Important Exam Questions: The Story of Village Palampur | Social Studies (SST) Class 9 PDF Download
Q1: What are the four factors of production required for farming in Palampur?
 View Answer
View Answer 
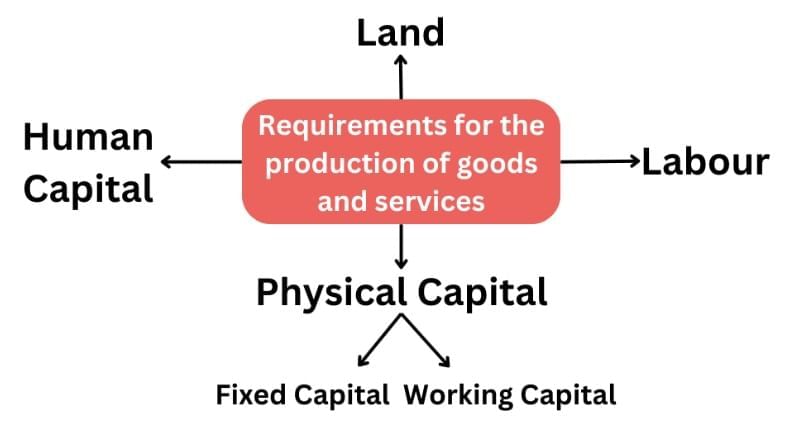
Answer: The four factors of production are:
- Land: Natural resources like soil and water.
- Labour: Workers, including skilled and manual labourers.
- Physical Capital: Fixed (e.g., tools, machines) and working capital (e.g., raw materials, cash).
- Human Capital: Knowledge and enterprise to combine the other factors effectively.
Q2: Assertion: Land is a fixed resource in Palampur.
Reason: No new land has been brought under cultivation since 1960, as all wastelands were converted by then.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Assertion: The Green Revolution increased crop production in Palampur but harmed soil fertility.
Q3: Why is land considered a fixed resource in Palampur?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Land is fixed in Palampur because there has been no increase in cultivable land since 1960, as all wastelands were converted by then, and no further land is available for expansion.
Q4: What is the main reason for the depletion of soil fertility in Palampur?
a) Use of traditional seeds
b) Overuse of chemical fertilizers
c) Lack of irrigation
d) Small landholdings
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: b) Overuse of chemical fertilizers
Q5: How has electricity transformed farming in Palampur?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Electricity has transformed farming by powering tube wells, replacing traditional Persian wheels. This enables efficient irrigation, allowing farmers to cultivate multiple crops annually and increase yields.
Q6: What is the Green Revolution, and how has it impacted Palampur?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: The Green Revolution refers to the significant increase in food grain production since the 1960s due to high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds, irrigation, and chemical fertilizers. In Palampur, it enabled farmers to grow three crops a year, but overuse of fertilizers has led to soil fertility loss.
Q7: Who provides labour for medium and large farmers in Palampur, and how are they paid?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Labour is provided by landless families or those with small plots. They are paid in cash, crops, or meals, with wages varying by region, crop, activity (e.g., sowing, harvesting), and duration (daily or yearly).
Q8: Explain how land is distributed among farmers in Palampur and its impact on their economic status.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: In Palampur, about one-third (150) of 450 families are landless, primarily Dalits. Of the remaining, 240 families own small plots (<2 hectares), and 60 families are medium or large farmers (>2 hectares, some >10 hectares).
Impact on Economic Status
- Landless Families: Rely on wages as farm labourers, earning low and variable income, leading to economic instability.
- Small Farmers: Cultivate their own land with family labour but have limited surplus due to small production, restricting their income.
- Medium and Large Farmers: Produce significant surplus, sell it in markets, and save earnings for capital, enabling investments in equipment, cattle, or businesses, improving their economic status.
Q9: Discuss the methods used to increase agricultural production on the same land in Palampur.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: In Palampur, farmers increase production on fixed land through:
- Multiple Cropping: Growing more than one crop annually on the same land, e.g., jowar and bajra (Kharif), potatoes (October–December), and wheat (Rabi).
- Modern Farming Methods: Using high-yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and improved irrigation (electric tube wells).
- Electricity: Powers tube wells, enabling efficient irrigation for multiple crops.
- Impact: These methods have increased yields, as seen in the Green Revolution, but overuse of fertilizers has depleted soil fertility, raising cultivation costs.
- Example: Farmers like Tejpal Singh use surplus earnings to invest in modern equipment, further boosting production.
Q10: What is the primary source of income in Palampur?
a) Dairy
b) Farming
c) Small-scale manufacturing
d) Transport
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: b) Farming
Q11: Evaluate the impact of the Green Revolution on farming in Palampur, highlighting both benefits and challenges.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Benefits are:
- Increased Production: The Green Revolution introduced HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation, enabling Palampur farmers to grow three crops (e.g., wheat, potatoes) annually, achieving self-sufficiency in food grains.
- Multiple Cropping: Electricity-powered tube wells facilitated irrigation, supporting crops like jowar, bajra, and wheat.
- Economic Gains: Medium and large farmers sell surplus produce, earning income for savings and investments (e.g., Tejpal Singh’s tractor purchase).
Challenges are:
- Soil Degradation: Overuse of chemical fertilizers has reduced soil fertility, requiring more inputs and increasing costs.
- Groundwater Depletion: Continuous tube well irrigation has lowered the water table, threatening sustainability.
- Environmental Impact: Chemical fertilizers pollute water sources and kill soil microorganisms, reducing long-term soil health.
Q12: Describe the non-farming activities in Palampur and their contribution to the village economy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Non-farming activities in Palampur include:
- Dairy: Families raise buffaloes, feeding them jowar and bajra, and sell milk to Raiganj’s collection centres for transport to towns, providing regular income.
- Small-Scale Manufacturing: Less than 50 people engage in simple, home-based production using family labour, contributing to local employment.
- Shopkeeping: Traders buy goods (e.g., rice, wheat, soap) from city wholesale markets and sell them in village stores, meeting local needs.
- Transport: Vehicles like rickshaws, jeeps, and tractors transport goods and people between Palampur and Raiganj, generating income for drivers.
Contribution: These activities diversify income sources, reduce dependence on farming, and support economic growth by providing jobs and services, especially for landless families and small farmers.
Q13: Explain the role of capital in Palampur’s farming and how different farmers access it.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- Role of Capital: Capital is essential for farming, including fixed capital (e.g., tractors, tube wells) and working capital (e.g., seeds, fertilizers). It enables farmers to purchase inputs and improve productivity.
- Access to Capital: Access to capital determines productivity and economic status, with large farmers benefiting more due to their savings, while small farmers face financial strain.
- Small Farmers: Borrow from large farmers, moneylenders, or traders at high interest rates, often facing repayment difficulties due to low surplus.
- Medium and Large Farmers: Use savings from surplus produce sales to fund capital needs, such as buying equipment or setting up tube wells, ensuring financial stability.
- Example: Tejpal Singh uses earnings to buy another tractor and lend to others, while small farmers struggle with debt.

Q14: Assertion: The Green Revolution increased crop production in Palampur but harmed soil fertility.
Reason: Overuse of chemical fertilizers depleted soil nutrients and killed beneficial microorganisms.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Q15: Which of the following is an example of fixed capital in farming?
a) Raw materials
b) Cash in hand
c) Tractors
d) Fertilizers
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: c) Tractors
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Important Exam Questions: The Story of Village Palampur - Social Studies (SST) Class 9
| 1. What are the main economic activities in Village Palampur? |  |
| 2. How does irrigation impact agriculture in Palampur? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the transportation system in Village Palampur? |  |
| 4. How do the villagers of Palampur contribute to the local economy? |  |
| 5. What challenges do the farmers in Palampur face? |  |
















