Complementary Angles Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 9 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Imagine you're slicing a pizza, and you cut two pieces that perfectly fit together to form a right angle. That’s the essence of complementary angles! In this exciting chapter, we dive into the world of angles that team up to make 90°, exploring their trigonometric ratios and how they simplify complex problems. From sine to tangent, we’ll uncover how these angles relate to each other in a right-angled triangle, making math both fun and intuitive. Get ready to discover the magic of complementary angles and their applications!
- Trigonometric ratios for standard angles (0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°) have been studied earlier.
- Focus of this chapter: Understanding trigonometric ratios of complementary angles.
- Learn how to apply these ratios in various mathematical problems.
Concept of Trigonometric Ratios of Complementary Angles
Definition: Two acute angles are complementary if their sum equals 90°.
Steps to Identify Complementary Angles:
- Add the two angles.
- Check if the sum is 90°.
Finding the Complement:
- Subtract the given angle from 90° to find its complement.
Complementary Angles for Sine (sin) and Cosine (cos)
In a right-angled triangle ABC (right angle at B), if ∠ACB = θ, then ∠CAB = 90° - θ.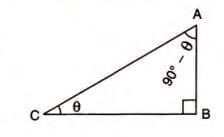 Steps to Derive Relationships:
Steps to Derive Relationships:
- sin θ = perpendicular/hypotenuse = AB/AC.
- cos (90° - θ) = base/hypotenuse = AB/AC.
- Thus, sin θ = cos (90° - θ).
- cos θ = base/hypotenuse = BC/AC.
- sin (90° - θ) = perpendicular/hypotenuse = BC/AC.
- Thus, sin (90° - θ) = cos θ.
Formulas:
- cos (90° - θ) = sin θ
- sin (90° - θ) = cos θ
- cos 47° = cos (90° - 43°) = sin 43°.
- sin 72° = sin (90° - 18°) = cos 18°.
- Expression becomes: (sin 43° / sin 43°)2 + (cos 18° / cos 18°)2 - 2 (1/√2)2.
- = 12 + 12 - 2 × 1/2 = 1 + 1 - 1 = 1.
- Answer: 1
Complementary Angles for Tangent (tan) and Cotangent (cot)
In triangle ABC (∠B = 90°), if ∠ACB = θ, then ∠CAB = 90° - θ.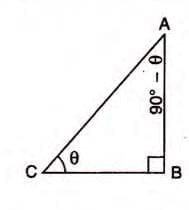
Steps to Derive Relationships:
- tan θ = perpendicular/base = AB/BC.
- cot (90° - θ) = base/perpendicular = AB/BC.
- Thus, tan θ = cot (90° - θ).
- cot θ = base/perpendicular = BC/AB.
- tan (90° - θ) = perpendicular/base = BC/AB.
- Thus, cot θ = tan (90° - θ).
Formulas:
- cot (90° - θ) = tan θ
- tan (90° - θ) = cot θ
- tan 72° = tan (90° - 18°) = cot 18°.
- cot 72° = cot (90° - 18°) = tan 18°.
- Expression becomes: (cot 18° / cot 18°) - (tan 18° / tan 18°).
- = 1 - 1 = 0.
- Hence Proved.
Complementary Angles for Secant (sec) and Cosecant (cosec)
Formulas:
- sec (90° - θ) = cosec θ
- cosec (90° - θ) = sec θ
- cosec 82° = cosec (90° - 8°) = sec 8°.
- Expression becomes: sec 8° - sec 8° = 0.
- Answer: 0
General Relationships for Complementary Angles A and B
If A + B = 90°, then A and B are complementary.
Formulas:
- sin A = cos B
- cos A = sin B
- tan A = cot B
- cot A = tan B
- sec A = cosec B
- cosec A = sec B
Additional Proofs and Evaluations
Proof in Triangle ABC:
- For triangle ABC, A + B + C = 180°.
- Thus, A + B = 180° - C.
- (A + B)/2 = 90° - C/2.
- sec ((A + B)/2) = sec (90° - C/2) = cosec (C/2).
- tan 53° = tan (90° - 37°) = cot 37°.
- cot 80° = cot (90° - 10°) = tan 10°.
- Expression becomes: (2 cot 37° / cot 37°) - (tan 10° / tan 10°).
- = 2 - 1 = 1.
- Answer: 1
- cot 37° = cot (90° - 53°) = tan 53°.
- tan 10° = tan (90° - 80°) = cot 80°.
- Expression: (2 tan 53° / tan 53°) - (cot 80° / cot 80°).
- = 2 - 1 = 1.
- sec (90° - 2A) = cosec 2A.
- Expression: cos 38° × cosec 2A = 1.
- cosec 2A = 1 / cos 38°.
- sin 2A = cos 38° = cos (90° - 52°) = sin 52°.
- sin 2A = sin 52° implies 2A = 52°.
- A = 26°.
- Answer: A = 26°
|
28 videos|171 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Complementary Angles Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 9 ICSE
| 1. What are complementary angles in trigonometry? |  |
| 2. How do the sine and cosine functions relate to complementary angles? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between tangent and cotangent for complementary angles? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the relationships for secant and cosecant in terms of complementary angles? |  |
| 5. What are some general relationships for complementary angles A and B in trigonometry? |  |















