SSS 2 Exam > SSS 2 Notes > Chemistry for SSS 2 > Mind Map: Periodic Table - Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties
Mind Map: Periodic Table - Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties | Chemistry for SSS 2 PDF Download
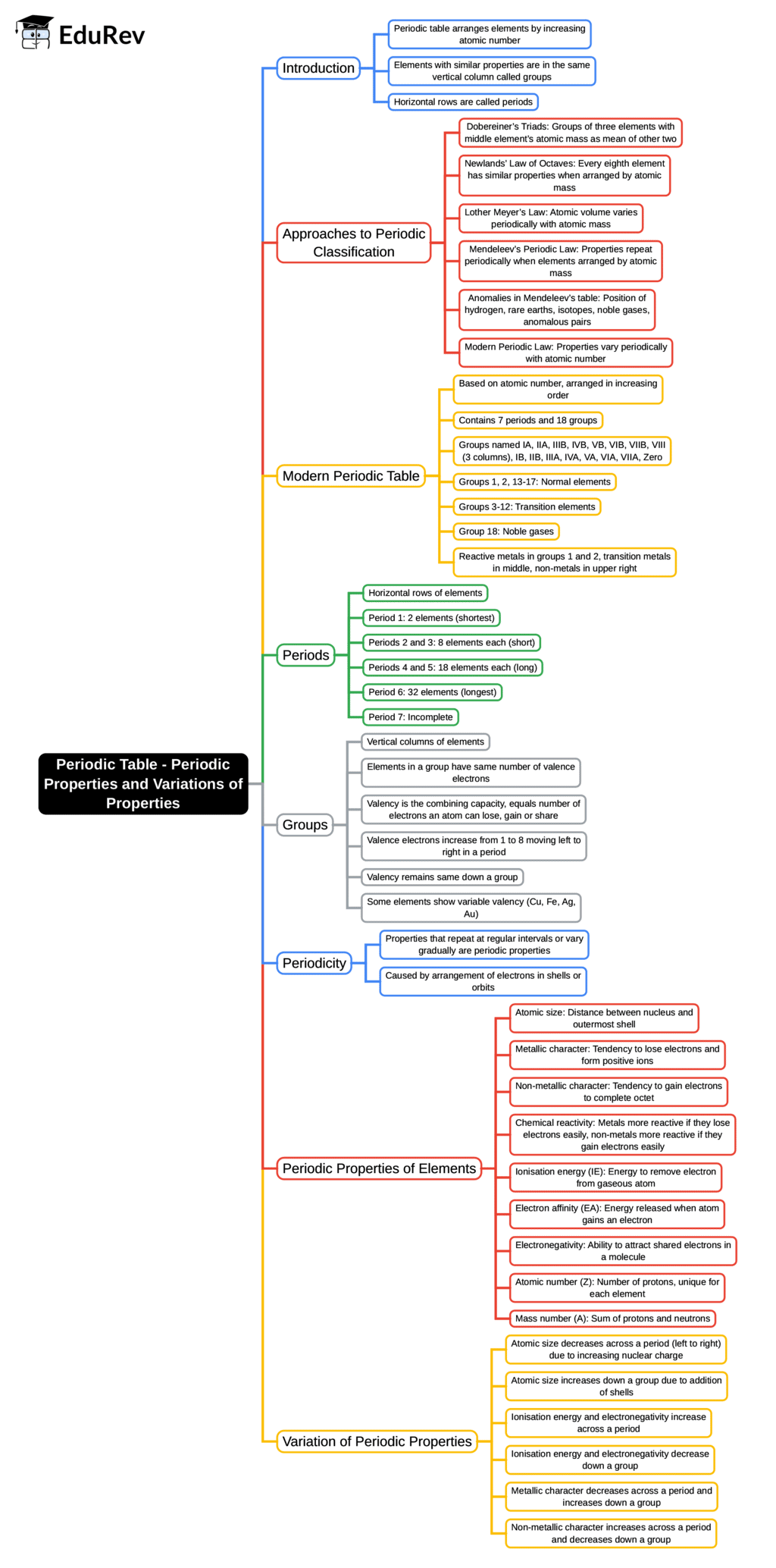
The document Mind Map: Periodic Table - Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties | Chemistry for SSS 2 is a part of the SSS 2 Course Chemistry for SSS 2.
All you need of SSS 2 at this link: SSS 2
|
1 videos|45 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Periodic Table - Periodic Properties and Variations of Properties - Chemistry for SSS 2
| 1. What are the periodic properties of elements in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. The periodic properties of elements include atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and electron affinity. Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period due to the increasing nuclear charge. Ionization energy, the energy required to remove an electron, tends to increase across a period and decreases down a group. Electronegativity, which measures an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond, also increases across a period and decreases down a group. Electron affinity refers to the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom, and it generally becomes more negative across a period and less negative down a group.
| 2. How does atomic radius change across a period and down a group? |  |
Ans. Atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right due to the increase in nuclear charge, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus. Conversely, atomic radius increases down a group because additional electron shells are added, which outweighs the effect of increased nuclear charge, resulting in a larger atomic size.
| 3. What is ionization energy and how does it vary in the periodic table? |  |
Ans. Ionization energy is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom or ion. In the periodic table, ionization energy increases across a period from left to right, as the increasing nuclear charge holds the electrons more tightly. It decreases down a group due to the increased distance of the outermost electrons from the nucleus and increased shielding effect from inner electrons, making it easier to remove an electron.
| 4. Describe the trend of electronegativity in the periodic table. |  |
Ans. Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. The electronegativity values generally increase across a period from left to right due to increasing nuclear charge and decrease down a group as the atoms become larger and the outer electrons are farther from the nucleus. This trend can be observed using the Pauling scale, where fluorine is the most electronegative element.
| 5. What is the significance of understanding periodic properties for studying chemical reactions? |  |
Ans. Understanding periodic properties is crucial for predicting how elements will react with one another. For example, elements with low ionization energies are more likely to lose electrons and form cations, making them more reactive metals. In contrast, elements with high electronegativity tend to gain electrons and form anions, making them more reactive nonmetals. This knowledge helps chemists predict the behavior of elements during chemical reactions, including bond formation and reactivity patterns.
Related Searches





















