Worksheet with Solutions: D and F - Block Elements | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section A: Fill In The Blanks |

|
| Section B. Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Section C: Assertion and Reason |

|
| Section D: Answer the following Questions |

|
Section A: Fill In The Blanks
Q1. There is a gradual decrease in the size of atoms or M³⁺ ions across the series in actinoids. This is called _______________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Actinoid contraction
Explanation: As we move across the actinoid series, the 5f electrons are poorly shielded, resulting in greater nuclear attraction. This causes a gradual decrease in atomic and ionic radii, known as actinoid contraction.
Q2: The d-block elements form _______________ compounds and complexes.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Coloured
Explanation: D-block elements often have partially filled d-orbitals, which allow d–d transitions. These transitions absorb certain wavelengths of light, leading to the appearance of coloured compounds.
Q3: The transition metals and their compounds are known for their _______________ activity.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Catalytic
Explanation: Transition metals can adopt multiple oxidation states and provide surface area for reactants to adsorb. This makes them efficient catalysts in many chemical reactions.
Q4: The d-block consisting of groups _______________ occupies the large middle section of the periodic table.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: 3 to 12
Explanation: Groups 3 to 12 in the periodic table include all the transition metals, which belong to the d-block. These elements fill the d-orbitals progressively.
Q4: K₂CrO₄ is _______________ in colour but K₂Cr₂O₇ is _______________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Yellow, Orange
Explanation:
Potassium chromate (K₂CrO₄) is yellow due to the presence of chromate ions, while potassium dichromate (K₂Cr₂O₇) is orange because of dichromate ions. Both are d-block compounds and show colour due to charge-transfer transitions.
Section B. Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Which of the following is the symbol for green vitriol?
(a) FeSO4.7H2O
(b) CuSO4.5H2O
(c) CaSO4.2H2O
(d) None of these
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (a) FeSO4.7H2O
Explanation:
Green vitriol is the common name for ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, i.e., FeSO₄·7H₂O.
CuSO₄·5H₂O is blue vitriol, and CaSO₄·2H₂O is gypsum
Q2. Which group of elements do transition elements belong to?
(a) p-block
(b) s-block
(c) d-block
(d) f-block
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (c) d-block
Explanation:
Transition elements are located in the d-block of the periodic table.
They span groups 3 to 12, and have partially filled d-orbitals either in the elemental state or in their ions.
Q3. Which of the following is a diamagnetic ion?
(a) Co2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Cu2+
(d) Zn2+
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d) Zn2+
Explanation:
Diamagnetic substances have no unpaired electrons.
Electronic configurations:
Zn²⁺ → [Ar] 3d¹⁰ → all paired → diamagnetic
Co²⁺ → 3d⁷ → unpaired e⁻ present → paramagnetic
Ni²⁺ → 3d⁸ → unpaired e⁻ → paramagnetic
Cu²⁺ → 3d⁹ → 1 unpaired e⁻ → paramagnetic
Q4. The colour of transition metal ions is caused by absorption of a specific wavelength. This results in
(a) d-s transition
(b) s-s transition
(c) s-t/transition
(d) d-d transition
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d) d-d transition
Explanation:
In transition metal ions, the colour arises due to electronic transitions between split d-orbitals (in presence of ligands).
This is called a d–d transition.
Absorption of visible light promotes an electron from a lower d-orbital to a higher d-orbital.
Q5. What is the sequence of the melting points of Cu, Ag, and Au?
(a) Cu > Ag > Au
(b) Cu >Au > Ag
(c) Au > Ag > Cu
(d) Ag > Au > Cu
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (b) Cu >Au > Ag.
Actual melting points:
Cu (Copper): 1085°C
Au (Gold): 1064°C
Ag (Silver): 962°C
Hence, order: Cu > Au > Ag
Section C: Assertion and Reason
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
Q.1. Assertion : Cuprous ion (Cu+) has unpaired electrons while cupric ion (Cu++) does not.
Reason : Cuprous ion (Cu+) is blue whereas cupric ion (Cu++) is colourless in the aqueous solution.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Explanation: The assertion is incorrect because Cu⁺ has no unpaired electrons, Cu²⁺ has one.
The reason is also incorrect, Cuprous ion (Cu+) is colorless whereas cupric ion (Cu++) is blue in the aqueous solution.
Q.2. Assertion : Transition metals show variable valency.
Reason : Transition metals have a large energy difference between the ns2 and (n – 1)d electrons.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Explanation:
Transition metals do show variable valency due to similar energy of (n-1)d and ns electrons.
Reason is incorrect because the energy difference is small, not large, allowing both sets of electrons to participate in bonding.
Q.3. Assertion : Transition metals are good catalysts.
Reason : V2O5 or Pt is used as catalyst in the preparation of H2SO4 by contact process.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Explanation:
Transition metals provide a surface for reactions and can change oxidation states easily, making them good catalysts.
V₂O₅ (in SO₂ to SO₃) and Pt are commonly used in catalytic processes.
Q.4. Assertion : Magnetic moment values of actinides are lesser than the theoretically predicted values.
Reason : Actinide elements are strongly paramagnetic
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Assertion is incorrect: The magnetic moments of actinides often exceed spin-only values due to significant orbital contribution.
Reason is also incorrect: They are paramagnetic, but the statement doesn’t relate properly to the assertion and lacks clarity.
Q.5. Assertion: In acid solution, permanganate is reduced to Mn2+ by an excess of reducing agent.
Reason: MnO4- reduced in Mn2+ in acidic medium and the product in the presence of an excess of permanganate is MnO2.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Explanation:
In acidic medium, KMnO₄ is reduced to Mn²⁺:
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → Mn²⁺ + 4H₂OAssertion is correct.
Reason is partially correct: The second part is confused—MnO₂ forms in neutral or slightly alkaline medium, not acidic.
Section D: Answer the following Questions
Q1. On the basis of Lanthanoid contraction, explain the following
(i) Nature of bonding in Lu2O3 and La2O3
(ii) Trends in the stability of oxo salts of lanthanides from La to Lu.
(iii) Stability of the complexes of lanthanides.
(iv) Radii of 4d and 5d block elements
(v) Trends in acidic character of lanthanide oxides.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(i) Due to lanthanide contraction, size reduces. With the size reduction, the covalent character increases. Therefore, Lu2O3 is more covalent than La2O3 .
(ii) Oxosalts contain oxygen as an anion. As the size of the cation reduces from La to Lu, according to Fajan’s rules, the polarising power of the cation will increase, and it will distort the cloud of oxygen(anion) significantly. Thus the bond weakens, and the stability also reduces.
(iii) As the size of the central atom reduces, the stability of the complex increases. A small metal ion with a greater charge attracts the ligands better.
(iv) In 5d block elements, the effective nuclear charge increases due to poor shielding of f orbitals, thereby reducing the size. This is called lanthanide contraction. So, the radii of 4d and 5d block elements end up being very similar.
(v) From La to Lu, the acidic character increases. As the size reduces from La to Lu, the ability to lose electrons(Lewis base character) reduces, so the acidity increases.
Q2. When orange solution containing Cr2O72- ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when H+ ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- The following reaction takes place when Cr2O72- is treated with an alkali,
(orange) Cr2O72- + OH– → 2CrO42- (yellow) - When the yellow solution is treated with an acid, we get back the orange solution
(yellow) 2CrO42- + 2H+ → Cr2O72– (orange) + H2O - This reaction is reversible under proper conditions.
Q3. The second and third rows of transition elements resemble each other much more than they resemble the first row. Explain why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Due to lanthanoid contraction, the atomic radii of the second and third-row transition elements are almost identical. So, they resemble each other much more than first-row elements.
Q4. While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital but reverse happens during the ionisation of the atom. Explain why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Atomic orbitals are filled in order of increasing energies. Since the energy of 3d orbital is more than 4s orbital, based on the (n+l) rule, it is filled after 4s orbital. But during ionisation, electrons in the outermost orbital are lost. Since 4s will be the outermost orbital, in this case, electrons from this orbital will be ionised first.
Q5. The halides of transition elements become more covalent with increasing oxidation state of the metal. Why?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: As the oxidation state increases, the size of the ion of the transition element decreases. As per Fajan’s rule, as the size of metal ions decreases, the covalent character of the bond formed increases. Therefore, the halides of transition elements become more covalent with the increasing oxidation state of the metal.
Q6. Explain the following observations :
(i) Generally there is an increase in density of elements from titanium (Z = 22) to copper (Z = 29) in the first series of transition elements.
(ii) Transition elements and their compounds are generally found to be good catalysts in chemical reactions.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (i) From titanium to copper the atomic size of elements decreases and mass increases as a result of which density increases.
(ii) The catalytic properties of the transition elements are due to the presence of unpaired electrons in their incomplete d- orbitals and variable oxidation states.
Q7. What is Lanthanoid contraction? What are its two consequences?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Lanthanoid contraction: The overall decrease in atomic and ionic radii with increasing atomic number is known as lanthanoid contraction. In going from La+3 to Lu+3 in lanthanoid series, the size of ion decreases. This decrease in size in the lanthanoid series is known as lanthanoid contraction. The lanthanoid contraction arises due to imperfect shielding of one 4f electron by another present in the same subshell.
Consequences :
(i) Similarity in properties: Due to lanthanoid contraction, the size of elements which follow (Hf – Hg) are almost similar to the size of the elements , of previous row (Zr – Cd) and hence these are difficult to separate. Due to small change in atomic radii, the chemical properties of lanthanoids are very similar due to which separation of lanthanoid becomes very difficult.
(ii) Basicity difference : Due to lanthanoid contraction, the size decreases from La+3 to Lu+3. Thus covalent character increases. Hence basic character of hydroxides also decreases i.e. why La(OH)3 is most basic while Lu(OH)3 is least basic.
Q8. Describe the oxidising action of potassium dichromate and write the ionic equations for its reaction with
(i) iodine (ii) H2S.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic medium using H2SO4.
K2Cr2O7 + 4H2SO4 → K2SO4 + Cr2(SO4)3 + 4H2O + 3[O]
Ionic reactions :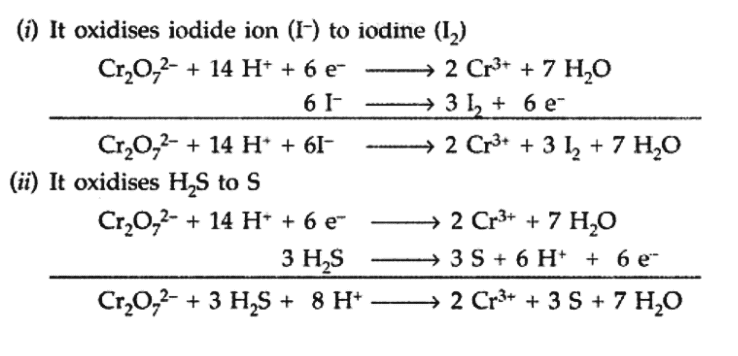
Q9. How would you account for the following :
(i) Many of the transition elements and their compounds can act as good catalysts.
(ii) The metallic radii of the third (5d) series of transition elements are virtually the same as those of the corresponding members of the second series.
(iii) There is a greater range of oxidation states among the actinoids than among the lanthanoids.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (i) The catalytic properties of the transition elements are due to the presence of unpaired electrons in their incomplete d-orbitals and variable oxidation states.
(ii) Due to lanthanoid contraction in second series after lanthanum, the atomic radii of elements of second and third series become almost same and hence show similarities in properties.
(iii) Because of very small energy gap between 5f, 6d and 7s subshells all their electrons can take part in bonding and shows variable oxidation states.
Q10. Complete the following chemical equations : 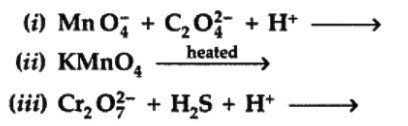
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: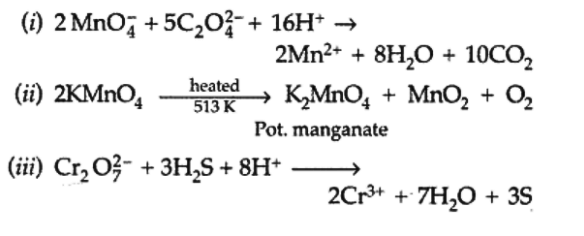
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet with Solutions: D and F - Block Elements - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are block elements in the periodic table? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of D and F block elements? |  |
| 3. How do D and F block elements differ from S and P block elements? |  |
| 4. What are some common uses of D and F block elements? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of D and F block elements? |  |




















