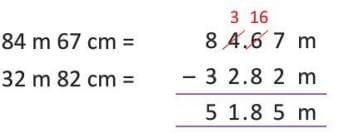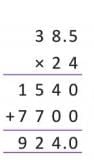Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Mathematics Class 5 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Metric System
Metric System Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Metric System |

|
| Conversion of Metric Measures |

|
| Four Basic Operations on Metric Measures |

|
| Word Problems on Metric Measures |

|
Introduction
Imagine measuring the world around you with a universal language that everyone understands! The metric system is like a magic ruler that helps us measure length, weight, and capacity in a simple and organized way. From tiny millimeters to vast kilometers, from light grams to heavy kilograms, and from small milliliters to large liters, this system makes measurements easy and fun. In this chapter, we'll explore how to use different units, convert them, and solve everyday problems with confidence!
Metric System
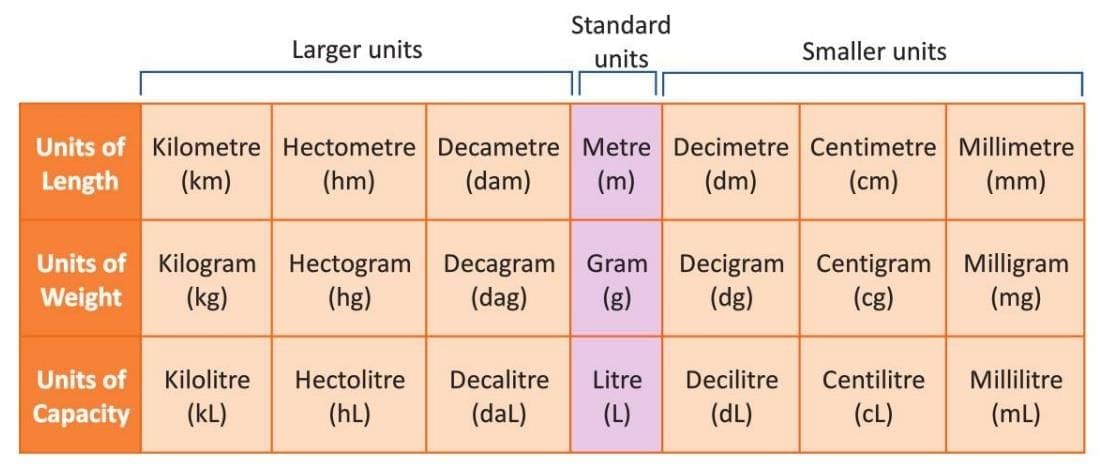
- Measurements use standard units in the metric system.
- Standard unit for length is the metre (m).
- Standard unit for weight is the gram (g).
- Standard unit for capacity is the litre (L).
- Larger and smaller units are created by adding prefixes to these standard units.
- Prefixes indicate how big or small a unit is compared to the standard unit.
Example: The table below shows different units for measuring length, weight, and capacity:
Prefixes in the Metric System
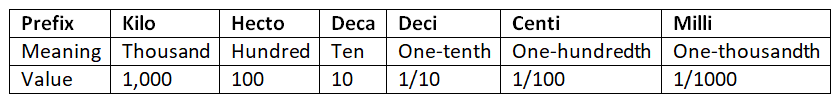
- Prefixes like kilo, hecto, deca, deci, centi, and milli are added to standard units.
- Each prefix has a specific meaning and value showing how big or small the unit is.
- Kilo means thousand (1,000).
- Hecto means hundred (100).
- Deca means ten (10).
- Deci means one-tenth (1/10).
- Centi means one-hundredth (1/100).
- Milli means one-thousandth (1/1000).
Example: The table below shows the meaning and value of prefixes:
Conversion of Metric Measures
Length
- Length measures things like height, distance, or size of objects.
- Small objects can be measured using a ruler with centimetre (cm) and millimetre (mm) markings.
- Each small division on a ruler is 1 millimetre (mm).
- To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit, multiply by 10 for each step down.
- To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit, divide by 10 (or multiply by 1/10) for each step up.
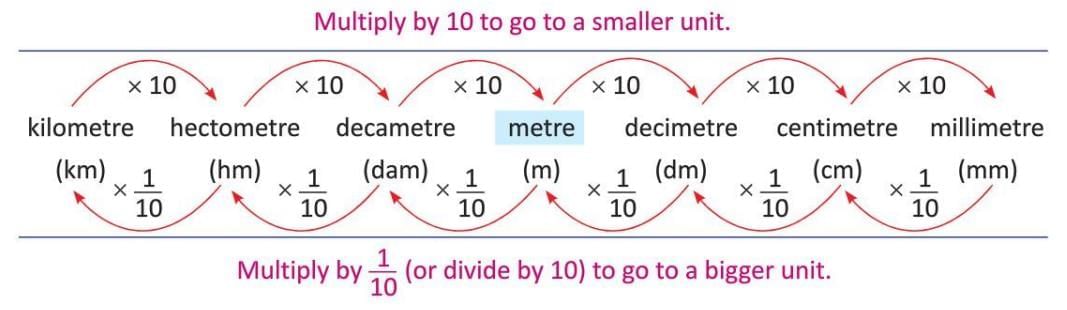
Example: Convert 5 hm to dm.
, multiply by 10 × 10 × 10 = 1,000).
So, 5 hm = 5,000 dm.
Expressing Length in Decimal Form
- Converting smaller units to larger units can be expressed as decimals.
- 1 m = 100 cm, so 1 cm = 1/100 m = 0.01 m.
- 1 km = 1,000 m, so 1 m = 1/1000 km = 0.001 km.
- Decimal point separates the larger unit (like km) from smaller units (like hm, dam, m).
Example: Express 14 km 6 hm 3 dam 7 m in km using decimal notation.
6 hm = 6/10 km = 0.6 km (1 hm = 1/10 km).
3 dam = 3/100 km = 0.03 km (1 dam = 1/100 km).
7 m = 7/1000 km = 0.007 km (1 m = 1/1000 km).
So, 14 km 6 hm 3 dam 7 m = 14.637 km.
Weight
- Weight has a standard unit of gram (g).
- Convert larger units to smaller units by multiplying by 10 for each step down.
- Convert smaller units to larger units by dividing by 10 for each step up.
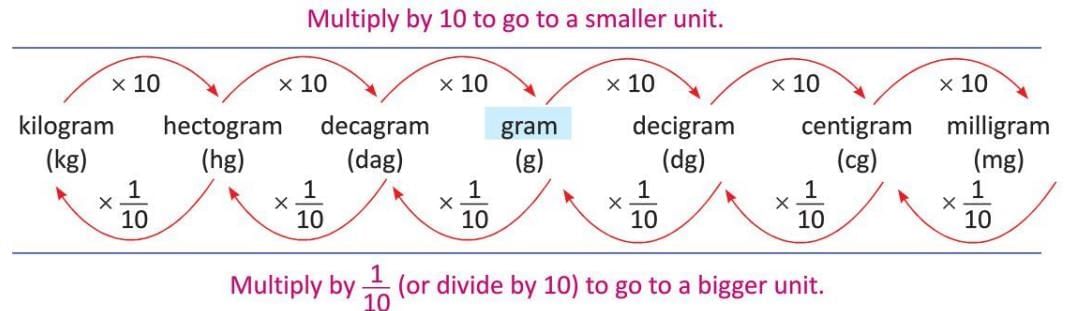
Example: Convert 4 hg to dg.
, multiply by 10 × 10 × 10 = 1,000).
So, 4 hg = 4,000 dg.
Expressing Weight in Decimal Form
- Weights can be expressed as decimals when converting to larger units.
- 1 kg = 1,000 g, so 1 g = 1/1000 kg = 0.001 kg.
- 1 g = 1,000 mg, so 1 mg = 1/1000 g = 0.001 g.
Example: Express 7 kg 3 hg 2 dag 7 g in kg using decimal notation.
3 hg = 3/10 kg = 0.3 kg (1 hg = 1/10 kg).
2 dag = 2/100 kg = 0.02 kg (1 dag = 1/100 kg).
7 g = 7/1000 kg = 0.007 kg (1 g = 1/1000 kg).
So, 7 kg 3 hg 2 dag 7 g = 7.327 kg.
Capacity
- Capacity has a standard unit of litre (L).
- Convert larger units to smaller units by multiplying by 10 for each step down.
- Convert smaller units to larger units by dividing by 10 for each step up.
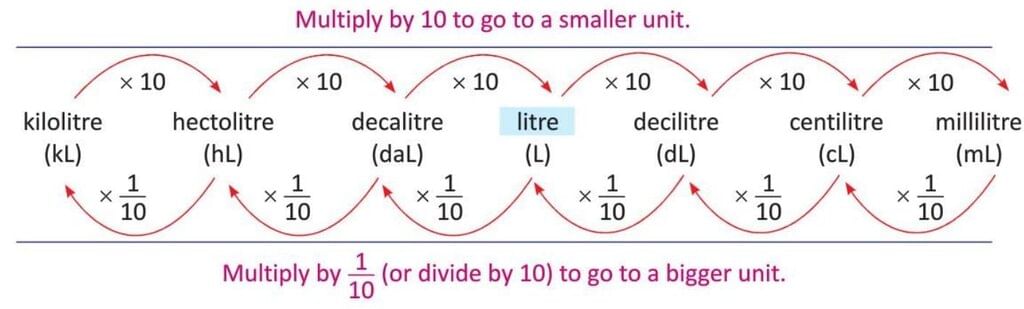
Example: Convert 8 L 3 daL to L.
So, 8 L 3 daL = 38 L.
Expressing Capacity in Decimal Form
- Capacities can be expressed as decimals when converting to larger units.
- 1 L = 1,000 mL, so 1 mL = 1/1000 L = 0.001 L.
- 1 kL = 1,000 L, so 1 L = 1/1000 kL = 0.001 kL.
Example: Express 6,214 L in kL using decimal notation.
So, 6,214 L = 6.214 kL.
Four Basic Operations on Metric Measures
- Metric measures can be added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided after converting to decimal form.
- Convert all measures to the same unit before performing operations.
- Place the decimal point correctly in the result for multiplication and division.
Addition
- Convert all measures to the same unit using decimal notation.
- Add the decimal numbers as usual.
Example: Add 5 km 3 hm 7 dam 9 m, 4 km 6 hm 1 m, and 2 hm 8 m.
5 km 3 hm 7 dam 9 m = 5 + 0.3 + 0.07 + 0.009 = 5.379 km.
4 km 6 hm 1 m = 4 + 0.6 + 0.001 = 4.601 km.
2 hm 8 m = 0.2 + 0.008 = 0.208 km.
So, the sum is 10.188 km.
Subtraction
- Convert all measures to the same unit using decimal notation.
- Subtract the decimal numbers as usual.
Example: Subtract 32 m 82 cm from 84 m 67 cm and express in metres.
84 m 67 cm = 84 + 0.67 = 84.67 m.
32 m 82 cm = 32 + 0.82 = 32.82 m.
So, the difference is 51.85 m.
Multiplication
- Convert the measure to decimal form in the required unit.
- Multiply as with whole numbers, ensuring the decimal point is placed correctly.
Example: Multiply 38 kg 500 g by 24.
So, the product is 924 kg.
Division
- Convert the measure to decimal form in the required unit.
- Divide as with whole numbers, placing the decimal point correctly in the quotient.
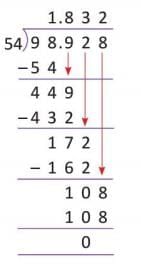
Example: Divide 98 kL 928 L by 54 and express in litres.
So, the quotient is 1,832 L.
Word Problems on Metric Measures
- Word problems involve applying addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division to solve real-life situations.
- Convert all measures to the same unit before calculating.
- Ensure the answer is in the unit asked for in the problem.
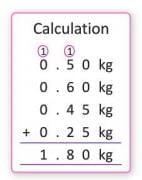
Example: Pari made fruit cream using 500 g apples, 600 g grapes, 450 g pomegranates, and 250 g bananas. How much fruit did she use?
Apples: 500 g = 0.5 kg.
Grapes: 600 g = 0.6 kg.
Pomegranates: 450 g = 0.45 kg.
Bananas: 250 g = 0.25 kg.
So, Pari used 1.80 kg of fruits.
The document Metric System Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE is a part of the Class 5 Course Mathematics Class 5 ICSE.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
123 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Metric System Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What are the common prefixes used in the Metric System? |  |
Ans. The common prefixes in the Metric System include kilo- (1,000), hecto- (100), deka- (10), deci- (0.1), centi- (0.01), and milli- (0.001). These prefixes help in understanding and converting different metric units.
| 2. How do you convert between different metric measures? |  |
Ans. To convert between metric measures, you can multiply or divide by powers of ten based on the prefixes. For example, to convert 5 kilometers to meters, you multiply by 1,000 (5 x 1,000 = 5,000 meters). Conversely, to convert 250 grams to kilograms, you divide by 1,000 (250 ÷ 1,000 = 0.25 kilograms).
| 3. What are the four basic operations on metric measures? |  |
Ans. The four basic operations on metric measures are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These operations can be performed on metric units as long as they are converted to the same unit before performing the calculations.
| 4. How can I solve word problems involving metric measures? |  |
Ans. To solve word problems involving metric measures, first identify the units involved and convert them to the same metric unit if necessary. Then, apply the appropriate mathematical operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division) based on the problem's context to find the solution.
| 5. Why is the Metric System important in everyday life? |  |
Ans. The Metric System is important in everyday life because it provides a universal standard for measurements. It is used in various fields such as science, medicine, and engineering, making it easier to communicate and compare measurements across different regions and disciplines.
Related Searches