Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Notes > Mathematics Class 6 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Fundamental Concepts of Geometry
Fundamental Concepts of Geometry Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 6 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Geometry is an exciting branch of mathematics that explores shapes, sizes, and positions of objects around us. Imagine looking at the majestic Gateway of India in Mumbai or even your own home—every corner, edge, and angle is a piece of geometry at work! From ancient times, people used geometry to measure land, build grand palaces, and create stunning art. Today, architects design towering buildings, carpenters craft furniture, and engineers construct bridges, all using geometry's magical rules of lines and angles. This chapter will take you on a journey to understand the basic building blocks of geometry, making you see the world through a geometric lens!
Point
- A point is a tiny dot that marks a specific position in space.
- It has no length, width, or thickness—just a location.
- Denoted by a capital letter like A, B, or C.
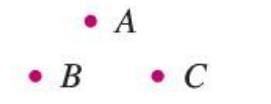
- Example: The tip of a sharp pencil represents a point, as it marks a single spot without any size.
Solved Example: Identify a point in your classroom.
The corner of your desk where two edges meet can be considered a point, as it marks a specific position.
The corner of your desk where two edges meet can be considered a point, as it marks a specific position.
Line

- A line is a straight path made of countless points, stretching endlessly in both directions.
- It has only length, no width or thickness.
- Denoted by a small letter (l, m, n) or as AB with arrows on both ends (
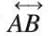 ).
). - An infinite number of lines can pass through a single point, and every line contains infinite points.
- Example: A straight line passing through points A and B, denoted as
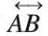 , extends forever in both directions.
, extends forever in both directions.
Line Segment

- A line segment is a part of a line with two fixed endpoints.
- It has a definite length but contains infinite points between its ends.
- Denoted
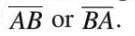 with a line over the letters.
with a line over the letters. - Example: The edge of a ruler is a line segment, as it has two endpoints and a measurable length.
Ray

- A ray is a part of a line that starts at one fixed point (initial point) and extends endlessly in one direction.
- It has one endpoint and is denoted as
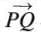 with an arrow over one end.
with an arrow over one end. - Two rays with the same initial point but extending in opposite directions are called opposite rays.
Solved Example: Draw opposite rays AB and AC.
Mark point A. Draw a ray starting at A through point B and another starting at A through point C in the opposite direction.
Mark point A. Draw a ray starting at A through point B and another starting at A through point C in the opposite direction.

Plane
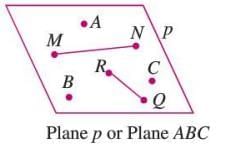
- A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in length and breadth.
- It contains infinite points and lines.
- Denoted by a small letter (p, q) or by three non-collinear points (Plane ABC).
- Example: The surface of a sheet of paper is like a plane, extending infinitely if not bound by edges.
Solved Example: Name a plane in your surroundings.
The top of a table is an example of a plane, as it represents a flat surface that could extend infinitely.
The top of a table is an example of a plane, as it represents a flat surface that could extend infinitely.
Space
- Space is a collection of all points, lines, and planes.
- It has infinite length, breadth, and height.
- Example: The interior of a room, including its walls, floor, and ceiling, is part of space.
Solved Example: Identify an example of space.
The area inside your classroom, containing all objects, walls, and floors, represents space.
The area inside your classroom, containing all objects, walls, and floors, represents space.
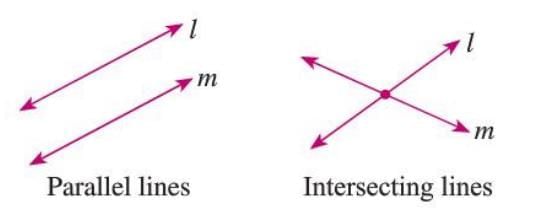
Parallel Lines
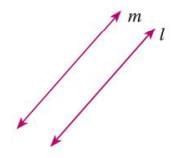
- Parallel lines are two lines in the same plane that never meet, no matter how far they extend.
- The distance between them remains constant.
- Denoted as l || m (read as "l is parallel to m").
- Example: In a figure, lines l and m are parallel, shown as l || m, maintaining the same distance apart.
Intersecting Lines
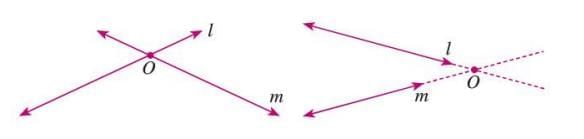
- Intersecting lines are two lines in the same plane that meet at a single point, called the point of intersection.
- Example: Lines l and m intersect at point O, where O is their common point.
Perpendicular Lines
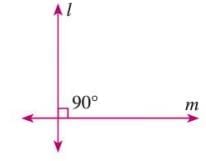
- Perpendicular lines are intersecting lines that meet at a 90° angle.
- Denoted as l ⊥ m (read as "l is perpendicular to m").
- Example: In a figure, line l is perpendicular to line m, forming a 90° angle, written as l ⊥ m.
Perpendicular Bisector
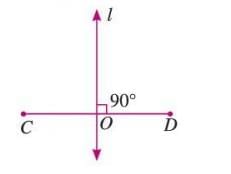
- A perpendicular bisector is a line that divides a line segment into two equal parts at a 90° angle.
- The point of intersection lies exactly midway between the segment’s endpoints.
- Example: Line l is the perpendicular bisector of segment CD, dividing it into two equal parts at point O, with l ⊥ CD.
Open and Closed Figures

- Open figures have different starting and ending points, so they don’t connect.
- Closed figures have the same starting and ending points, forming a complete boundary.
- Example: A triangle is a closed figure, while a single line segment with two distinct endpoints is an open figure.
Triangle
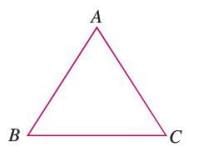
- A triangle is a closed figure formed by three line segments joined at their endpoints.
- Denoted as △ABC, with sides AB, BC, and CA.
- It has three vertices (A, B, C) and three angles (angle A, angle B, angle C).
- Example: In △ABC, the sides are AB, BC, and CA, meeting at vertices A, B, and C.
Solved Example: Draw triangle ABC.
Mark points A, B, and C. Connect A to B, B to C, and C to A with line segments to form △ABC.
Mark points A, B, and C. Connect A to B, B to C, and C to A with line segments to form △ABC.
Rectangle
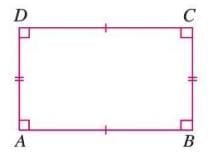
- A rectangle is a closed figure with four line segments where opposite sides are equal and all angles are 90°.
- Formula: In rectangle ABCD, AB = DC, AD = BC, and angle A = angle B = angle C = angle D = 90°.
- Example: In rectangle ABCD, opposite sides AB and DC are equal, and all angles are 90°.
Square
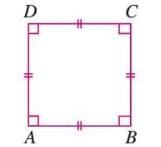
- A square is a closed figure with four equal line segments and all angles at 90°.
- Formula: In square ABCD, AB = BC = CD = DA, and angle A = angle B = angle C = angle D = 90°.
- Example: In square ABCD, all sides (AB, BC, CD, DA) are equal, and all angles are 90°.
Circle
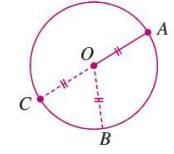
- A circle is a closed figure where all points are equidistant from a fixed point called the center.
- The distance from the center to any point on the circle is the radius.
- In a circle with center O, OA = OB = OC = radius.
- Example: In a circle with center O, points A, B, and C on the circle are all at the same distance (radius) from O.
Interior, Exterior, and Boundary of Closed Figures
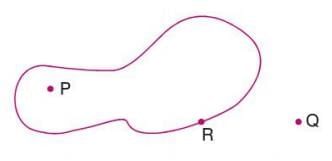
- A closed figure divides a plane into three parts:
- Interior: All points inside the figure.
- Exterior: All points outside the figure.
- Boundary: All points on the figure’s edge.
- The interior plus the boundary is called the region of the figure.
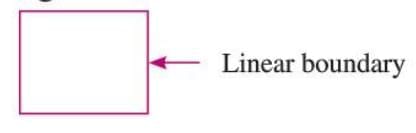
Curvilinear and Linear Boundaries
- A curvilinear boundary consists only of curved lines.
- A linear boundary consists only of straight line segments.
- Example: A circle has a curvilinear boundary, while a square has a linear boundary.
Incidence Properties
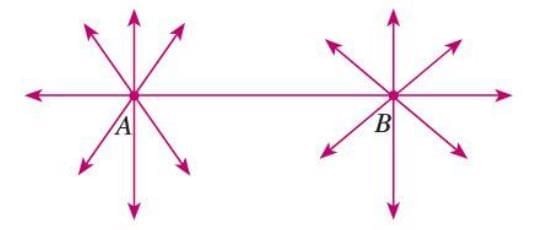
- Incidence properties describe relationships between points and lines.
- Property 1: Only one line can pass through two distinct points in a plane.
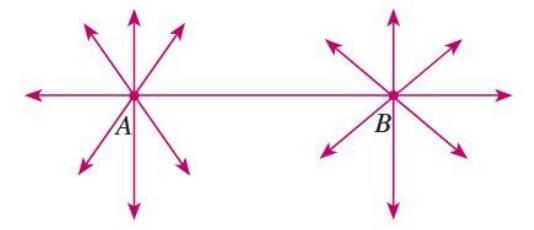
- Property 2: Two different lines in a plane are either parallel or intersect at exactly one point.
- Example: For two points A and B, only one line passes through both, but infinite lines can pass through A alone.
Collinear and Non-collinear Points
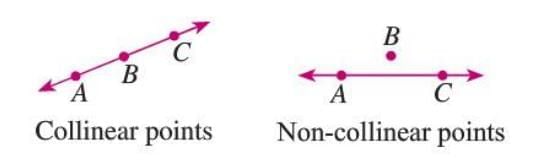
- Collinear points are three or more points that lie on the same straight line.
- Non-collinear points do not lie on the same line.
- The line containing collinear points is called the line of collinearity.
- Example: Points A, B, and C are collinear if they lie on the same line; otherwise, they are non-collinear.
Concurrent and Non-concurrent Lines
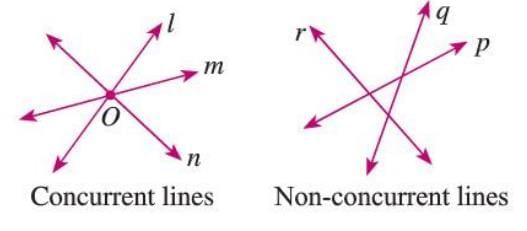
- Concurrent lines are three or more lines that pass through the same point, called the point of concurrence.
- Non-concurrent lines do not share a common point.
- Example: Lines l, m, and n are concurrent if they meet at point O; otherwise, they are non-concurrent.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Draw a circle with center O and radius 4 cm. Mark points A and B on the circle and verify that OA = OB.
Solution: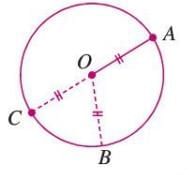
Solution:

- Mark point O as the center.
- Use a compass set to 4 cm to draw a circle.
- Mark points A and B anywhere on the circle’s boundary.
- Measure OA and OB with a ruler; both are 4 cm, confirming OA = OB = radius.
Example 2: Draw a rectangle ABCD with AB = 5 cm and BC = 2 cm. Identify a pair of parallel lines.
Solution: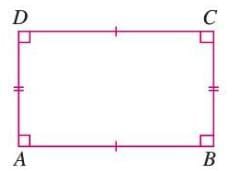
Solution:

- Draw point A, then AB = 5 cm horizontally.
- Draw BC = 2 cm vertically upward from B at 90° to AB.
- Draw CD = 5 cm horizontally from C, parallel to AB.
- Draw DA = 2 cm vertically downward to A, parallel to BC.
- AB and CD are parallel (opposite sides of the rectangle).
The document Fundamental Concepts of Geometry Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 6 ICSE is a part of the Class 6 Course Mathematics Class 6 ICSE.
All you need of Class 6 at this link: Class 6
|
44 videos|201 docs|24 tests
|
FAQs on Fundamental Concepts of Geometry Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 6 ICSE
| 1. What is the difference between a line and a line segment? |  |
Ans.A line is a straight path that extends infinitely in both directions with no endpoints, whereas a line segment has two distinct endpoints and is a part of a line.
| 2. How do we define a ray in geometry? |  |
Ans.A ray is a part of a line that starts at one endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction. It has one endpoint and continues endlessly in the other direction.
| 3. What are parallel lines, and how are they different from intersecting lines? |  |
Ans.Parallel lines are lines in a plane that never meet and are always the same distance apart. In contrast, intersecting lines are lines that cross each other at a certain point.
| 4. What is meant by perpendicular lines in geometry? |  |
Ans.Perpendicular lines are two lines that intersect at a right angle (90 degrees). This means they create four right angles at the point of intersection.
| 5. Can you explain what a plane is in geometric terms? |  |
Ans.A plane is a flat, two-dimensional surface that extends infinitely in all directions. It has no thickness and is defined by three non-collinear points.
Related Searches





















