SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Mind Map: Force
Mind Map: Force | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
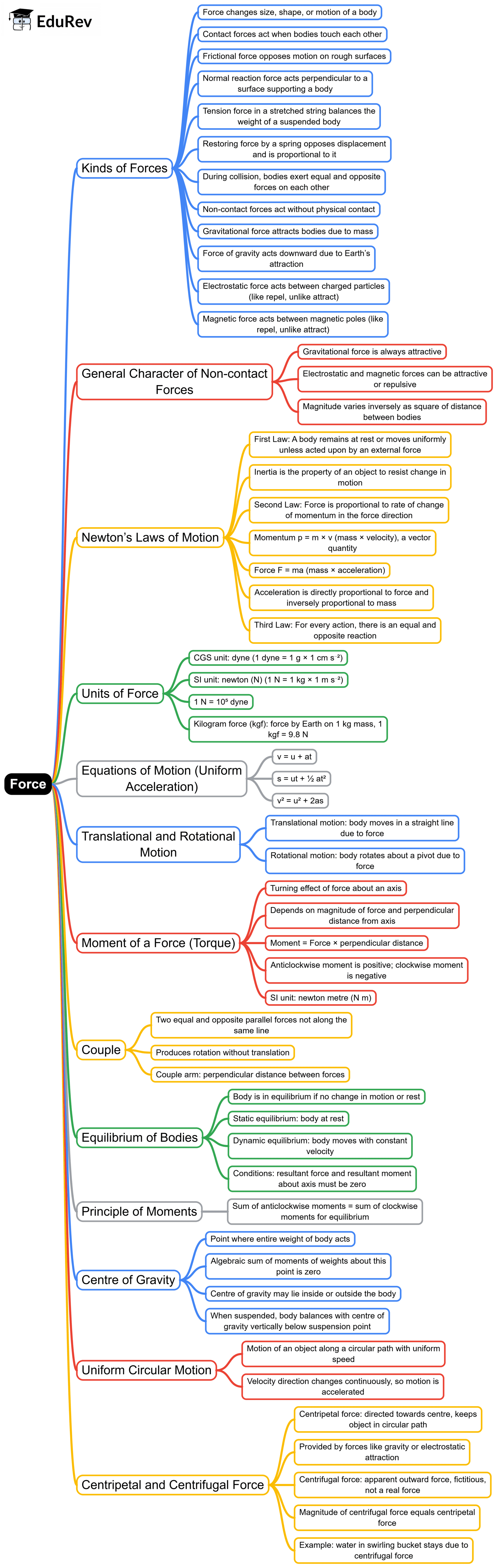
The document Mind Map: Force | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
482 videos|1427 docs|310 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Force - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the definition of force in physics? |  |
Ans. Force is defined as any interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. The standard unit of force is the Newton (N), which is defined as the amount of force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass by one meter per second squared (1 N = 1 kg·m/s²).
| 2. What are the different types of forces? |  |
Ans. There are several types of forces in physics, including:
1. Gravitational Force: The attractive force between two masses.
2. Frictional Force: The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another.
3. Normal Force: The support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object.
4. Tension Force: The force transmitted through a string, rope, or wire when it is pulled tight.
5. Applied Force: The force that is applied to an object by a person or another object.
| 3. How does Newton's First Law of Motion relate to force? |  |
Ans. Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by a net external force. This law highlights the concept of inertia, which is the tendency of objects to resist changes in their state of motion. Thus, it emphasizes that a force is necessary to change an object's motion.
| 4. What is the relationship between mass and force according to Newton's Second Law? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the relationship between mass (m), force (F), and acceleration (a) is given by the equation F = m·a. This law indicates that the force acting on an object is equal to the mass of that object multiplied by its acceleration. Therefore, for a given force, an increase in mass will result in a decrease in acceleration, while a decrease in mass will result in an increase in acceleration.
| 5. What is the significance of the Law of Universal Gravitation? |  |
Ans. The Law of Universal Gravitation states that every point mass attracts every other point mass in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This law is significant because it explains the gravitational force between objects, such as planets, moons, and other celestial bodies, and it helps us understand the motion of these bodies in space. The formula for this law is F = G(m₁·m₂)/r², where G is the gravitational constant.
Related Searches



















