Lines and Angles Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 7 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Imagine looking at a tall building, a sturdy bridge, or even a simple piece of furniture like a chair. Ever wondered what makes them stand so perfectly? It’s all about lines and angles! These are the building blocks of geometry that architects, engineers, and carpenters use to create the world around us. In this exciting chapter, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of points, lines, rays, planes, and angles. We’ll explore how lines can be parallel or perpendicular, how angles come in different sizes, and how they work together when lines cross each other. Get ready to see the magic of geometry in everyday life!
Point

- A point marks a specific position in space.
- It has no length, width, or thickness.
- Represented by a small dot and named with capital letters like A, B, C.
- Example: In a diagram, a dot labeled A represents Point A, showing a precise location without any size.
Line

- A line is a straight path made of countless points.
- It extends endlessly in both directions and has only length.
- Denoted as
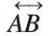 or by small letters like l, m, n.
or by small letters like l, m, n. - Arrows on both ends show it goes on forever.
Line Segment

- A line segment is a part of a line with two fixed endpoints.
- It has a definite length but contains infinite points.
- Denoted as
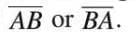
Ray

- A ray is a part of a line starting at one point and extending endlessly in one direction.
- It has one endpoint called the initial point.
- Denoted with an arrow, like
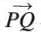 .
.
Plane
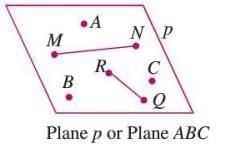
- A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in length and breadth.
- It contains infinite points and lines.
- Denoted by small letters like p, q, or by three non-collinear points, e.g., ABC.
- Example: In a figure, plane p or plane ABC represents a flat surface extending infinitely, marked by points A, B, and C.
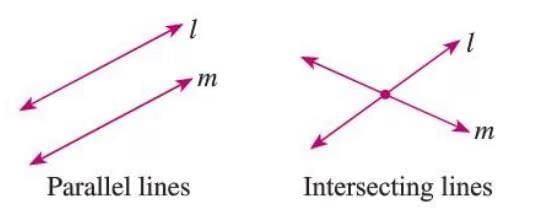
Parallel Lines
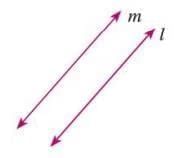
- Parallel lines are two lines in the same plane that never meet, no matter how far they extend.
- The distance between them stays constant.
- Denoted as m || l (m is parallel to l).
- Example: In a diagram, lines m and l are parallel, written as m || l, and they never intersect.
Intersecting Lines
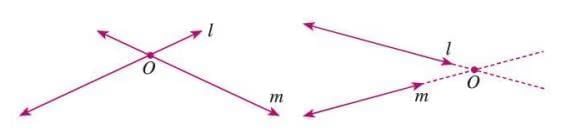
- Intersecting lines are two lines in the same plane that meet at one common point.
- The common point is called the point of intersection.
- Example: In a figure, lines m and n intersect at point O, which is their point of intersection.
Perpendicular Lines
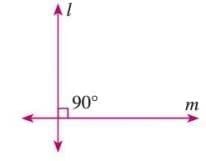
- Perpendicular lines are intersecting lines that form a 90° angle at their point of intersection.
- Denoted as m ⊥ n (m is perpendicular to n).
- Example: In a diagram, line m is perpendicular to line n, forming a 90° angle, written as m ⊥ n.
Properties of Lines
- Infinite straight lines can pass through a single point.
- Only one unique line can pass through two distinct points in a plane.
- Two lines in a plane either intersect at one point or are parallel.
Collinear Points
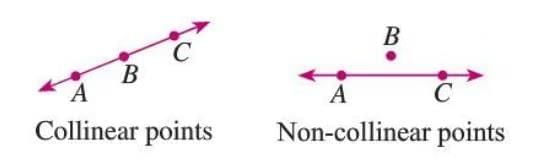
- Three or more points are collinear if they lie on the same straight line.
- If they don’t lie on the same line, they are non-collinear.
Concurrent Lines
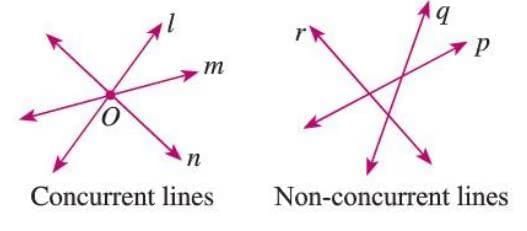 Three or more lines are concurrent if they all pass through the same point.
Three or more lines are concurrent if they all pass through the same point.- The common point is called the point of concurrence.
Angle
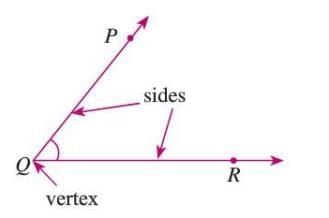
- An angle forms when two rays share the same starting point.
- The shared point is called the vertex, and the rays are the arms or sides.
- Denoted as ∠PQR, ∠Q (by vertex), or ∠1, ∠a, etc.
Measurement of an Angle
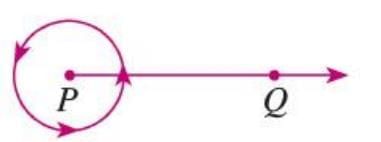
- An angle’s size is the amount one arm rotates to meet the other.
- Measured in degrees (°), where one full rotation around the vertex is 360°.
- 1° is divided into 60 minutes (60'), and 1 minute is divided into 60 seconds (60").
- Example: A ray PQ completing one full rotation around point P forms an angle of 360°.
Types of Angles
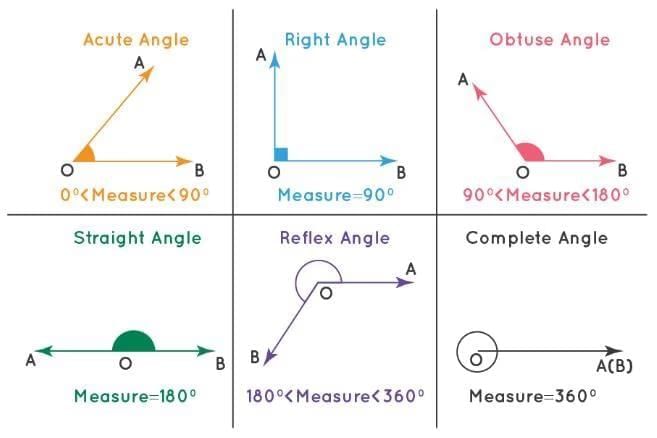 Acute Angle
Acute Angle
- An angle measuring more than 0° but less than 90°.
- Example: Angles of 25°, 38°, or 88° are acute angles.
Right Angle
- An angle measuring exactly 90°.
- Example: An angle of 90° is a right angle, often seen in perpendicular lines.
Obtuse Angle
- An angle measuring more than 90° but less than 180°.
- Example: Angles of 91°, 101°, or 178° are obtuse angles.
Straight Angle
- An angle measuring exactly 180°.
- Example: An angle of 180° is a straight angle, forming a straight line.
Reflex Angle
- An angle measuring more than 180° but less than 360°.
- Example: Angles of 183°, 190°, or 325° are reflex angles.
Some Special Angles
Zero Angle
- An angle formed when a ray’s initial and final positions are the same, with no rotation.
- Measures 0°.
Complete Angle
- An angle formed when a ray completes one full rotation and returns to its starting position.
- Measures 360°.
Relation Between Two Angles
Complementary Angles
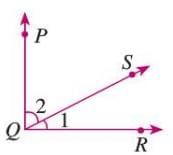 Two angles whose measures add up to 90°.
Two angles whose measures add up to 90°.- Each angle is the complement of the other.
- Example: In a figure, ∠1 + ∠2 = 90°, so ∠1 and ∠2 are complementary angles.
Supplementary Angles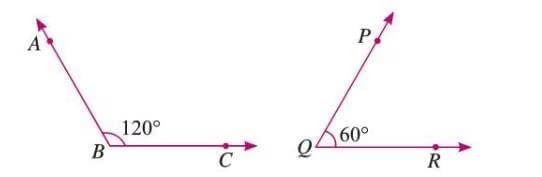
- Two angles whose measures add up to 180°.
- Each angle is the supplement of the other.
Adjacent Angles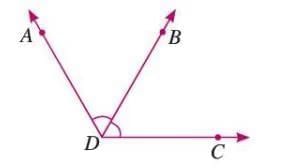
- Two angles that share a common vertex and a common arm.
- The other arms lie on opposite sides of the common arm.
Linear Pair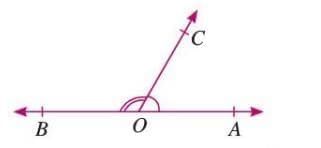
- Two adjacent angles whose measures add up to 180°.
Vertically Opposite Angles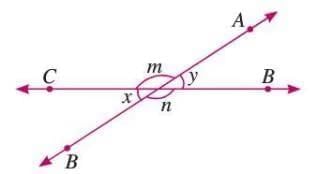
- Angles formed on opposite sides when two lines intersect at a point.
- They are always equal.
Transversal
- A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines at different points.
- It creates eight angles when cutting two lines.
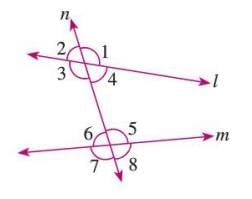
Interior Angles
- Angles formed between two lines intersected by a transversal.
- Example: In a figure, angles 3, 4, 5, and 6 are interior angles between lines q and r cut by transversal p.
Exterior Angles
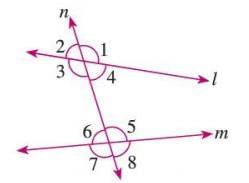
- Angles formed outside the two lines intersected by a transversal.
- Example: In a figure, angles 1, 2, 7, and 8 are exterior angles outside lines q and r cut by transversal p.
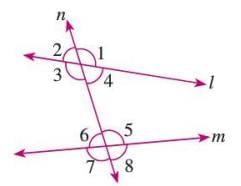
Co-interior Angles
- Interior angles on the same side of the transversal.
- Also called allied angles.
- Example: In a figure, angles 3 and 6, and angles 4 and 5 are pairs of co-interior angles.
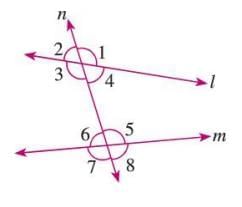
Exterior Allied Angles
- Exterior angles on the same side of the transversal.
- Example: In a figure, angles 1 and 8, and angles 2 and 7 are pairs of exterior allied angles.
Alternate Angles
- Angles on opposite sides of the transversal, either both interior or both exterior, but not adjacent.
- Example: In a figure, angles 3 and 5, and angles 4 and 6 are alternate interior angles, while angles 1 and 7, and angles 2 and 8 are alternate exterior angles.
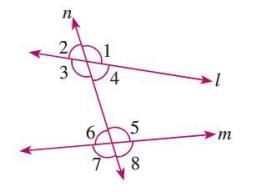
Corresponding Angles
- Non-adjacent angles where one is interior and one is exterior, on the same side of the transversal.
- Example: In a figure, angles 1 and 5, 4 and 8, 2 and 6, and 3 and 7 are pairs of corresponding angles.
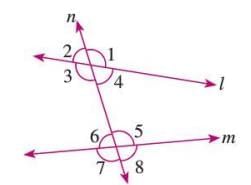
Relation Between the Angles Made by a Transversal with Parallel Lines
- When a transversal intersects two parallel lines:
- Alternate angles are equal.
- Corresponding angles are equal.
- Interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary (add up to 180°).
Example: In a figure, lines v and w are parallel, cut by transversal u, so ∠4 = ∠6, ∠3 = ∠5 (alternate angles), ∠1 = ∠5, ∠4 = ∠8 (corresponding angles), and ∠4 + ∠5 = 180°, ∠3 + ∠6 = 180° (co-interior angles).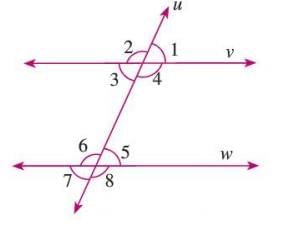
Conditions for Parallelism
- Two lines are parallel if any of these conditions are met when cut by a transversal:
- A pair of alternate angles are equal.
- A pair of corresponding angles are equal.
- Interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.
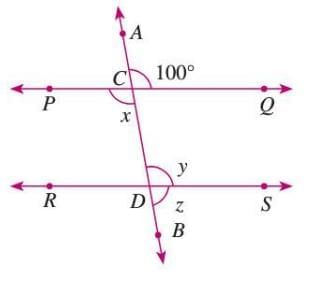
- Example: In a figure, if ∠PCD = 50° and ∠PCD + ∠CDR = 50° + 130° = 180°, then lines PQ and RS are parallel because the co-interior angles are supplementary.
|
47 videos|118 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Lines and Angles Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 7 ICSE
| 1. What is the difference between a line and a line segment? |  |
| 2. How do parallel lines differ from intersecting lines? |  |
| 3. What are perpendicular lines and how can they be identified? |  |
| 4. Can you explain what a ray is and how it differs from a line segment? |  |
| 5. What are the properties of lines that are important for understanding angles? |  |
















