Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Chemistry Class 7 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Matter and Its Composition
Matter and Its Composition Chapter Notes | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Matter |

|
| Particle Theory of Matter |

|
| States of Matter |

|
| Composition of Matter |

|
| Differences Between the Three States of Matter |

|
Introduction
Everything around us, like the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the objects we touch, is made of matter. This chapter explains what matter is, its properties, and how it exists in different forms. It also covers the tiny particles that make up matter and the forces that hold them together. Through simple activities and examples, we will learn about the three states of matter—solids, liquids, and gases—and how they differ from each other.Matter
- Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
- Examples include humans, rocks, trees, buildings, and clouds.
- Understanding matter helps us understand the world around us.
Properties of Matter
Matter has two main properties: it has mass and occupies space.Matter Has Mass
- Mass is the amount of matter in an object.
- More matter means more mass.
Activity 1.1
Aim: To show that matter has mass.
Materials:2 balloons, thread, meter scale, needle.
Procedure:
- Blow air into two balloons and tie them with equal-length threads.
- Hang the balloons on both ends of a meter scale.
- Make a loop with thread at the center of the scale to balance it.
- Prick one balloon with a needle.
Observation: The scale tilts toward the inflated balloon.
Conclusion: The inflated balloon is heavier because it contains air, proving that air (matter) has mass.
Matter Occupies Space
- Matter takes up space, meaning its particles move within that space.
- Everything, like water or sand, occupies space.
Activity 1.2
Aim: To show that matter occupies space.
Materials:Two 250 mL beakers, water, sand, spoon.
Procedure:
- Take two 250 mL beakers.
- Fill both beakers halfway with water.
- Note the water level in both beakers.
- Add four spoons of sand to one beaker.
- Observe the water level again.
Observation: The water level rises in the beaker with sand.
Conclusion: Sand takes up space, causing the water level to increase, proving that matter occupies space.
Particle Theory of Matter
- Matter is made of tiny particles too small to see without a microscope.
- Different substances have different types and sizes of particles.
- Particles are held together by forces called interparticle or intermolecular forces.
- The space between particles is called interparticle space.
Arrangement of Particles in Solids
- Solids have strong intermolecular forces that hold particles tightly together.
- The interparticle space in solids is very small.
- Particles in solids vibrate in fixed positions but do not move around.
Arrangement of Particles in Liquids
- Liquids have weaker intermolecular forces than solids.
- The interparticle space in liquids is larger than in solids.
- Particles in liquids can slide past each other, allowing liquids to flow.
Arrangement of Particles in Gases
- Gases have very weak intermolecular forces.
- The interparticle space in gases is very large.
- Particles in gases move freely in all directions.
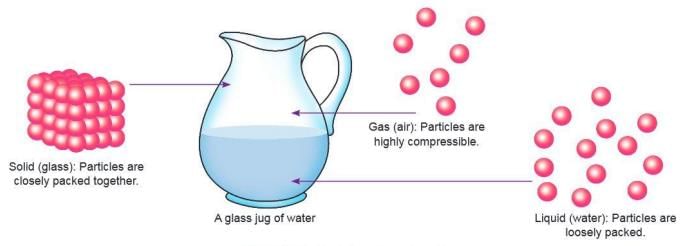
States of Matter
- Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas.
- Each state has unique properties based on particle arrangement and forces.
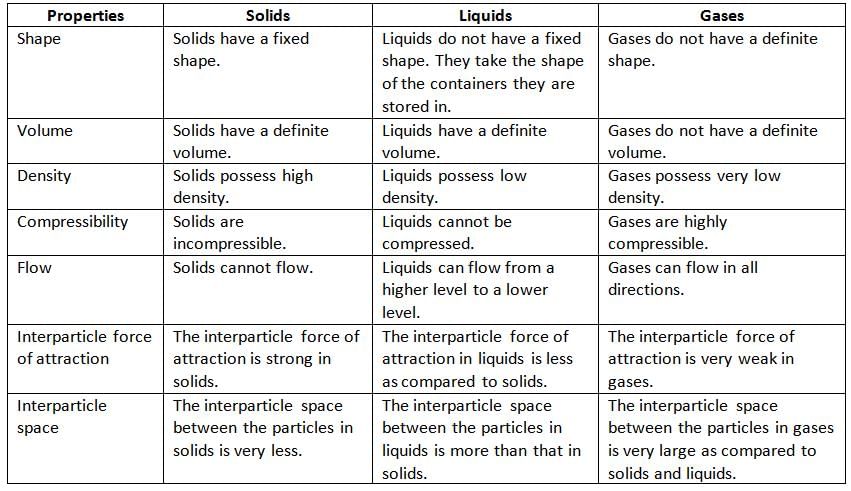
Solids
- Solids have a fixed shape, mass, and volume.
- The shape of a solid can change with external force (e.g., hammering metal).
- Solids are rigid and hard due to closely packed molecules and strong intermolecular forces.
- Solids cannot be compressed because particles are too close, and forces resist further compression.
- Solids have high density due to tightly packed molecules.
- Examples: Chalk, stone, pen, table.
Liquids
- Liquids have a fixed volume but no fixed shape; they take the shape of their container.
- Liquids can flow because their molecules are loosely packed with weaker forces.
- Liquids cannot be compressed due to strong repulsive forces when particles are pushed closer.
- Liquids have lower density than solids due to larger intermolecular spaces.
- Examples: Water, milk, juice, kerosene, petrol.
Gases
- Gases have no fixed shape or volume; they spread to fill their container.
- Gases can flow because their molecules are far apart with very weak forces.
- Gases are highly compressible because their molecules can be pushed closer together.
- Gases have very low density due to large intermolecular spaces.
- Examples: Oxygen, carbon dioxide, Compressed Natural Gas (CNG), Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG).
- CNG is used as a clean fuel in vehicles, and LPG is used as cooking gas.
Composition of Matter
- Matter is made of substances combined in different ways.
- A pure substance has fixed chemical properties (how it reacts with other substances) and physical properties (color, taste, smell, state, boiling/melting points).
- Pure substances can be elements or compounds.
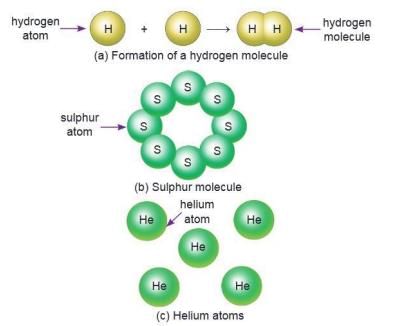
Elements
- An element is a substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances by chemical processes.
- There are 118 known elements, e.g., gold, silver, iron, sodium, sulphur, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, carbon.
- Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms.
- An atom is the smallest unit of an element with all its characteristics.
- Some elements’ atoms combine to form molecules (e.g., two oxygen atoms form an oxygen molecule, eight sulphur atoms form a sulphur molecule).
- Noble gases (helium, neon, argon, krypton, radon, xenon) exist as single atoms, not molecules.
Compounds
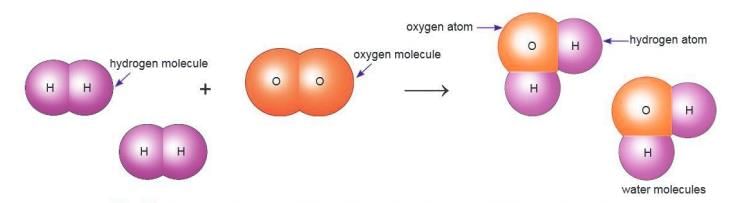
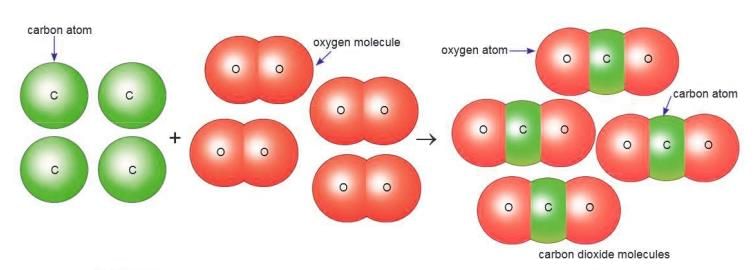
A compound is a substance made of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion.
- Example: Water has hydrogen and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio.
- Example: Carbon dioxide has carbon and oxygen in a 1:2 ratio.
- Other examples: Ammonia (nitrogen and hydrogen), sulphur dioxide (sulphur and oxygen).
- Compounds have different properties from their constituent elements.
Differences Between the Three States of Matter
Nature Care
- Water exists in all three states of matter.
- Water scarcity is a major issue today.
- Ways to conserve water at home:
- Turn off taps when not in use.
- Fix leaking pipes.
- Use a bucket instead of a shower for bathing.
- Reuse water from washing vegetables for plants.
- Collect rainwater for household use.
Glossary
- Mass: The measure of quantity of matter contained in a substance.
- Solid: A state of matter that has a definite mass, shape, and volume.
- Liquid: A state of matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape.
- Gas: A state of matter that neither has a definite volume nor a definite shape.
- Pure substance: A substance having fixed chemical and physical properties.
- Element: A substance that cannot be broken into simpler substances by a chemical process.
- Atom: The smallest unit of an element having all the characteristics of that element.
- Molecules: Atoms of certain elements combined together.
- Compound: A substance which consists of two or more elements combined together chemically in a fixed proportion.
- Interparticle force: The force of attraction existing between the particles in matter.
- Interparticle space: The distance between the particles in matter.
Points To Remember
- Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space.
- The three states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas.
- Solids have a definite shape, mass, and volume; they are rigid, incompressible, and have high density.
- Liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape; they can flow, are incompressible, and have lower density than solids.
- Gases have no definite shape or volume; they can flow, are highly compressible, and have very low density.
- Matter consists of substances combined in different forms.
- A pure substance has fixed chemical and physical properties and can be an element or compound.
- An element cannot be broken into simpler substances and is made of atoms.
- An atom is the smallest unit of an element with all its characteristics.
- Some elements’ atoms form molecules; noble gases exist as single atoms.
- A compound is made of two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion.
- The particle theory of matter says matter is made of tiny particles.
- Solids have strong interparticle forces and small interparticle spaces.
- Liquids have weaker interparticle forces and larger interparticle spaces than solids.
- Gases have very weak interparticle forces and very large interparticle spaces.
The document Matter and Its Composition Chapter Notes | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE is a part of the Class 7 Course Chemistry Class 7 ICSE.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
33 videos|58 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Matter and Its Composition Chapter Notes - Chemistry Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What is matter and why is it important in science? |  |
Ans. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. It is important in science because it makes up everything around us, from the air we breathe to the objects we interact with daily. Understanding matter helps scientists study the physical world and the various processes that occur within it.
| 2. What is the particle theory of matter? |  |
Ans. The particle theory of matter states that all matter is made up of tiny particles that are in constant motion. These particles are too small to be seen with the naked eye, and their arrangement and movement determine the properties of different materials. This theory helps explain phenomena like changes in state and temperature effects on matter.
| 3. What are the three states of matter? |  |
Ans. The three states of matter are solids, liquids, and gases. Solids have a fixed shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container, and gases have neither a fixed shape nor volume, expanding to fill the available space.
| 4. How do the states of matter differ from one another? |  |
Ans. The states of matter differ primarily in terms of particle arrangement, energy, and movement. In solids, particles are closely packed and vibrate in place; in liquids, particles are close but can move around each other, allowing them to flow; in gases, particles are far apart and move freely at high speeds, occupying more space.
| 5. What is the composition of matter? |  |
Ans. The composition of matter refers to the types of particles that make up a substance and how they are arranged. Matter can be composed of elements, which are pure substances made of one type of atom, or compounds, which are made of two or more different types of atoms chemically combined. Understanding composition is essential for studying chemical reactions and properties of materials.
Related Searches















