BMAT Exam > BMAT Notes > Physics for BMAT (Section 2) > Mind Map: Matter
Mind Map: Matter | Physics for BMAT (Section 2) PDF Download
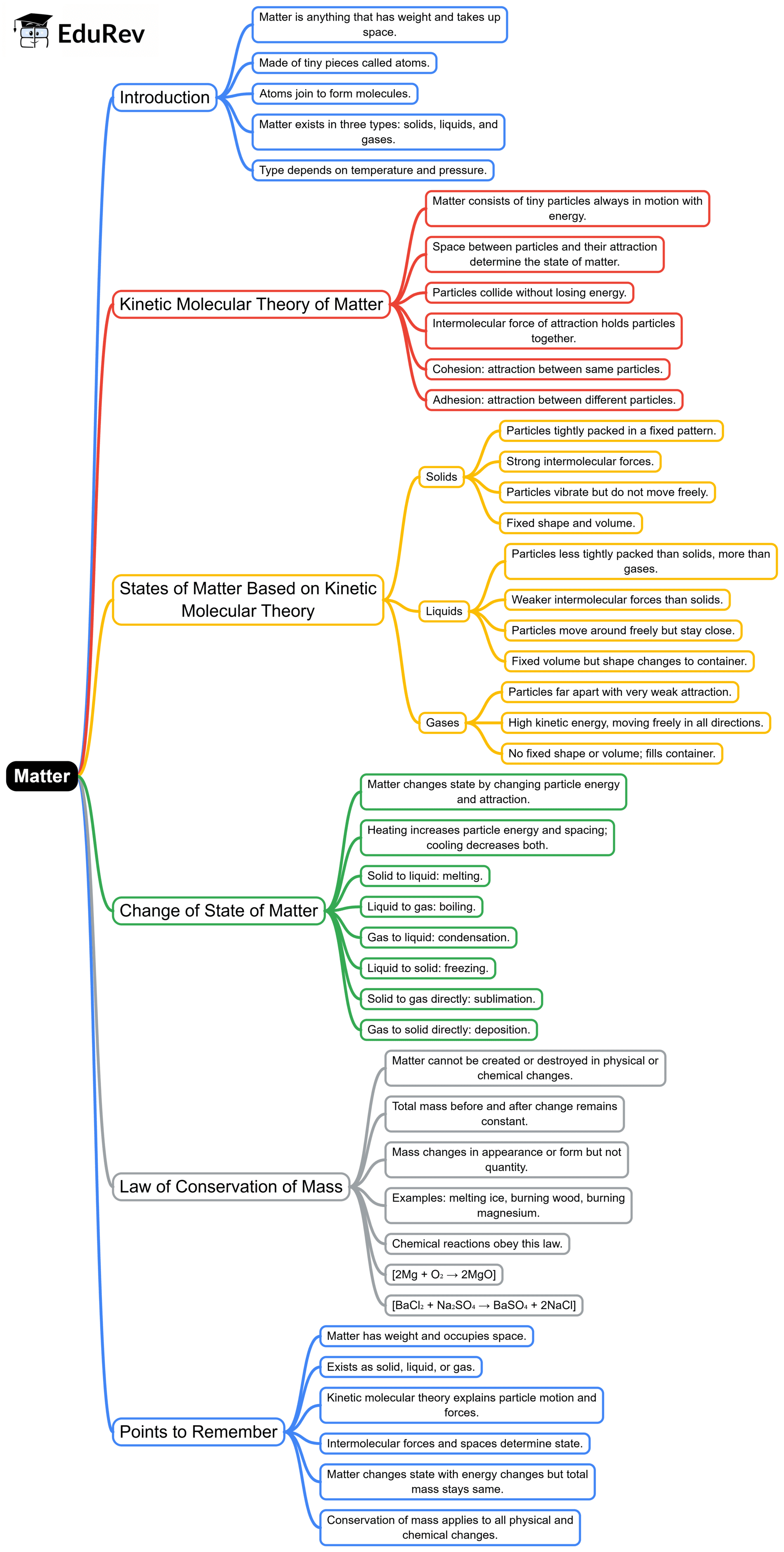
The document Mind Map: Matter | Physics for BMAT (Section 2) is a part of the BMAT Course Physics for BMAT (Section 2).
All you need of BMAT at this link: BMAT
|
46 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Matter - Physics for BMAT (Section 2)
| 1. What is matter and how is it classified? |  |
Ans. Matter is any substance that has mass and occupies space. It is classified into three main states: solids, liquids, and gases. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container, and gases have neither a definite shape nor volume, expanding to fill the available space.
| 2. What are the fundamental properties of matter? |  |
Ans. The fundamental properties of matter include mass, volume, density, and state. Mass is the amount of matter in an object, volume is the space it occupies, density is the mass per unit volume, and the state refers to its physical form (solid, liquid, gas).
| 3. How does matter change states? |  |
Ans. Matter changes states through processes such as melting, freezing, condensation, evaporation, sublimation, and deposition. For example, when heat is applied to ice (solid), it melts into water (liquid). Conversely, cooling water can cause it to freeze into ice.
| 4. What is the difference between mixtures and pure substances? |  |
Ans. A pure substance consists of only one type of particle and has consistent properties throughout, such as distilled water (H₂O) or elements like gold (Au). A mixture, however, contains two or more substances that are physically combined, such as saltwater or air, and can be separated into its components.
| 5. What role do atoms and molecules play in matter? |  |
Ans. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, and they combine to form molecules. Molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together, and they determine the chemical properties of a substance. For example, a water molecule (H₂O) is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Related Searches





















