Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Chemistry Class 10 ICSE > Mind Map: Chemical Bonding - Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds
Mind Map: Chemical Bonding - Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
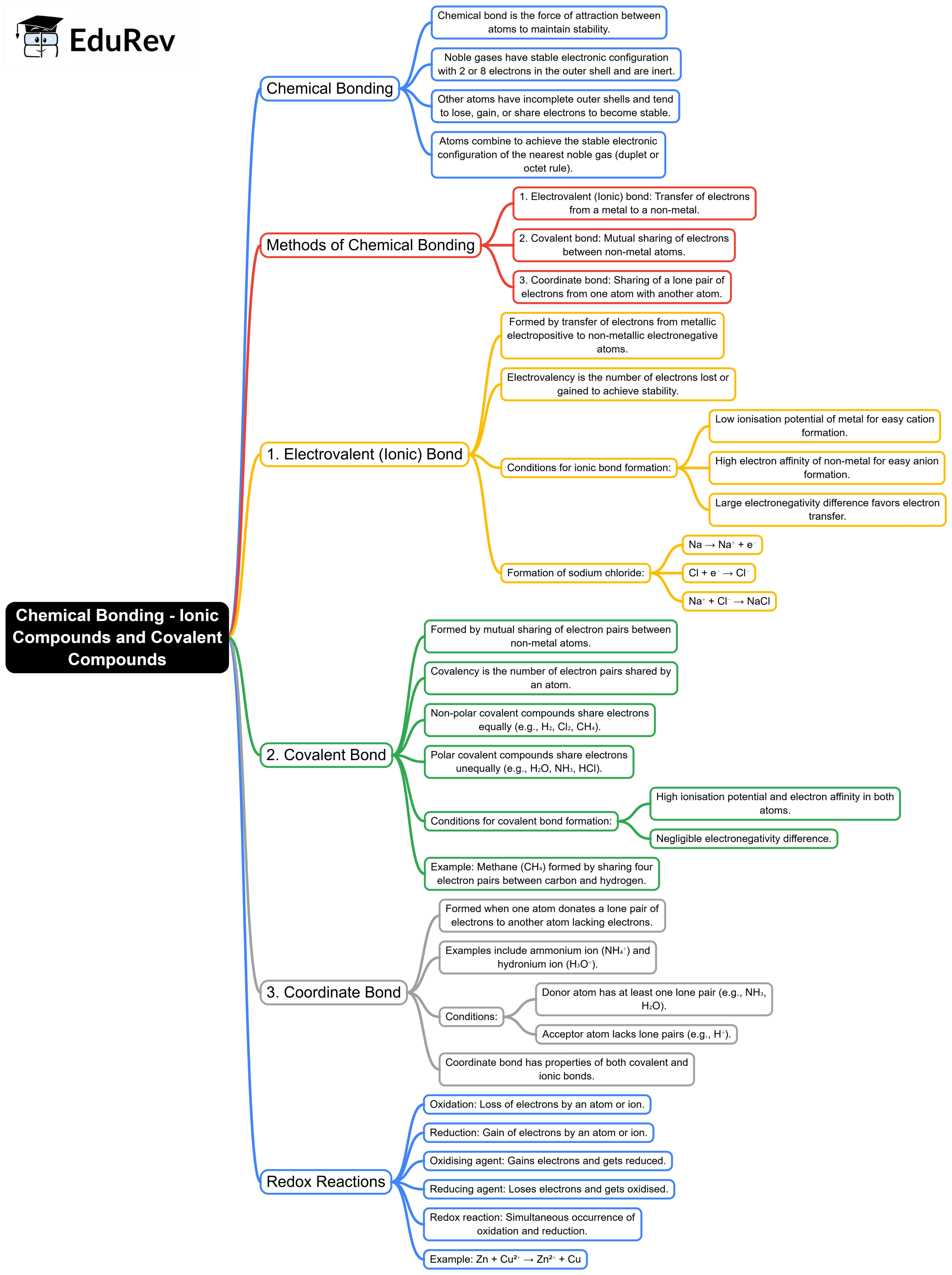
The document Mind Map: Chemical Bonding - Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds | Chemistry Class 10 ICSE is a part of the Class 10 Course Chemistry Class 10 ICSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
40 videos|140 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Chemical Bonding - Ionic Compounds and Covalent Compounds - Chemistry Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What are ionic compounds and how are they formed? |  |
Ans.Ionic compounds are formed through the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of ions. This typically occurs between metals and nonmetals. The metal atom loses electrons, becoming a positively charged ion (cation), while the nonmetal atom gains those electrons, becoming a negatively charged ion (anion). The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions leads to the formation of ionic bonds, creating a stable ionic compound, such as sodium chloride (NaCl).
| 2. What are covalent compounds and what distinguishes them from ionic compounds? |  |
Ans.Covalent compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals share electrons to achieve a full outer shell, resulting in the formation of covalent bonds. Unlike ionic compounds, which involve the transfer of electrons and the formation of charged ions, covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons. A common example of a covalent compound is water (H₂O), where oxygen shares electrons with two hydrogen atoms.
| 3. What properties do ionic compounds exhibit? |  |
Ans.Ionic compounds generally exhibit several distinct properties: they have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic forces between ions, they are usually soluble in water, and they can conduct electricity when dissolved in water or melted, as the ions are free to move. Additionally, ionic compounds tend to form crystalline structures, which contribute to their hardness.
| 4. What are the key characteristics of covalent compounds? |  |
Ans.Covalent compounds typically have lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds, as the forces holding the molecules together are weaker. They may or may not be soluble in water, depending on their polarity. Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity in solid or liquid form, as there are no free-moving charged particles. These compounds often exist as gases or liquids at room temperature.
| 5. How can you differentiate between ionic and covalent compounds based on their formulas? |  |
Ans.Ionic compounds often consist of a metal and a nonmetal, and their formulas typically reflect the ratio of cations to anions that balances the overall charge, such as NaCl or MgO. In contrast, covalent compounds usually involve only nonmetals and are represented by formulas that indicate the number of atoms involved in the molecule, such as CO₂ or CH₄. Additionally, ionic compounds form lattice structures, while covalent compounds form discrete molecules.
Related Searches





















