SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Mind Map: Electrolytes, Non-Electrolytes and Electrolysis
Mind Map: Electrolytes, Non-Electrolytes and Electrolysis | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
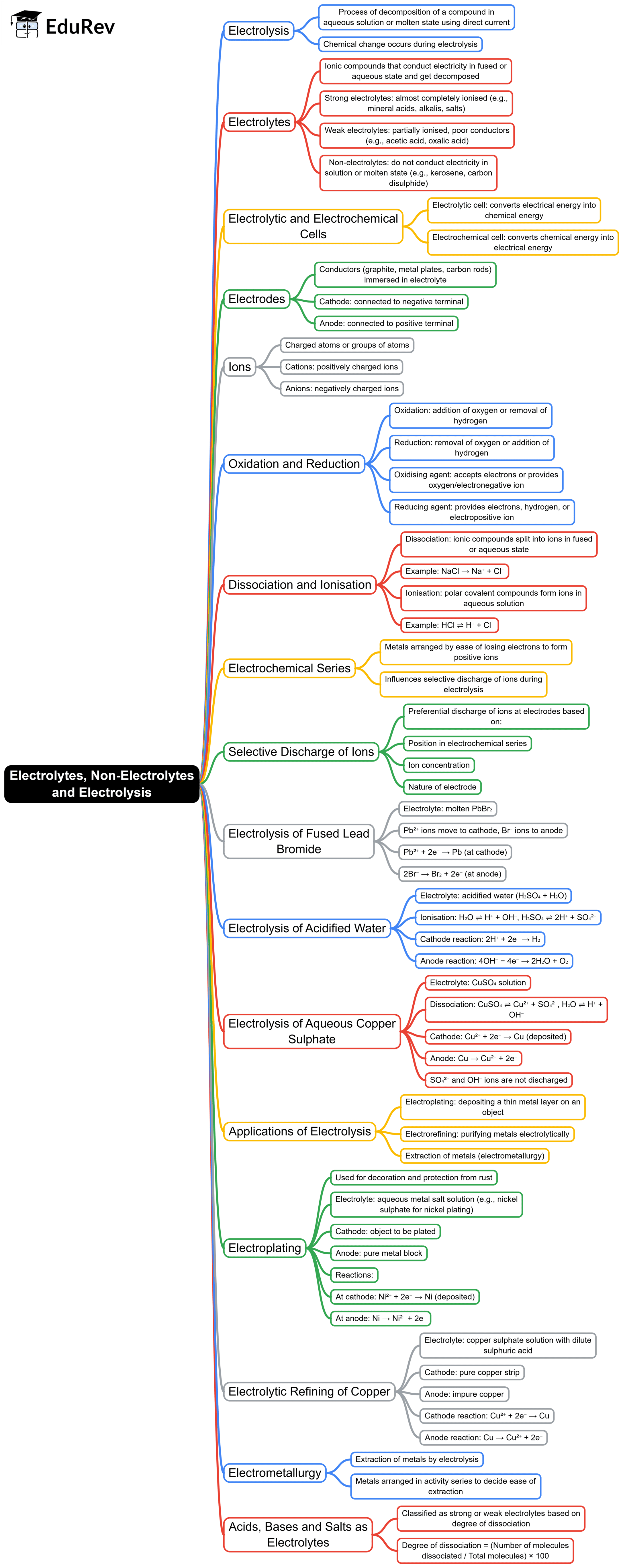
The document Mind Map: Electrolytes, Non-Electrolytes and Electrolysis | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
529 videos|2117 docs|339 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Electrolytes, Non-Electrolytes and Electrolysis - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are electrolytes and how do they function in solutions? |  |
Ans. Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. Common electrolytes include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium chloride (CaCl₂). They play crucial roles in various physiological processes, such as maintaining fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions.
| 2. What is the difference between electrolytes and non-electrolytes? |  |
Ans. The main difference between electrolytes and non-electrolytes lies in their ability to conduct electricity when dissolved in water. Electrolytes dissociate into ions and can conduct electrical current, while non-electrolytes, such as glucose or urea, do not dissociate into ions and therefore do not conduct electricity. Non-electrolytes remain intact in solution and do not affect the conductivity.
| 3. How does electrolysis work and what are its applications? |  |
Ans. Electrolysis is a chemical process that uses an electric current to drive a non-spontaneous reaction. During electrolysis, an electrolyte solution is decomposed into its individual components at the electrodes. Applications of electrolysis include electroplating, water splitting to produce hydrogen and oxygen gases, and the extraction of metals from ores.
| 4. What are some common examples of electrolytes found in the human body? |  |
Ans. Common electrolytes in the human body include sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), calcium (Ca²⁺), magnesium (Mg²⁺), chloride (Cl⁻), bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), and phosphate (PO₄³⁻). These electrolytes are essential for various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve transmission, hydration, and maintaining acid-base balance.
| 5. How can the concentration of electrolytes in a solution be measured? |  |
Ans. The concentration of electrolytes in a solution can be measured using various methods, including conductivity measurements, titration, and ion-selective electrodes. Conductivity measurements assess the ability of the solution to conduct electricity, which correlates with the concentration of ions present. Ion-selective electrodes provide a direct measurement of specific ions in solution, allowing for precise determination of electrolyte concentrations.
Related Searches
















