Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Mathematics Class 5 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Roman Numerals
Roman Numerals Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Dive into the fascinating world of Roman numerals, a system crafted by the ancient Romans that’s still used today in clocks, book chapters, and movie sequels! Unlike the numbers we use daily, Roman numerals use special letters to represent values, making them a unique and fun way to explore numbers. In this chapter, we’ll uncover how these symbols work, how to convert between Roman and regular numbers, and even how to do simple math with them. Get ready to step back in time and master this ancient number system!

Roman Numeral System
- Roman numerals were developed by the ancient Romans as one of the earliest number systems.
- It uses seven unique symbols, each with a specific value, to represent numbers.
- The system does not include a symbol for zero.
- Numbers are formed by combining these symbols.
- The seven symbols and their values are:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1,000
- Example: The symbol X represents 10 in the Hindu-Arabic numeral system.
Rules for Writing Hindu-Arabic Numbers Using Roman Numerals
Rule 1
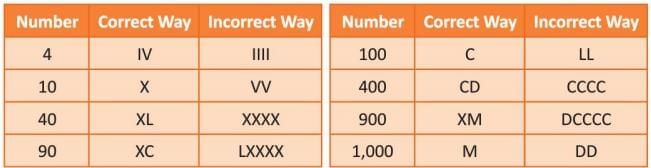
- A Roman numeral can be repeated up to three times in a row.
- When repeated, the values are added together to get the final number.
- Only I, X, C, and M can be repeated; V, L, and D cannot.
- Example: III = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3
Rule 2
- If a smaller value numeral is placed to the right of a larger value numeral, their values are added.
- Example: VI = V + I = 5 + 1 = 6
Rule 3
- If a smaller value numeral is placed to the left of a larger value numeral, the smaller value is subtracted from the larger value.
- V, L, and D cannot be subtracted.
- I can only be subtracted from V and X.
- X can only be subtracted from L and C.
- C can only be subtracted from D and M.
- Example: IV = V - I = 5 - 1 = 4
Rule 4
- If a smaller numeral is between two larger numerals, subtract the smaller numeral’s value from the larger numeral to its right, then add the result to the leftmost numeral.
- Example: XIV = 10 + (5 - 1) = 10 + 4 = 14
Rule 5
- Placing a bar over a Roman numeral multiplies its value by 1,000.
- Example: V̅ = 5 × 1,000 = 5,000
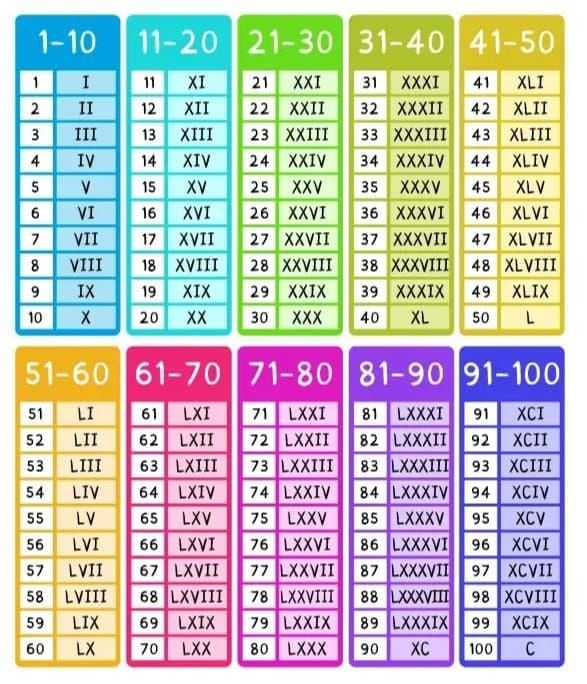
Roman Numerals up to Hundred
- Roman numerals from 1 to 100 follow the rules above to represent numbers.
Writing Roman Numerals Using Hindu-Arabic Numerals
- To convert Hindu-Arabic numbers to Roman numerals, use the rules to combine symbols.
- For numbers like 4 and 9, use subtraction (e.g., IV instead of IIII, IX instead of VIIII).
- For larger numbers, break them into expanded form and convert each part.
- Example: 428 = 400 + 20 + 8 = CD + XX + VIII = CDXXVIII
Addition and Subtraction of Roman Numerals
Steps to add or subtract Roman numerals:
- Convert the Roman numerals to Hindu-Arabic numbers.
- Perform the addition or subtraction.
- Convert the result back to Roman numerals.
- Example: XLV + LXIII = 45 + 63 = 108 = CVIII
The document Roman Numerals Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE is a part of the Class 5 Course Mathematics Class 5 ICSE.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
138 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Roman Numerals Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What are Roman numerals and how are they different from Hindu-Arabic numbers? |  |
Ans.Roman numerals are a numeral system originating from ancient Rome that uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet (I, V, X, L, C, D, M) to represent values. Unlike Hindu-Arabic numbers, which are based on a place value system and include zero, Roman numerals do not have a symbol for zero and do not utilize a positional system. For example, the number 4 is represented as IV in Roman numerals, while it is simply written as 4 in Hindu-Arabic.
| 2. What are the basic rules for writing Hindu-Arabic numbers using Roman numerals? |  |
Ans.The basic rules include using specific letters to represent values: I for 1, V for 5, X for 10, L for 50, C for 100, D for 500, and M for 1000. When a smaller numeral appears before a larger numeral, it is subtracted (e.g., IV for 4). If a smaller numeral appears after a larger one, it is added (e.g., VI for 6). Repeating a numeral up to three times indicates addition (e.g., III for 3), but a numeral can’t be repeated more than three times.
| 3. How do you convert Hindu-Arabic numbers to Roman numerals up to 100? |  |
Ans.To convert Hindu-Arabic numbers to Roman numerals up to 100, break the number down into tens and units. For example, to convert 57: 50 is represented as L and 7 is represented as VII, so 57 is LVII. Each numeral must follow the rules of addition and subtraction based on their values.
| 4. Can you explain how to perform addition and subtraction using Roman numerals? |  |
Ans.Addition in Roman numerals involves combining the values of the numerals and then simplifying if necessary. For example, to add VI (6) and IV (4), you combine them to get X (10). For subtraction, ensure you follow the rules of placing a smaller numeral before a larger one to indicate subtraction. For example, if you subtract III (3) from X (10), you represent it as VII (7).
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when working with Roman numerals? |  |
Ans.Common mistakes include not following the rules for numeral placement, such as incorrectly subtracting or adding numerals. For instance, writing IIX instead of VIII for 8 is incorrect, as you should not place a smaller numeral before a larger one unless it is to indicate subtraction. Additionally, not adhering to the limit of repeating numerals can lead to errors, such as writing XXXX instead of XL for 40.
Related Searches




















