Numbers 201 to 999 Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 2 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Counting numbers beyond 200 is like going on a fun adventure with numbers! In this chapter, we will explore how to read, write, and understand numbers from 201 to 999. We'll learn to break them down, compare them, and even arrange them in order, making numbers easy and exciting to work with!
Number Names
Number names for 3-digit numbers are written by stating the hundreds place first, followed by the tens and ones places together. Start with the word for the hundreds digit, add "hundred," and then write the name for the tens and ones as a two-digit number.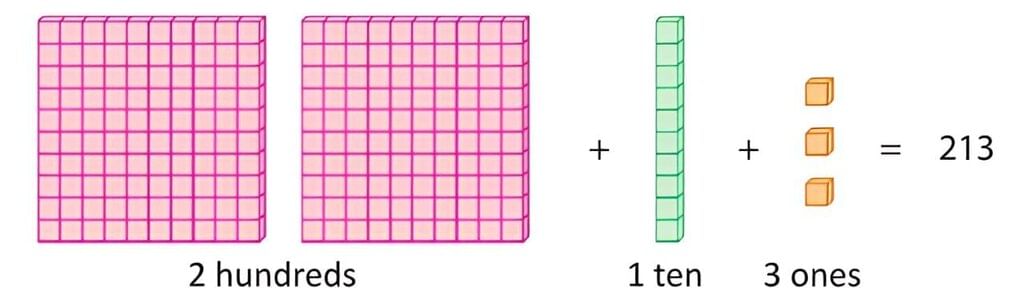
For example, to write 213:
- Step 1: Identify the hundreds digit (2), so write "two hundred."
- Step 2: Look at the tens and ones (13), which is "thirteen."
- Step 3: Combine them to get "two hundred thirteen."
Numbers from 201 to 300
These numbers start with 2 hundreds (200) and go up to 3 hundreds (300). Each number is formed by combining 2 hundreds with different tens and ones.
For example, to understand 265:
- Step 1: Recognise 2 hundreds (200).
- Step 2: Add 6 tens (60).
- Step 3: Add 5 ones (5).
- Step 4: Combine to get 265, written as "two hundred sixty-five."
Numbers from 301 to 400
These numbers start with 3 hundreds (300) and go up to 4 hundreds (400). They are formed by combining 3 hundreds with various tens and ones.
For example, to understand 357:
- Step 1: Start with 3 hundreds (300).
- Step 2: Add 5 tens (50).
- Step 3: Add 7 ones (7).
- Step 4: Combine to get 357, written as "three hundred fifty-seven."
Numbers from 401 to 500
These numbers start with 4 hundreds (400) and go up to 5 hundreds (500). They are formed by combining 4 hundreds with different tens and ones.
For example, to understand 444:
- Step 1: Start with 4 hundreds (400).
- Step 2: Add 4 tens (40).
- Step 3: Add 4 ones (4).
- Step 4: Combine to get 444, written as "four hundred forty-four."
Numbers from 501 to 600
These numbers start with 5 hundreds (500) and go up to 6 hundreds (600). They are formed by combining 5 hundreds with various tens and ones.
For example, to understand 543:
- Step 1: Start with 5 hundreds (500).
- Step 2: Add 4 tens (40).
- Step 3: Add 3 ones (3).
- Step 4: Combine to get 543, written as "five hundred forty-three."
Numbers from 601 to 700
These numbers start with 6 hundreds (600) and go up to 7 hundreds (700). They are formed by combining 6 hundreds with different tens and ones.
For example, to understand 636:
- Step 1: Start with 6 hundreds (600).
- Step 2: Add 3 tens (30).
- Step 3: Add 6 ones (6).
- Step 4: Combine to get 636, written as "six hundred thirty-six."
Numbers from 701 to 800
These numbers start with 7 hundreds (700) and go up to 8 hundreds (800). They are formed by combining 7 hundreds with various tens and ones.
For example, to understand 755:
- Step 1: Start with 7 hundreds (700).
- Step 2: Add 5 tens (50).
- Step 3: Add 5 ones (5).
- Step 4: Combine to get 755, written as "seven hundred fifty-five."
Numbers from 801 to 900
These numbers start with 8 hundreds (800) and go up to 9 hundreds (900). They are formed by combining 8 hundreds with different tens and ones.
For example, to understand 818:
- Step 1: Start with 8 hundreds (800).
- Step 2: Add 1 ten (10).
- Step 3: Add 8 ones (8).
- Step 4: Combine to get 818, written as "eight hundred eighteen."
Numbers from 901 to 999
These numbers start with 9 hundreds (900) and go up to 999. They are formed by combining 9 hundreds with various tens and ones.
For example, to understand 939:
- Step 1: Start with 9 hundreds (900).
- Step 2: Add 3 tens (30).
- Step 3: Add 9 ones (9).
- Step 4: Combine to get 939, written as "nine hundred thirty-nine."
Counting Numbers Using Abacus
An abacus helps represent numbers using beads for hundreds, tens, and ones. Each column on the abacus shows a place value: hundreds, tens, or ones. To show a number, move the correct number of beads in each column.
 For example, to show 208:
For example, to show 208:
- Step 1: Move 2 beads in the hundreds column (2 hundreds).
- Step 2: Move 0 beads in the tens column (0 tens).
- Step 3: Move 8 beads in the ones column (8 ones).
- Step 4: The abacus shows 208, or "two hundred eight."
Face Value and Place Value
Face Value: The actual value of a digit as it appears in the number.
Place Value: The value of a digit based on its position (hundreds, tens, or ones).
For example, in 849:

Expanded Form and Short Form
Expanded Form: Shows a number as the sum of its hundreds, tens, and ones.
Short Form: The standard way of writing a number.
For example, for 365:
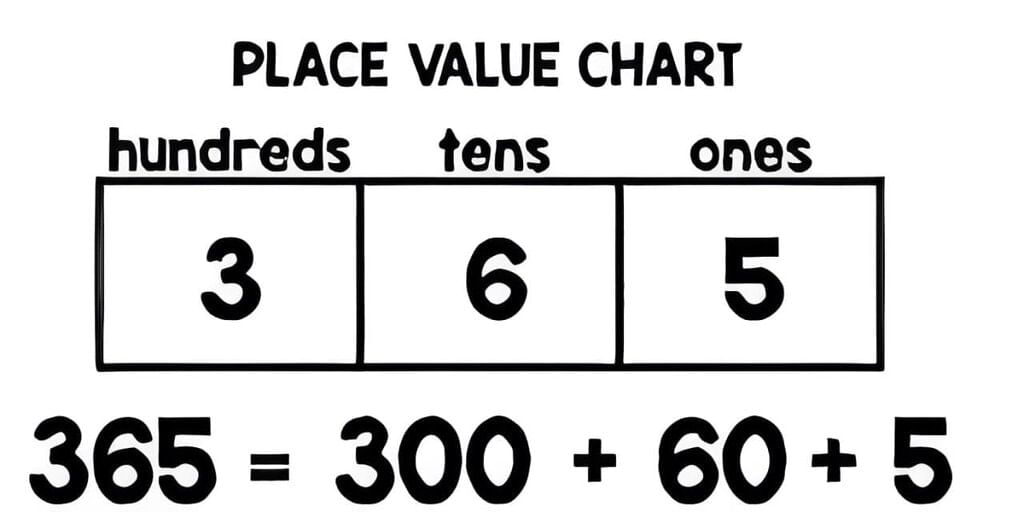
- Step 1: Break it into 3 hundreds (300), 6 tens (60), and 5 ones (5).
- Step 2: Write expanded form as 300 + 60 + 5.
- Step 3: The short form is 365.
Comparing Numbers
To compare 3-digit numbers, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Compare the hundreds digits. The number with the larger hundreds digit is greater.
- Step 2: If the hundreds are the same, compare the tens digits.
- Step 3: If hundreds and tens are the same, compare the ones digits.
For example, to compare 876 and 765:
- Step 1: Compare hundreds: 8 (in 876) is greater than 7 (in 765).
- Step 2: Since 8 > 7, we conclude 876 > 765.
Before, After and Between
- Before: The number that comes just before a given number (subtract 1).
- After: The number that comes just after a given number (add 1).
- Between: The number that lies between two given numbers.
For example, for 454:

- Step 1: Before 454 is 454 - 1 = 453.
- Step 2: After 454 is 454 + 1 = 455.
- Step 3: Between 453 and 455 is 454.
Ordering of Numbers
- Ascending Order: Arrange numbers from smallest to largest.
- Descending Order: Arrange numbers from largest to smallest.
For example, to arrange 384, 362, 405, 500:
- Step 1: Compare hundreds digits to find the smallest and largest.
- Step 2: Arrange from smallest to largest for ascending: 362, 384, 405, 500.

- Step 3: Arrange from largest to smallest for descending: 500, 405, 384, 362.
Forming Numbers
- Numbers can be formed by arranging given digits in different orders.
- Greatest Number: Arrange digits in descending order (largest to smallest).
- Smallest Number: Arrange digits in ascending order (smallest to largest).
- For example, using digits 3, 9, 1:
- Step 1: For greatest, arrange in descending order: 9, 3, 1 = 931.
- Step 2: For the smallest, arrange in ascending order: 1, 3, 9 = 139.
|
50 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Numbers 201 to 999 Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 2 ICSE
| 1. What are number names and why are they important for students? |  |
| 2. How can I help my child learn numbers from 201 to 999 effectively? |  |
| 3. Are there any patterns in the number names from 201 to 999 that can assist in learning? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of learning number names for future math skills? |  |
| 5. How can practice with number names enhance a child's confidence in math? |  |
















