest term.
- Step 1: Identify the fractions: Mrs. Jha has 1/2 kg, and Mrs. Dua has 3/2 kg.
- Step 2: Check if they are like fractions: Both have the same denominator, 2, so they are like fractions.
- Step 3: Add the fractions: Add the numerators (1 + 3 = 4) and keep the denominator (2). So, 1/2 + 3/2 = 4/2.
- Step 4: Simplify to the lowest term: 4/2 can be simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 2. So, 4 ÷ 2 / 2 ÷ 2 = 2/1 = 2 kg.
- Answer: They bought 2 kg of sugar.
Problem 2: Subtracting Like Fractions
Question: Maya weighed two pieces of metal for an experiment. The first piece weighed 5/6 g, and the second piece weighed 1/6 g. What is the difference between the weights of these two pieces of metal?
- Step 1: Identify the fractions: The first metal weighs 5/6 g, and the second metal weighs 1/6 g.
- Step 2: Check if they are like fractions: Both have the same denominator, 6, so they are like fractions.
- Step 3: Subtract the fractions: Subtract the numerators (5 − 1 = 4) and keep the denominator (6). So, 5/6 − 1/6 = 4/6.
- Step 4: Simplify to the lowest term: 4/6 can be simplified by dividing both numerator and denominator by 2. So, 4 ÷ 2 / 6 ÷ 2 = 2/3 g.
- Answer: The second metal is 2/3 g less than the first metal.
|
98 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Fractions Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 4 ICSE
| 1. What is a fraction and how is it structured? |  |
| 2. What are some common fractions that I should know? |  |
| 3. How do you find a fraction of a collection? |  |
| 4. What are like fractions and how do I add them? |  |
| 5. Can you explain how to solve a word problem involving fractions? |  |
















