Respiration in Plants Chapter Notes | Biology Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Plants, like all living organisms, need energy to perform their functions. This chapter explores the two types of respiration (aerobic and anaerobic), how respiratory gases are exchanged through diffusion, and several engaging experiments to illustrate plant respiration.
What is Respiration?
- All living cells in plants require energy for activities like protein synthesis, starch production, mineral absorption, and cell wall formation.
- Energy is obtained by breaking down glucose, a simple carbohydrate, using oxygen.
- The overall chemical reaction for respiration is: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy.
- Key characteristics of respiration:
- Glucose breakdown occurs in multiple chemical steps, not a single step.
- Two main phases: Glycolysis (in cytoplasm, glucose → pyruvate) and Krebs cycle (in mitochondria, pyruvate → CO₂ + H₂O + ATP).
- Each step is catalyzed by specific enzymes.
- Energy is stored as ATP (adenosine triphosphate), not just released as heat.
- ATP is the energy currency of the cell, converted to ADP when used, and regenerated from ADP when more glucose is broken down.
- One mole of glucose yields 38 ATP molecules on complete oxidation.
- Respiration is a catabolic process (breaks down molecules to release energy).
- Metabolic activities in organisms:
- Anabolic: Constructive processes that consume energy (e.g., building proteins).
- Catabolic: Destructive processes that release energy (e.g., respiration).
Respiration vs. Burning (Combustion)
Respiration and burning both release energy, CO₂, and water, but they differ significantly:
Respiration:
- Occurs in multiple chemical steps.
- Catalyzed by enzymes.
- Biochemical process.
- Produces ATP and some heat.
- No light energy produced.
- Cellular process.
- Occurs at body temperature.
Burning:
- Occurs in a single step.
- Triggered by heat.
- Physico-chemical process.
- Releases all energy as heat and light.
- Produces light energy.
- Non-cellular process.
- Requires high temperature (ignition point).
The Entire Plant Respires
- Every plant part (leaves, stem, roots, even deep cells) respires.
- Oxygen enters through:
- Stomata in leaves.
- Lenticels in stems.
- General surface of roots.
- Soil tilling creates air spaces, providing oxygen to roots; waterlogged or compact soil lacks air, affecting root respiration.
- During the day, leaves produce oxygen via photosynthesis, some used in respiration, the rest diffused out.
- CO₂ from respiration in leaves is used in photosynthesis during the day.
- At night, leaves take in oxygen from the atmosphere and release CO₂.
- Sleeping under trees at night releases minimal CO₂, but bird droppings, insects, or snakes pose real dangers.
- Sleeping under trees during the day is beneficial due to oxygen from photosynthesis and cooling from transpiration.
Two Kinds of Respiration - Aerobic and Anaerobic
A. Aerobic Respiration
- Uses free oxygen for complete glucose oxidation.
- Chemical reaction: C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + 38 ATP.
- Occurs normally throughout a plant’s life.
- Produces CO₂, water, and a large amount of energy (38 ATP per glucose molecule).
B. Anaerobic Respiration
- Occurs temporarily in the absence of oxygen (e.g., in fruits, seeds, or germinating seeds).
- Chemical reaction: C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂ + 2 ATP.
- Produces ethanol, CO₂, and a small amount of energy (2 ATP per glucose molecule).
- Incomplete glucose breakdown; cannot sustain plant parts for long, leading to death after a few days.
- Some microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi like yeast) respire anaerobically throughout life.
Differences Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Aerobic:
- Requires oxygen.
- Complete glucose breakdown.
- End products: CO₂ and water.
- High energy yield (38 ATP).
- Normal throughout life.
Anaerobic:
- No oxygen required.
- Incomplete glucose breakdown.
- End products: Ethanol and CO₂.
- Low energy yield (2 ATP).
- Temporary, short-term process.
Experiments on Respiration in Plants
1. Experiment to Prove Oxygen is Used Up in Respiration
- Setup: Two flasks (A with germinating bean seeds, B with boiled seeds + antiseptic).
- Wet cotton provides water; soda lime absorbs CO₂ in both flasks.
- After a few days, flask A’s delivery tube shows a higher water level rise, indicating oxygen use by germinating seeds.
- Burning paper test: Flame extinguishes in flask A (no oxygen) but burns briefly in flask B (oxygen present).
- Flask B is the control (identical setup but with dead seeds).
- Slight water rise in flask B’s tube due to minimal environmental changes or residual gases.
2. Experiment to Prove Carbon Dioxide is Produced During Respiration in Germinating Seeds
- Setup: Flask A with soaked seeds, flask B with boiled seeds + antiseptic; both with wet cotton-wool.
- After a few days, seeds in flask A germinate, while flask B seeds do not.
- Test: Tilt flasks over limewater test-tubes; flask A’s gas turns limewater milky (CO₂ present), flask B’s gas does not.
- Alternative setup: Flask C with germinating seeds, air cleared of CO₂ enters via soda lime; flask D’s limewater turns milky, proving CO₂ from seeds.
3. Experiment to Prove Carbon Dioxide is Produced by Green Plants During Respiration
- Setup: Small potted plant (e.g., Geranium) in a bell-jar on a vaselined glass sheet, kept in the dark.
- Air pump draws air through soda lime (removes CO₂) and limewater (flask A, stays clear).
- Air exiting bell-jar passes through limewater (flask B), which turns milky due to CO₂ from plant respiration.
- Dark condition prevents photosynthesis, ensuring CO₂ is from respiration only.
4. Experiment to Show Heat is Evolved During Respiration
- Setup: Two thermos flasks (A with live soaked seeds, B with boiled seeds + antiseptic).
- Thermometers inserted, flasks plugged with cotton wool.
- After hours, flask A’s thermometer shows a temperature rise (heat from respiring seeds), while flask B shows no change.
5. Experiment to Demonstrate Anaerobic Respiration
- Setup: Soaked, peeled peas in a test-tube filled with mercury, inverted in a mercury beaker.
- After two days, mercury level falls due to gas release; gas is CO₂ (tested by potassium hydroxide absorbing CO₂, raising mercury level).
- Control: Boiled, sterilized seeds show no gas release.
- Mercury is used to create an oxygen-free environment; water cannot exclude oxygen.
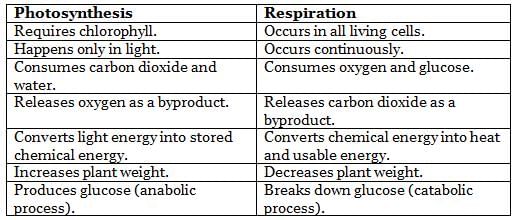
Respiration Contrasted with Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis and respiration in plants are fundamentally opposing processes, where the inputs of one are the outputs of the other, making them complementary. This interplay explains why plant respiration experiments are not conducted during the day in light.
The comparison between photosynthesis and respiration
Respiration in Plants Compared with Respiration in Animals
Basic respiration processes are similar in plants and animals.
Differences in plants:
- No gaseous transport; gases diffuse cell-to-cell (unlike blood transport in animals).
- Anaerobic respiration produces ethanol (not lactic acid as in animals).
- Produces less heat compared to animals.
Points to Remember
- Respiration breaks down glucose to produce ATP energy.
- Two phases: Glycolysis (cytoplasm) and Krebs cycle (mitochondria).
- Enzyme-driven process with multiple steps.
- Oxygen enters via stomata (leaves), lenticels (stems), and root surfaces.
- Aerobic respiration: Uses O₂, produces CO₂, H₂O, 38 ATP; normal process.
- Anaerobic respiration: No O₂, produces ethanol, CO₂, 2 ATP; temporary.
- Respiration is opposite to photosynthesis in gas exchange, energy, and weight changes.
|
18 videos|101 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Respiration in Plants Chapter Notes - Biology Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What is respiration in plants and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How does respiration differ from combustion? |  |
| 3. What are the two types of respiration in plants? |  |
| 4. What experiments can be conducted to demonstrate respiration in plants? |  |
| 5. How does respiration in plants compare to respiration in animals? |  |
















