Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Chemistry Class 7 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Atoms Structure
Atoms Structure Chapter Notes | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
The chapter on Atomic Structure introduces you to the fascinating world of atoms and molecules, the tiny building blocks of everything around us. You'll learn what atoms, molecules, and radicals are, and how they combine to form different substances. This chapter also explains concepts like valency, atomicity, and ions, which help us understand how elements interact in chemical reactions. By exploring the structure of atoms and their role in the periodic table, you'll discover how scientists use these ideas to write chemical formulas and study compounds.Atoms and Molecules
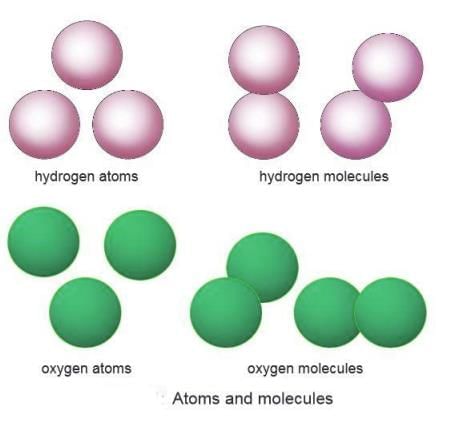
Atoms
It is the smallest piece of an element that participates in a chemical reaction. An atom cannot exist on its own; it combines with other atoms or molecules. An atom of an element displays all the features of that element. For example, all atoms of the element oxygen are the same.- Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms: Everything around us, like oxygen or iron, is made up of very small units called atoms.
- Atoms take part in chemical reactions but cannot exist alone: Atoms join with other atoms to form substances during reactions, but they cannot stay by themselves.
- Atoms cannot be divided, created, or destroyed: You cannot break an atom into smaller pieces, and you cannot make or destroy an atom.
- Atoms of one element are the same but different from atoms of other elements: All atoms of one element, like all oxygen atoms, are identical, but they are different from atoms of another element, like hydrogen atoms.
- An atom shows all the properties of its element: An atom of an element has all the characteristics of that element, for example, an oxygen atom has the properties of oxygen.
Structure of an Atom
- An atom is made of smaller particles called subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- Electrons are negatively charged particles with one unit of negative charge.
- Protons are positively charged particles with one unit of positive charge.
- Neutrons have no charge (neutral).
- Protons and neutrons are inside the nucleus and are called nucleons.
- The number of electrons outside the nucleus equals the number of protons inside, making the atom neutral.
- Atomic number (Z): The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
- Mass number (A): The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
Molecules
A molecule is the tiniest unit of an element or compound, made up of a group of atoms. It is created when two or more atoms, either of the same element or different elements, join together.- A molecule is the smallest unit of an element or compound made of two or more atoms.
- Molecules form when atoms of the same or different elements combine.
- Examples: Water (H₂O) has one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms; Nitrogen (N₂) has two nitrogen atoms.
Molecule of an Element
- Formed when atoms of the same element join together.
- Example: Two hydrogen atoms form a hydrogen molecule (H₂).
- Hydrogen or oxygen atoms cannot exist alone; they form molecules like H₂ or O₂.
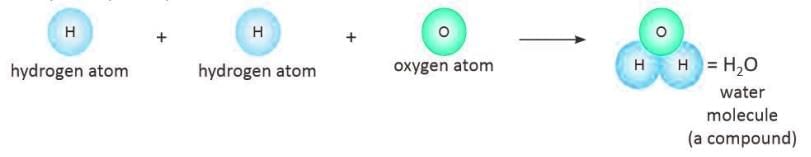
Molecule of a Compound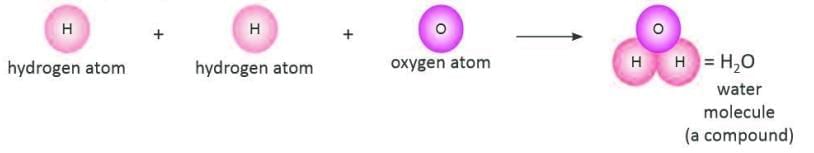 Formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed proportion by mass.
Formed when atoms of different elements combine in a fixed proportion by mass.
- Example: Two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom form a water molecule (H₂O).
- Example: One sodium atom and one chlorine atom form sodium chloride (NaCl).
Compounds can be broken into their elements, e.g., passing electricity through acidulated water splits it into hydrogen and oxygen gases.

What Happens When Two Atoms Combine
- When atoms get close, they form a molecule by sharing or transferring electrons.
- This forms a chemical bond that holds the atoms together.
- Example: Sodium (Na) gives an electron to chlorine (Cl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl).
Atomicity
- Atomicity is the number of atoms in a molecule of an element.
- Monoatomic molecules: Have one atom (e.g., Sodium - Na, Zinc - Zn, Magnesium - Mg).
- Diatomic molecules: Have two atoms (e.g., Hydrogen - H₂, Oxygen - O₂, Nitrogen - N₂).
- Triatomic molecules: Have three atoms (e.g., Ozone - O₃).
- Polyatomic molecules: Have more than three atoms (e.g., Phosphorus - P₄, Sulphur - S₈).
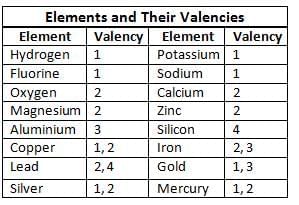
Valency
- Valency is the ability of an element to combine with another by donating or accepting electrons.
- It is always a whole number.
- Valency helps in writing chemical formulas of compounds.
- Monovalent: Elements with valency 1 (e.g., Hydrogen, Sodium).
- Divalent: Elements with valency 2 (e.g., Oxygen, Magnesium).
- Trivalent: Elements with valency 3 (e.g., Aluminium).
- Tetravalent: Elements with valency 4 (e.g., Silicon).
- Some elements like iron, copper, lead, mercury, and tin have variable valencies (e.g., Copper: 1 or 2).
- Noble gases (e.g., Helium, Neon) have a valency of 0.
- Valency can be found by the number of hydrogen atoms an element combines with or replaces in a compound.
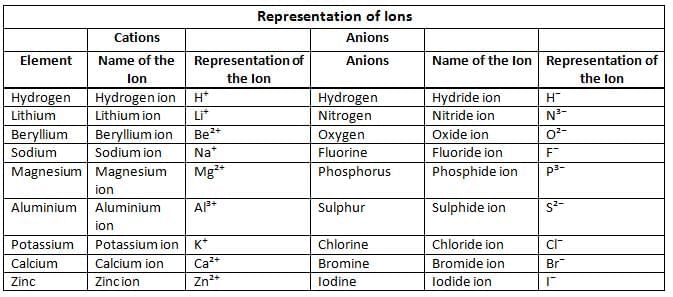
Ions
- An ion is a particle with a positive or negative charge.
- Cation: A positively charged ion formed by losing electrons (e.g., Sodium ion - Na⁺).
- Anion: A negatively charged ion formed by gaining electrons (e.g., Chloride ion - Cl⁻).
Radicals
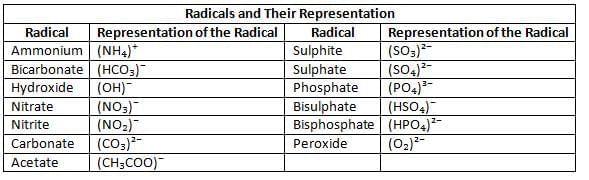
- A radical is a group of atoms of different elements that act as a single unit and carry a charge.
- Radicals cannot exist independently and combine with other radicals or elements.
- Example: Potassium nitrate (KNO₃) is made of potassium (K⁺) and nitrate (NO₃⁻) radicals.
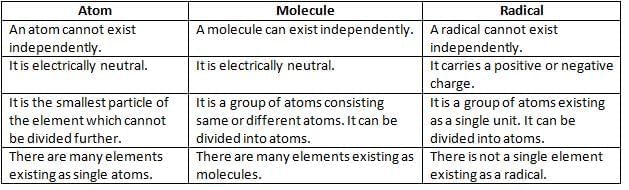
Differences between Atoms, Molecules, and Radicals
Periodic Table
- The periodic table arranges elements in order of increasing atomic numbers in a table format.
- There are 118 known elements in the periodic table.
- Elements with similar properties are placed in the same column.
- The table has 18 vertical columns called groups (numbered 1 to 18) and 7 horizontal rows called periods.
- Elements in the same group have the same valency and similar properties.
- Example: Sodium and potassium in group 1 both have valency 1.
- Valency of an element can be found using its group number in the periodic table.
- The first 20 elements are arranged in the periodic table as shown in Figure 4.2.
Know Your Scientist (Dmitri Mendeleev)
- Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, a Russian chemist, created the periodic table.
- He formulated the Periodic Law and predicted properties of undiscovered elements.
- He also corrected the properties of some known elements using the periodic table.
Writing the Chemical Formula of a Compound
- A chemical formula shows the number of atoms of each element in a molecule of a compound.
- To write a chemical formula, you need to know the symbols and valencies of the elements or radicals in the compound.
Rules for writing a chemical formula
- Write the symbols of the elements or radicals in the compound.
- Write the valency of each element or radical.
- Swap the valency numbers and write them as subscripts (ignore + and - signs).
- If the valencies can be divided by a common number, simplify the formula.
For Example: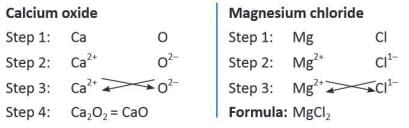
Significance of a Chemical Formula
- A chemical formula tells us:
- The name of the compound.
- It represents one molecule of the compound.
- The elements or ions present in the compound.
- The number of each element or ion in one molecule of the compound.
- The molecular mass (total mass of all atoms in the molecule) can be calculated using the formula.
- Example: Water (H₂O):
- Elements are hydrogen and oxygen.
- One molecule has two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Molecular mass is found by adding the masses of all atoms in the molecule.
Glossary
- Atom: The smallest particle of matter that cannot be divided.
- Molecule: The smallest unit of an element or compound made of a group of atoms.
- Molecule of an element: Atoms of the same element joined together.
- Molecule of a compound: Atoms of different elements combined in a fixed proportion by mass.
- Atomicity: The number of atoms in a molecule of an element.
- Valency: The ability of an element to combine with another.
- Monovalent: Elements with valency 1.
- Divalent: Elements with valency 2.
- Trivalent: Elements with valency 3.
- Tetravalent: Elements with valency 4.
- Variable valency: Elements like iron, copper, lead, and mercury that have more than one valency.
- Ion: A particle with a positive or negative charge.
- Cation: A positively charged ion.
- Anion: A negatively charged ion.
- Radical: A group of atoms acting as a single unit with a charge.
- Periodic table: A table arranging elements by increasing atomic numbers.
- Chemical formula: A formula showing the number of atoms of each element in a compound.
Points To Remember
- An atom is the smallest particle of matter that cannot exist alone and combines with other atoms or molecules.
- A molecule forms when two or more atoms of the same or different elements combine.
- Atoms combine in whole numbers to form a molecule.
- Molecules are of two types: molecule of an element and molecule of a compound.
- Molecule of an element: Atoms of the same element join together.
- Molecule of a compound: Atoms of different elements combine in a fixed proportion by mass.
- Atomicity: Number of atoms in a molecule (monoatomic, diatomic, triatomic, polyatomic).
- Valency: Ability of an element to combine, always a whole number, used to write chemical formulas.
- Monovalent (valency 1), Divalent (valency 2), Trivalent (valency 3), Tetravalent (valency 4).
- Some elements like iron and copper have variable valencies.
- Ion: A charged particle, either a cation (positive) or anion (negative).
- Radical: A group of atoms acting as a single unit with a charge, cannot exist alone.
The document Atoms Structure Chapter Notes | Chemistry Class 7 ICSE is a part of the Class 7 Course Chemistry Class 7 ICSE.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
33 videos|58 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Atoms Structure Chapter Notes - Chemistry Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What are atoms and how do they differ from molecules? |  |
Ans. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, consisting of a nucleus made up of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. Molecules, on the other hand, are formed when two or more atoms bond together. The key difference is that atoms are single units, while molecules are combinations of two or more atoms, which can be the same or different elements.
| 2. What is atomicity and how is it determined? |  |
Ans. Atomicity refers to the number of atoms present in a molecule. It can be determined by observing the types of elements that combine to form the molecule. For example, a diatomic molecule like oxygen (O2) has an atomicity of 2, while a triatomic molecule like water (H2O) has an atomicity of 3.
| 3. What is valency and why is it important in chemistry? |  |
Ans. Valency is the measure of the ability of an atom to combine with other atoms, determined by the number of electrons in its outer shell. It is important because it helps predict how atoms will bond with one another to form molecules, thus influencing the chemical behavior and properties of substances.
| 4. What are ions and how do they form? |  |
Ans. Ions are charged particles that form when atoms gain or lose electrons. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positively charged ion (cation), while gaining electrons results in a negatively charged ion (anion). This charge difference is crucial in chemical reactions and the formation of compounds.
| 5. What are radicals and how do they differ from regular molecules? |  |
Ans. Radicals are molecules that contain an unpaired electron, making them highly reactive. Unlike regular molecules, which have all electron pairs filled, radicals can readily participate in chemical reactions to seek stability. This difference in electron configuration is what sets radicals apart from stable molecules.
Related Searches





















