Energy Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Energy and Work and Their Units |

|
| Various forms of energy and their interconversion |

|
| Points To Remember |

|
| Glossary |

|
Introduction
Energy is the ability to do work, and it is very important for all living things. We need energy to do our daily activities like playing, running, studying, and even resting. This chapter will teach us what energy is, how it helps us do work, the different types of energy, and how energy can change from one form to another. We will also learn about a special rule called the law of conservation of energy, which tells us that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed.
Energy and Work and Their Units
Energy and Work and Their Relation
- All living things need energy to do their daily tasks so they can live.
- Some activities like playing, cycling, and moving heavy things need a lot of energy.
- Other activities like reading, singing, and writing need less energy.
- Some things our body makes, like heat, also need energy.
- When we do heavy tasks, we use energy from animals like bullocks for plowing fields, horses for pulling carts, and camels for carrying things.
- If animals cannot do the work, we use machines that run on petrol, diesel, coal, or electricity to do heavy work.
- The ability to do work is called energy.
- We use the word "energy" a lot in our daily life, but in science, it has a special meaning.
- Here are some examples to understand energy:
- When a raised hammer hits a nail into a piece of wood, it does work by pushing the nail inside the wood.
- When a striker hits a carrom coin on a board, it makes the coin move, which is also work.
- When a child winds up a toy car and places it on the floor, the toy car moves because it has the ability to do work, which means it has energy.
- Here are some examples to understand energy:
- Any object that can do work has energy.
- When an object does work, it loses energy, and when an object gains energy, it can do work.
- So, energy is the ability of an object to do work.
- In simple words, the capacity of a body to do work is called energy.
- The total amount of work a body can do is the same as its energy.
- A body with more energy can do more work because it can move faster or lift things higher.
- For example, if a body does 100 J of work to move from one place to another, its energy is 100 J.
- If a body does 100 J of work to lift something above the ground, its energy is also 100 J.
What Is Work?
- In daily life, work can mean many things, like a teacher teaching in class or students studying while sitting on benches.
- But in physics, work is done only when a body moves because of a force.
- When you read, write, or sing, you are doing mental work, not physical work.
- When a girl cycles, she does physical work because her body moves.
- When a worker carries bricks, he does physical work because the bricks move.
- When a car or train moves, it does mechanical work because it moves.
- But if you push a wall with all your force and it doesn’t move, no work is done because there is no movement.
- If you push a table and it moves, then work is done because the table moved.
Factors Determining Work
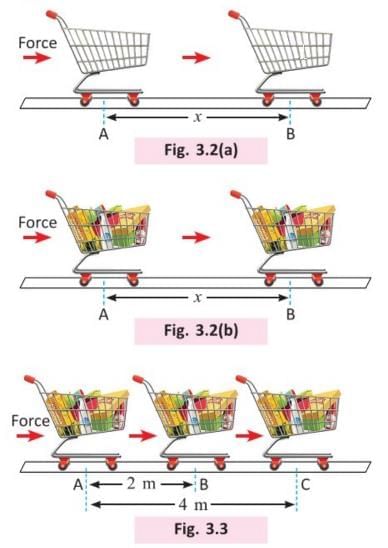
- Let’s say you are pushing a trolley from position A to position B through a distance x with some force.
- Some work is done because the trolley moved.
- Now, if the trolley is filled with luggage and moved the same distance x from A to B, more force is needed, so more work is done.
- Work done by a body depends on the force applied and the distance the body moves.
- Let’s take another example: a trolley filled with luggage is moved from A to B by some force, a distance of 2 meters.
- Now, if the same trolley is moved a longer distance, say 4 meters, with the same force, the work done will be double because the distance is double.
- So, we can say that the more the distance a body moves, the more work is done.
- In science, work is the product of force and the distance through which the force acts.
- The formula for work is: W = F × S
- Here, W is work, F is force, and S is the displacement (distance moved in the direction of the force).
- If there is no movement, even if force is applied, the work done is zero.
- So, W = F × 0 = 0 (if there is no displacement).
- If the force is applied at right angles to the direction of movement, the work done is also zero.
- For example, if you carry a heavy bag on your shoulders and stand still, the weight of the bag acts downward, but you are not moving up or down, so no work is done in the direction of the force.
- But if you start walking on flat ground with the bag on your shoulders, the displacement is sideways, not in the direction of the force (which is downward), so no work is done in the direction of the force.
Note:
- In physics, energy is measured in joules, not calories, even though both units are related to energy.
- In physics, 1 g of water needs 1 calorie of heat to raise its temperature by 1°C.
- 1 calorie is equal to 4.2 joules.
- 1 kilocalorie is equal to 4200 joules.
Units of Work
- In the SI system, the unit of work is joule.
- When a force of 1 newton causes a displacement of 1 meter in its own direction, the work done is said to be 1 joule.
So, 1 J = 1 N × 1 m. - 1 joule is the work done when a force of 1 newton moves a body 1 meter in the direction of the force.
- Another unit of energy is calorie, which is used to measure heat energy.
- 1 calorie is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1°C.
- A bigger unit is kilocalorie, which is used to measure the heat energy of a body.
- 1 kilocalorie is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1000 grams (1 kg) of water by 1°C.
So, 1 kilocalorie = 1000 calories.
Various forms of energy and their interconversion
Forms of energy
Energy can be of many types depending on how it is used or stored.
1. Mechanical energy: Mechanical energy is the energy a body has because of its movement or position.
It is of two types:
(a) Potential Energy:
- This is the energy a body has because of its position or shape.
- Examples:
- When you lift a brick to the top of a building, it gains potential energy due to its height.
- When you pull the string of a bow with an arrow, the bow's shape changes and stores potential energy.
(b) Kinetic Energy:
- This is the energy a body has because of its motion.
- The kinetic energy depends on the mass and speed of the body.
- Examples:
- A fast-moving water stream can turn the blades of a water mill.
- A moving bat can hit a cricket ball far.
- A speeding train, a flying airplane, and flowing water all have kinetic energy because they are moving.
2. Heat energy
- Heat energy is produced when we burn fuels like wood, coal, or gas.
- We call this heat energy steam power when it heats water to make steam.
- Example: In a pressure cooker, gas burns to produce heat, which turns water into steam and lifts the cooker's weight.
- Heat energy can do work, like cooking food or moving a train.
- Fact: In 1765, James Watt, a scientist, noticed that heat energy from steam could move a train engine.
- Heat energy from burning coal turns water into steam, which moves turbines to make electricity.
- Vehicles like cars, trucks, and trains use heat energy from burning fuels like diesel, petrol, or CNG to move.
- Our body also uses heat energy from food to do work, like walking or running.
3. Light energy
- Light energy is the energy that helps us see things around us.
- Light does not move objects because it is a very weak form of energy.
- Light energy can make tiny dust particles move, showing that it can do work.
4. Sound energy
- Sound energy is the energy produced by vibrating objects.
- Sound is weak and cannot move objects, but it can make things vibrate.
- Example: When a metro train moves, its sound makes the ear membrane vibrate, and we hear the noise.
- Sound can do work, like shaking buildings when a supersonic plane breaks the sound barrier.
- Thunder from clouds also shakes buildings, showing sound can do work.
5. Electric energy
- Electric energy is very important in our daily life.
- It is used to run ceiling fans, table fans, juicers, and grinders by making their motors spin.
- Electric energy powers heavy machines, metro trains, and mopeds.
- It is used in heating devices like heaters, geysers, and electric stoves.
- Electric energy lights up bulbs, tube lights, and CFLs.
6. Magnetic energy
- A magnet, like iron or nickel, can attract magnetic objects.
- This ability to attract or move things is called magnetic energy.
- Example: Cranes use magnets to lift heavy iron loads or separate iron scrap from waste.
- Magnetic energy is used in electric motors, generators, microphones, and electric tubes.
7. Chemical energy
- Chemical energy is the energy stored in fuels like coal, oil, gas, diesel, petrol, or CNG.
- This energy helps vehicles like cars, trucks, buses, or trains move.
- Chemical energy in food helps our body do work.
- Chemical energy is a hidden energy released as heat when substances change.
- Example: When we eat food, its chemical energy turns into heat energy to keep us warm.
- Batteries and electric cells also store chemical energy, which turns into electric energy.
8. Nuclear energy
- Nuclear energy comes from the nucleus of an atom, made of protons and neutrons.
- It is released when a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter ones or two light nuclei combine into one.
- Nuclear energy is released as heat and light.
- It can be used for good things, like producing electricity in nuclear power stations.
- It can also be harmful, like in atom bombs or hydrogen bombs, which cause huge damage in wars.
- In nuclear power stations, nuclear energy heats water to make steam, which runs turbines to produce electricity.
Inter-conversion of energy
Energy can change from one form to another. This is called inter-conversion of energy.
- Mechanical energy into heat, light, and sound energy
- When you rub your hands, mechanical energy changes into heat energy due to friction.
- When you hit two stones together, mechanical energy changes into heat, light, and sound energy.
- When a knife blade is sharpened on a rotating grinding stone, mechanical energy changes into heat, light, and sound energy.
- When brakes are applied to a moving car or machine, mechanical energy changes into heat and sound energy due to friction.
- Mechanical energy into potential energy and kinetic energy
- When you wind a watch, the mechanical energy of your hand changes into potential energy of the spring inside the watch.
- The potential energy of the spring then changes into kinetic energy to move the watch hands.
- When an arrow is pulled in a bow, the mechanical energy changes into potential energy of the bowstring.
- When the arrow is released, the potential energy of the string changes into kinetic energy of the arrow.
- Potential energy of water in hydroelectric dams into electric energy
- In hydroelectric dams, water stored in a reservoir has potential energy.
- When the water is released through a chute, its potential energy changes into kinetic energy.
- The kinetic energy of the flowing water turns the blades of a turbine and dynamo.
- The dynamo then converts this energy into electric energy.
- Chemical energy into light energy
- When a torch is switched on, the chemical energy in its cells changes into electric energy.
- The electric energy then passes through the bulb and changes into heat and light energy.
- Electric energy into heat energy
- When electric energy passes through devices like heaters, hot plates, geysers, toasters, or electric irons, it changes into heat energy.
- This happens because of the resistance in the heating element.
- Heat energy into electric energy
- In thermal power stations, coal or natural gas is burned to produce heat energy.
- This heat energy turns water into steam, which gains kinetic energy.
- The steam then spins the turbine and dynamo, converting the kinetic energy into electric energy.
- Electric energy into magnetic energy
- In devices like electromagnets, relays, and solenoids, electric energy passes through an insulated copper coil.
- This electric energy then changes into magnetic energy.
- Electric energy into light energy
- In lighting devices like fluorescent lights (CFL), tube lights, and compact bulbs, electric energy changes into heat energy first.
- The heat energy then changes into light energy.
- Light energy into electric energy
- In photovoltaic cells (solar panels), the light energy from the Sun is directly converted into electric energy.
- Solar panels are used all over the world to harness the light energy of the Sun.
- Sound energy into electric energy: When we speak into a microphone, the sound energy changes into varying electrical impulses.
- Electric energy into sound energy: When varying electrical impulses pass through a speaker, radio, or audio system, they change into sound energy.
- Chemical energy into mechanical energy
- The chemical energy in fuels like petroleum, natural gas, or diesel changes into heat energy when burned.
- This heat energy then changes into kinetic energy to move vehicles.
- Electric energy into chemical energy: During the charging of lead-acid batteries, electric energy changes into chemical energy.
- Light energy into chemical energy: During photosynthesis in plants, light energy changes into chemical energy stored in carbohydrates.
Sun: The ultimate source of energy
All forms of energy on Earth come from the Sun, either directly or indirectly. The Earth gets more energy from the Sun in one year than all countries use together.
- Solar energy provides the wind energy, tidal energy, and energy of seawaves
- The Sun's heat causes winds to blow, which gives wind energy.
- The Sun's heat also causes tides and waves in the sea, giving tidal energy and seawave energy.
- Solar energy causes large scale evaporation of water
- The Sun's heat evaporates water from oceans, rivers, and lakes to form clouds.
- Clouds bring rain, which fills dams and rivers with water.
- This water is used in hydroelectric power plants to make electricity.
- The Sun's light energy is stored in plants during photosynthesis as chemical energy.
- Plants turn this light energy into chemical energy, which forms fossil fuels like coal over millions of years.
- When fossil fuels like coal are burned, their chemical energy turns into heat energy for work.
- If plants are not used as fossil fuels, their chemical energy can turn into biogas when they decay.
- Biogas burns to produce heat energy.
- Animals eat plants, and the chemical energy in plants turns into heat energy during respiration.
- This heat energy helps animals stay warm and do activities.
- When animals die, their bodies turn into petroleum and natural gas over millions of years.
- Petroleum and natural gas are used as fuels to produce heat energy for industries.
- Solar energy provides light energy: The Sun's light energy helps us see things around us.
Law of conservation of energy
- The law of conservation of energy says that energy cannot be created or destroyed.
- Energy only changes from one form to another.
- The total energy in a system always stays the same.
- Example: In a hydroelectric dam, the potential energy of stored water changes into kinetic energy when released.
- The kinetic energy of water turns the turbine and dynamo to produce electric energy.
- Some energy is used to move the turbine and dynamo, but some energy is wasted as heat.
- Not all energy can be converted into the desired form; some energy is always wasted.
- This wasted energy does not disappear; it changes into other forms like heat or sound.
- In any energy conversion, the best efficiency is about 80%, meaning some energy is always lost as waste.
- Example: In our body, about 3/4th of the chemical energy from food keeps us warm, and the rest is used for activities.
Points To Remember
- Work done is the product of force and the distance through which force acts.
- Unit of work or energy is joule (J).
- Energy can exist in various forms, such as mechanical energy, heat energy, light energy, sound energy, magnetic energy, electric energy, nuclear energy, muscular energy, etc.
- According to the law of conservation of energy, energy can neither be created nor be destroyed and the sum total of energy in the universe remains constant.
- Sun is the ultimate source of energy. All kinds of energy on Earth have come from the Sun directly or indirectly.
Glossary
- Work: When a force causes displacement in its own direction.
- Energy: Ability to do work.
- Potential Energy: The energy possessed by a body on account of its position or configuration.
- Kinetic Energy: The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion.
- Heat Energy: The energy released when we burn fuel like coal, oil, or gas. Light Energy: A form of energy in presence of which other objects are seen.
- Sound Energy: The energy possessed by a vibrating body.
- Magnetic Energy: A form of energy which is capable of causing motion in the magnetic substances like iron, steel, etc.
- Chemical Energy: A kind of hidden energy in the atoms of elements or compounds.
- Nuclear Energy: The energy holding the nuclear particles (protons and neutrons) within the nucleus of an atom.
|
28 videos|152 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Energy Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 4
| 1. What are the different forms of energy? |  |
| 2. How does energy inter-convert between different forms? |  |
| 3. Why is the sun considered the ultimate source of energy? |  |
| 4. What is the law of conservation of energy? |  |
| 5. How is work related to energy? |  |




















