Aids To Health Chapter Notes | Biology Class 10 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
"Aids to Health" explores the various natural and artificial methods to protect the human body from diseases, emphasizing the importance of personal hygiene and community efforts in maintaining health. It covers the body's defense mechanisms, including immunity, and the role of vaccinations, antitoxins, antiseptics, disinfectants, and antibiotics in preventing and treating infections. This knowledge is essential for leading a healthy life and understanding how to combat disease-causing germs effectively.
Need to Keep Healthy
- Staying healthy requires personal and community efforts to prevent diseases.
- Personal care includes regular bathing, brushing teeth, exercising, eating a balanced diet, and getting adequate rest.
- Community efforts involve keeping surroundings clean by avoiding garbage accumulation and stagnant water to prevent the growth of disease-spreading insects and pests.
- World Health Day, celebrated on April 7, promotes awareness about maintaining health at all levels.
Immunity
Immunity refers to the body’s ability to defend itself against diseases. Harmful substances, such as pollutants (toxic chemicals) and germs, constantly threaten the body and can enter through four main routes:
- Directly through the skin.
- Via mucous membranes in the eyes, nose, urinary, or genital tracts.
- Through consumed food or water.
- Through inhaled air.
The body’s defense mechanism operates in two ways: it prevents the entry of these harmful agents and, if they do enter, it neutralizes them to prevent harm.
Defense System Levels:
A. Local Defense System (Preventing Entry of Germs): This acts as a barrier to block germs at entry points and includes:
- Protective mechanical barriers (e.g., skin).
- Expulsion of germs (e.g., coughing or sneezing to remove them).
- Germ-killing secretions (e.g., mucus or enzymes).
- Germ-fighting white blood cells (WBCs).
B. Immune System: This system combats germs that have entered body tissues, neutralizing or eliminating them to prevent disease.
Local Defence System
- The local defense system prevents germs from entering the body through various barriers and mechanisms.
- It includes protective mechanical barriers, germ expulsion, germ-killing secretions, and germ-fighting white blood cells (WBCs).
Protective Mechanical Barriers:
- Skin: The outer tough layer made of keratin protein is nearly impermeable to germs. Germs settle on the skin through air or contact but are removed by washing with soap and water. Cuts or scratches allow germ entry, which blood clotting helps prevent.
- Hairs: Hairs on the skin and in nostrils trap dust and germs, preventing their entry.
- Mucus: Slimy mucus in the nasal passages and windpipe traps bacteria. Cilia in the windpipe move mucus with trapped germs out of the body.
Thrown Out, If Entered:
- Coughing, sneezing, vomiting, and diarrhea expel germs or foreign objects from the respiratory and digestive systems.
Germ-Killing Secretions:
- Saliva, sweat, tears, and nasal secretions contain substances that kill germs.
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) in the stomach destroys germs entering with food.
Germ-Fighting White Blood Cells (WBCs):
- Phagocytes (WBCs) move out of blood capillaries (diapedesis) and engulf germs (phagocytosis), destroying them.
- Pus in a wound consists of destroyed germs, dead WBCs, and damaged tissue cells.
Merits of Local Defence Systems
- Act instantly to block germs.
- Work without prior exposure to infections.
- Effective against a wide range of infectious agents.
Immune System
- The immune system fights germs or their toxins that enter deeper body tissues through special entry mechanisms or breaches in barriers.
- It uses antibodies (special proteins) to neutralize germs and antitoxins to counteract their poisons, providing immunity.
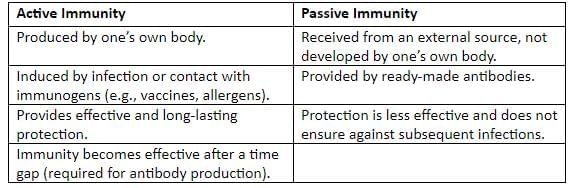
- Immunity is the body’s ability to resist diseases after infection by harmful germs or to render foreign substances (bacteria, viruses, toxins) harmless.
Kinds of Immunity
Innate Immunity (Natural/Native):
- Present due to genetic makeup, without external stimulation or prior infection.
- Non-specific Innate Immunity: General resistance to all infections (e.g., humans are immune to certain plant or animal diseases).
- Specific Innate Immunity: Resistance to specific germs (e.g., humans are immune to dog distemper, a disease fatal to 50% of infected dogs).
Acquired Immunity:
- Developed during a person’s lifetime through infection or external sources.
Actively Acquired Immunity:
- Developed due to previous infection (naturally acquired active immunity, e.g., immunity to measles after one infection) or artificial introduction of antigens via vaccines (artificially acquired active immunity).
- Lymphocytes produce antibodies that circulate in blood and lymph to kill germs or killer cells that attack specific antigens on germs.
- Long-lasting due to memory lymphocytes.
Passively Acquired Immunity:
- Provided by ready-made antibodies from external sources, not produced by the individual’s body.
- Naturally Acquired Passive Immunity: Mother’s antibodies transferred to the fetus via the placenta.
- Artificially Acquired Passive Immunity: Antibodies from animals (e.g., horses) injected into patients, such as antivenin for snake bites or anti-diphtheria injections. Institutions like Haffkine’s Institute (Bombay) and Kasauli prepare such antisera.
Antibodies
Antibodies are specialized chemicals in the blood that combat germs or their secretions. Their key characteristics include:
- Nature: Antibodies are proteins, specifically immunoglobulins.
- Production: They are produced by specialized lymphocytes (found in lymph nodes, spleen, blood, and lymph) when exposed to antigens (chemicals on germ cells).
- Variety: The body can produce an unlimited range of antibodies.
- Specificity: Each antibody targets a specific antigen, neutralizing only that particular type.
- Function: Antibodies recognize and bind to their specific antigen, rendering it harmless. The bound antigen is then destroyed and eliminated by the body.
- Innate Presence: Some individuals are born with certain antibodies, providing natural immunity against specific diseases, even if germs bypass initial defenses like barriers or phagocytic white blood cells.
- Duration of Immunity: Antibody-mediated immunity may be short-term (e.g., for common cold or cholera) or long-term (e.g., for smallpox or measles).
Differences Between Active and Passive Immunity:
Vaccination And Immunisation
- Vaccination involves introducing dead or weakened germs or their substances into the body to build resistance against specific diseases (prophylaxis).
- Vaccines, injected or taken orally (e.g., polio drops), stimulate WBCs to produce antibodies against specific diseases.
- Immunisation is the process of developing resistance to disease-causing germs or toxins by introducing killed germs or substances to produce antibodies.
Four Categories of Vaccines:
- Killed germs: TAB vaccine (typhoid), Salk’s vaccine (polio), rabies vaccine.
- Living weakened germs: Measles vaccine, BCG vaccine (tuberculosis).
- Living fully poisonous germs: Cowpox virus vaccine for smallpox (no longer used as smallpox is eradicated).
- Toxoids: Inactivated bacterial toxins (e.g., diphtheria, tetanus) treated with formalin to retain antibody-producing ability.
National Immunisation Schedule:
- 3–12 months: DTP (3 doses, 4–6 weeks apart), Polio (oral, 3 doses, 4–6 weeks apart), BCG (intradermal).
- 9–15 months: Measles vaccine (1 dose).
- 18–24 months: DTP booster, Polio booster.
- 5–6 years: DT (diphtheria, tetanus) booster, Typhoid (TAB) vaccine (2 doses, 1–2 months apart).
- 10 years: Tetanus toxoid booster, Typhoid vaccine booster.
- 16 years: Tetanus toxoid booster.
- Mothers (during pregnancy):
- Previously immunised: One tetanus toxoid booster 4 weeks before delivery.
- Non-immunised: Two tetanus toxoid doses (first: 16–24 weeks, second: 24–32 weeks of pregnancy).
Abbreviations:
- DTP: Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (whooping cough).
- DT: Diphtheria, Tetanus.
- BCG: Bacillus of Calmette and Guerin (tuberculosis).
Antitoxins (Antibodies)
- Toxins are poisonous substances produced by animals, plants, or bacteria (e.g., snake venom, bacterial toxins).
- Antitoxins (now called antibodies) are blood serum proteins produced in response to toxins or antigens.
- For diseases like diphtheria, pre-prepared antibodies from animals (e.g., horses, rabbits) are injected for passive immunisation.
- Antisera, such as antivenin for snake bites, are prepared at institutes like Haffkine’s Institute (Bombay) and Kasauli.
Antiseptics And Disinfectants
Antiseptics
- Antiseptics are mild chemicals applied to the body to kill germs without harming the skin.
- Examples: Lysol, carbolic acid, iodine, benzoic acid, mercurochrome, boric acid, antibiotic creams.
- Caution: Avoid using commercial names (e.g., Dettol, Savlon) in exams; mention active ingredients instead.
Disinfectants
- Disinfectants are strong chemicals applied to surfaces where germs thrive, not safe for human skin.
- Examples: Cresol, phenol, lysol, 40% formalin, lime, Bordeaux mixture, DDT.
- Physical disinfectants like strong heat and boiling also kill germs.
- Deodorants are neither antiseptics nor disinfectants; they only mask bad smells.
Differences Between Antiseptics and Disinfectants:
- Antiseptics: Mild, safe for skin, applied on body (e.g., iodine).
- Disinfectants: Strong, harmful to skin, applied on surfaces (e.g., phenol).
Antibiotics - Penicillin And Others
Antibiotics are chemicals produced by microorganisms (e.g., fungi, bacteria) that kill or inhibit other microorganisms.
Discovery of Penicillin:
- Discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928 from Penicillium notatum mould, which inhibited Staphylococcus bacteria growth.
- Named penicillin in 1929, first used on humans in the 1940s, effective against infections like gonorrhea.
- Commercial penicillin is produced from Penicillium chrysogenum or synthetically.
Other Antibiotics:
- Streptomycin (from Streptomyces bacterium), chloromycetin, aureomycin, ampicillin.
- Many antibiotics are now synthetically produced.
How Antibiotics Work:
- Penicillin: Prevents bacterial cell wall formation, stopping growth and multiplication.
- Streptomycin: Binds to bacterial ribosomes, preventing protein synthesis, halting bacterial growth.
Uses of Antibiotics:
- Treat infections in medicine.
- Preserve fresh meat and fish.
- Prevent infections in animal feed.
- Control plant pathogens.
Sulphonamide Group Of Medicines
- Since ancient times, humans have sought new medicines to treat diseases, experimenting with various plant and animal products, many of which were effective. They also tested different chemical substances, some of which produced positive results, leading to the development of chemotherapy, a treatment method using chemicals.
- In 1910, a drug called Salvarsan, derived from an arsenic compound, was introduced. It was effective against syphilis and sleeping sickness germs but often proved toxic to patients.
- In the 1930s, a class of chemicals called sulphonamides was discovered, proving effective against many bacterial infections. Examples include sulphadiazine and sulphanilamide, synthetic drugs that disrupt bacterial metabolism, killing the bacteria. Today, sulphonamides are rarely used alone and are typically combined with antibiotics for specific conditions.
|
55 videos|189 docs|21 tests
|
FAQs on Aids To Health Chapter Notes - Biology Class 10 ICSE
| 1. What is the importance of maintaining good health and how does it relate to immunity? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between vaccination and immunization? |  |
| 3. How do antitoxins work in the body? |  |
| 4. What role do antiseptics and disinfectants play in maintaining health? |  |
| 5. What are antibiotics, and how did penicillin change medicine? |  |
















