Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Mathematics Class 4 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Measurement
Measurement Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Measurement of Length |

|
| Measurement of Weight |

|
| Measurement of Capacity |

|
| Estimation and Verification of Length, Weight and Capacity |

|
Introduction
Measurement is like a magic tool that helps us understand the world around us! Imagine trying to build a toy house without knowing how long the walls should be or how much water a bucket can hold. In this exciting chapter, we dive into the world of measuring length, weight, and capacity using standard units like metres, kilograms, and litres. We’ll learn how to switch between different units, add or subtract measurements, and even multiply or divide them to solve everyday problems. Get ready to explore how measurements make our lives easier and more organized!
Measurement of Length
- Length measurement tells us how long, short, tall, or far something is.
- Standard units are centimetres (cm), metres (m), and kilometres (km).
- Metre (m) is the basic unit for measuring length.
- Use centimetres for small objects like books or pencils.
- Use metres for larger things like tables or room heights.
- Use kilometres for long distances, like between two cities.
- Example: The distance between Delhi and Agra is measured in kilometres, while the length of a pencil is measured in centimetres.
Conversion of Units of Length
- Units like centimetres, metres, and kilometres can be converted into each other.
- Understand the relationship between units to convert them easily.
Metres to Centimetres
- 1 metre equals 100 centimetres (1 m = 100 cm).
- Multiply the number of metres by 100 to convert to centimetres.
- For metres and centimetres together, multiply metres by 100 and add the centimetres.
- Example: To convert 5 m to centimetres, calculate 5 × 100 = 500 cm. For 6 m 98 cm, do (6 × 100) + 98 = 600 + 98 = 698 cm.
Centimetres to Metres
- The last two digits of a centimetre value represent centimetres.
- The remaining digits represent metres.
- Divide the total centimetres by 100 to get metres and take the remainder as centimetres.
- Example: To convert 432 cm, divide 432 by 100: 432 ÷ 100 = 4 m with 32 cm left, so it’s 4 m 32 cm.
Kilometres to Metres
- 1 kilometre equals 1,000 metres (1 km = 1,000 m).
- Multiply the number of kilometres by 1,000 to convert to metres.
- For kilometres and metres together, multiply kilometres by 1,000 and add the metres.
- Example: To convert 10 km to metres, calculate 10 × 1,000 = 10,000 m. For 5 km 308 m, do (5 × 1,000) + 308 = 5,000 + 308 = 5,308 m.
Metres to Kilometres
- The last three digits of a metre value represent metres.
- The remaining digits represent kilometres.
- Divide the total metres by 1,000 to get kilometres and take the remainder as metres.
- Example: To convert 9,734 m, divide 9,734 by 1,000: 9,734 ÷ 1,000 = 9 km with 734 m left, so it’s 9 km 734 m.
Addition and Subtraction of Lengths
- Arrange lengths in columns by their units (metres, centimetres, or kilometres).
- Add or subtract the values in each column separately.
- For addition, if centimetres exceed 100, convert to metres (100 cm = 1 m).
- For subtraction, borrow from the larger unit if needed (1 m = 100 cm).
- Example: To add 9 m 56 cm and 13 m 78 cm,
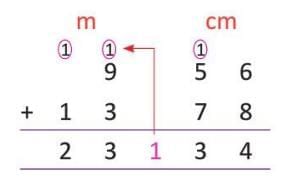
- first add centimetres: 56 + 78 = 134 cm = 1 m 34 cm. Then add metres: 9 + 13 + 1 = 23 m. Total is 23 m 34 cm.
Multiplication and Division of Lengths
- Convert larger units to smaller units before multiplying or dividing.
- Perform the multiplication or division.
- Convert the result back to the desired units if needed.
- Example: To multiply 4 m 33 cm by 5, convert to centimetres:
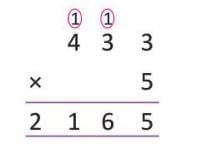 (4 × 100) + 33 = 433 cm. Then 433 × 5 = 2,165 cm = 21 m 65 cm.
(4 × 100) + 33 = 433 cm. Then 433 × 5 = 2,165 cm = 21 m 65 cm.
Measurement of Weight
- Weight measures how heavy or light an object is.
- Standard units are kilograms (kg) and grams (g).
- Use kilograms for heavy objects like bags of cereals.
- Use grams for light objects like a leaf or a needle.
- Example: The weight of a bag of cereals is measured in kilograms, while a feather’s weight is measured in grams.
Conversion of Units of Weight
- Units like kilograms and grams can be converted into each other.
Kilograms to Grams
- 1 kilogram equals 1,000 grams (1 kg = 1,000 g).
- Multiply the number of kilograms by 1,000 to convert to grams.
- For kilograms and grams together, multiply kilograms by 1,000 and add the grams.
- Example: To convert 5 kg 250 g to grams, calculate (5 × 1,000) + 250 = 5,000 + 250 = 5,250 g.
Grams to Kilograms
- The last three digits of a gram value represent grams.
- The remaining digits represent kilograms.
- Divide the total grams by 1,000 to get kilograms and take the remainder as grams.
- Example: To convert 2,350 g to kilograms, divide 2,350 by 1,000: 2,350 ÷ 1,000 = 2 kg with 350 g left, so it’s 2 kg 350 g.
Addition and Subtraction of Weights
- Arrange weights in columns by their units (kilograms, grams).
- Add or subtract the values in each column separately.
- For addition, if grams exceed 1,000, convert to kilograms (1,000 g = 1 kg).
- For subtraction, borrow from the larger unit if needed (1 kg = 1,000 g).
- Example: To add 23 kg 245 g, 38 kg 325 g, and 17 kg 461 g,
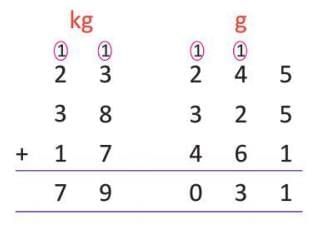 add grams: 245 + 325 + 461 = 1,031 g = 1 kg 31 g.
add grams: 245 + 325 + 461 = 1,031 g = 1 kg 31 g.- Add kilograms: 23 + 38 + 17 + 1 = 79 kg.
- Total is 79 kg 31 g.
Multiplication and Division of Weights
- Convert larger units to smaller units before multiplying or dividing.
- Perform the multiplication or division.
- Convert the result back to the desired units if needed.
- Example: To multiply 3 kg 125 g by 4, convert to grams: (3 × 1,000) + 125 = 3,125 g. Then 3,125 × 4 = 12,500 g = 12 kg 500 g.
Measurement of Capacity
- Capacity measures how much a container can hold.
- Standard units are litres (L) and millilitres (mL).
- Use litres for large quantities like water or milk.
- Use millilitres for small quantities like syrups or soft drinks.
- Example: The capacity of a water tank is measured in litres, while a spoonful of syrup is measured in millilitres.
Conversion of Units of Capacity
- Units like litres and millilitres can be converted into each other.
Litres to Millilitres
- 1 litre equals 1,000 millilitres (1 L = 1,000 mL).
- Multiply the number of litres by 1,000 to convert to millilitres.
- For litres and millilitres together, multiply litres by 1,000 and add the millilitres.
- Example: To convert 17 L to millilitres, calculate 17 × 1,000 = 17,000 mL. For 24 L 451 mL, do (24 × 1,000) + 451 = 24,000 + 451 = 24,451 mL.
Millilitres to Litres
- The last three digits of a millilitre value represent millilitres.
- The remaining digits represent litres.
- Divide the total millilitres by 1,000 to get litres and take the remainder as millilitres.
- Example: To convert 36,957 mL to litres, divide 36,957 by 1,000: 36,957 ÷ 1,000 = 36 L with 957 mL left, so it’s 36 L 957 mL.
Addition and Subtraction of Capacities
- Arrange capacities in columns by their units (litres, millilitres).
- Add or subtract the values in each column separately.
- For addition, if millilitres exceed 1,000, convert to litres (1,000 mL = 1 L).
- For subtraction, borrow from the larger unit if needed (1 L = 1,000 mL).
- Example: To add 3 L 215 mL, 4 L 380 mL, and 6 L 79 mL,
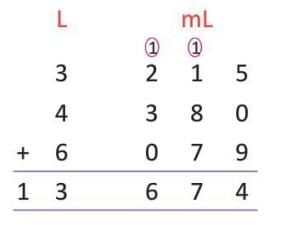 add millilitres: 215 + 380 + 79 = 674 mL. Add litres: 3 + 4 + 6 = 13 L. Total is 13 L 674 mL.
add millilitres: 215 + 380 + 79 = 674 mL. Add litres: 3 + 4 + 6 = 13 L. Total is 13 L 674 mL.
Multiplication and Division of Capacities
- Convert larger units to smaller units before multiplying or dividing.
- Perform the multiplication or division.
- Convert the result back to the desired units if needed.
- Example: To multiply 4 L 362 mL by 3,
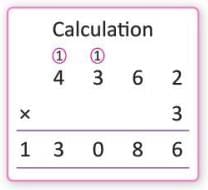 convert to millilitres: (4 × 1,000) + 362 = 4,362 mL. Then 4,362 × 3 = 13,086 mL = 13 L 86 mL.
convert to millilitres: (4 × 1,000) + 362 = 4,362 mL. Then 4,362 × 3 = 13,086 mL = 13 L 86 mL.
Estimation and Verification of Length, Weight and Capacity
- Estimation uses approximate values to guess measurements.
- Use everyday objects for estimation, like a finger for centimetres or a bottle for litres.
- Verify by measuring with tools like a measuring tape, weighing scale, or measuring cylinder.
- Example: Estimate the length of a book using the width of your finger (about 1 cm) and verify with a measuring tape.
The document Measurement Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 4 ICSE is a part of the Class 4 Course Mathematics Class 4 ICSE.
All you need of Class 4 at this link: Class 4
|
98 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Measurement Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 4 ICSE
| 1. What are the standard units of measurement for length, weight, and capacity? |  |
Ans. The standard unit of measurement for length is meters (m), for weight is grams (g) or kilograms (kg), and for capacity is liters (L). These units are part of the metric system, which is widely used around the world.
| 2. How can I estimate the length of an object without a ruler? |  |
Ans. You can estimate the length of an object by using everyday items for comparison. For example, you can use a pen or a piece of paper to measure the object by counting how many times it fits along the length. Alternatively, you can use your body parts, like your foot or hand, as a rough measurement tool.
| 3. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
Ans. Mass refers to the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms or grams, and does not change regardless of location. Weight, on the other hand, is the force exerted by gravity on that mass and can vary depending on the gravitational field, typically measured in newtons (N) or pounds (lbs).
| 4. How can I verify the weight of an object accurately? |  |
Ans. To verify the weight of an object accurately, you should use a calibrated scale. Ensure that the scale is placed on a flat surface, and zero it out before placing the object on it. This will give you an accurate reading of the object's weight.
| 5. What are some common tools used for measuring capacity? |  |
Ans. Common tools used for measuring capacity include measuring cups, measuring spoons, and graduated cylinders. These tools are designed to measure liquid volumes accurately, with measuring cups typically used in cooking and graduated cylinders used in scientific experiments.
Related Searches














