Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Economics Class 12 > Cheat Sheet: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal
Cheat Sheet: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal | Economics Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Background |

|
| Liberalisation |

|
| Privatisation |

|
| Globalisation |

|
| Indian Economy During Reforms: An Assessment |

|
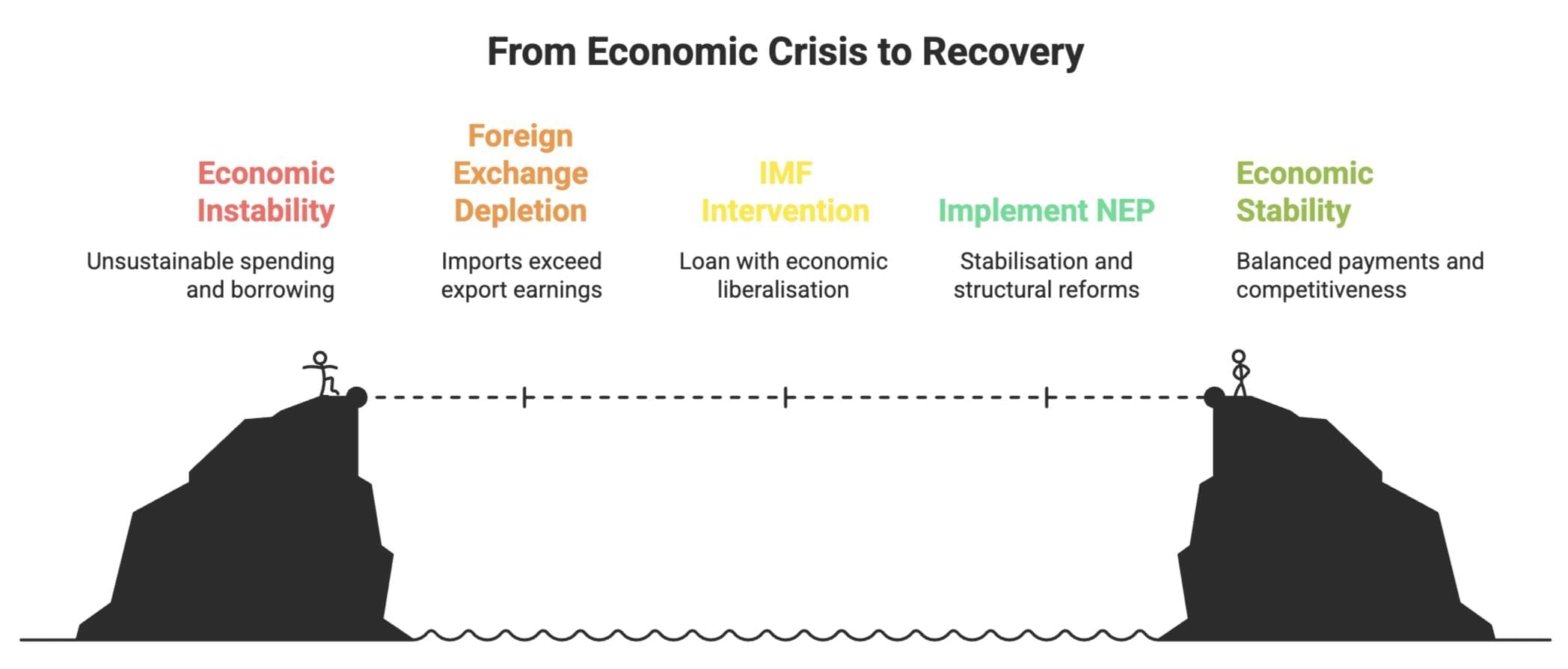
Post-independence, India adopted a mixed economy blending capitalism and socialism. The 1991 economic crisis, triggered by external debt and critically low foreign reserves, led to the New Economic Policy (NEP) emphasised liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation. This cheat sheet outlines the crisis, NEP reforms, and their economic impacts.
Background
- Crisis Origins: 1980s mismanagement; government spending exceeded revenue from taxes and public enterprises, leading to heavy borrowing.
- Foreign Exchange Crisis: Imports outstripped export earnings, reducing reserves to cover only two weeks of imports by 1991.
- Spending Drivers: High expenditure on the social sector, defence, and development to tackle unemployment, poverty, and population growth.
- Outcomes: Rising prices, inability to service foreign loans, shortage of lenders.
- Response: $7 billion loan from World Bank/IMF, requiring economic liberalisation, reduced government role, and trade barrier removal.
- New Economic Policy (NEP): Stabilisation for balance of payments/inflation; structural reforms for efficiency/competitiveness.

Liberalisation
Liberalisation removed restrictive regulations to boost economic growth, with major reforms in 1991.
Deregulation of Industrial Sector
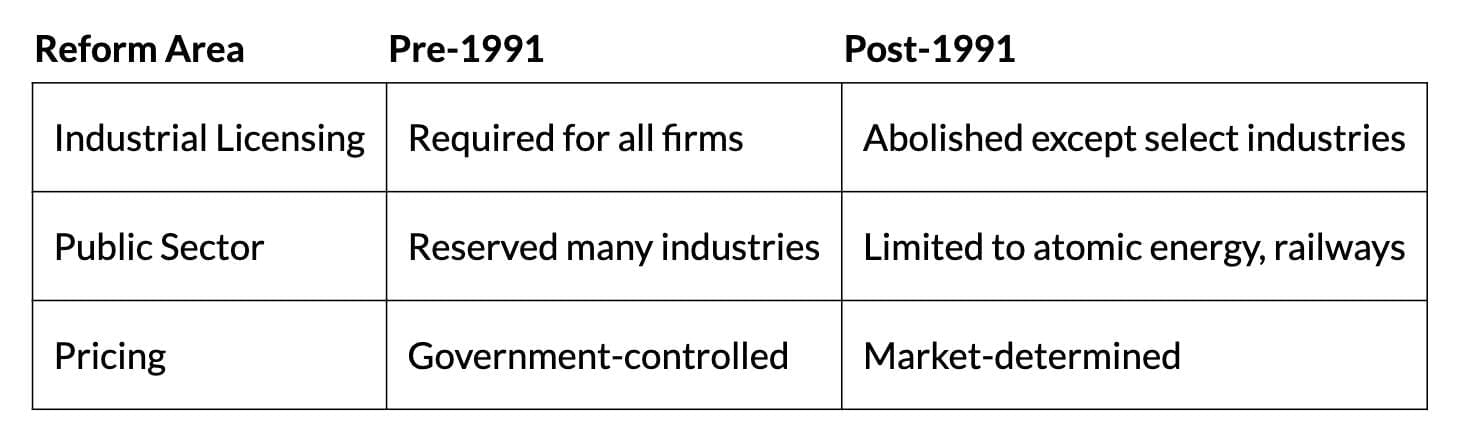
- Pre-1991 Controls: Industrial licensing, private sector restrictions, small-scale production limits, price/distribution controls.
- Reforms: Abolished licensing (except for alcohol, cigarettes, hazardous chemicals, explosives, electronics, aerospace, pharmaceuticals); reserved atomic energy, select railways for the public sector; de-reserved small-scale goods; introduced market-driven pricing.
Financial Sector Reforms
- Objective: Shift RBI from regulator to facilitator, enhancing financial sector autonomy.
- Changes: Established private banks, raised foreign investment limit to ~74%, allowed branch expansion, permitted Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) in markets.
Tax Reforms
- Direct Taxes: Reduced income/corporate tax rates to reduce evasion, promote savings.
- Indirect Taxes: Goods and Services Tax (GST, 2016), unified market, reduced evasion.
- Simplification: Streamlined procedures, lowered rates for compliance.
Foreign Exchange Reforms
- Rupee devalued in 1991 to increase foreign exchange inflow.
- Shifted to market-determined exchange rates.
Trade and Investment Policy Reforms
- Pre-1991: High tariffs, import restrictions, and licensing slowed manufacturing.
- Reforms: Abolished import licensing (except hazardous goods), removed quantitative restrictions by 2001, reduced tariffs, and eliminated export duties.
Privatisation
- Definition: Transfer of government enterprises to the private sector via ownership withdrawal or sale.
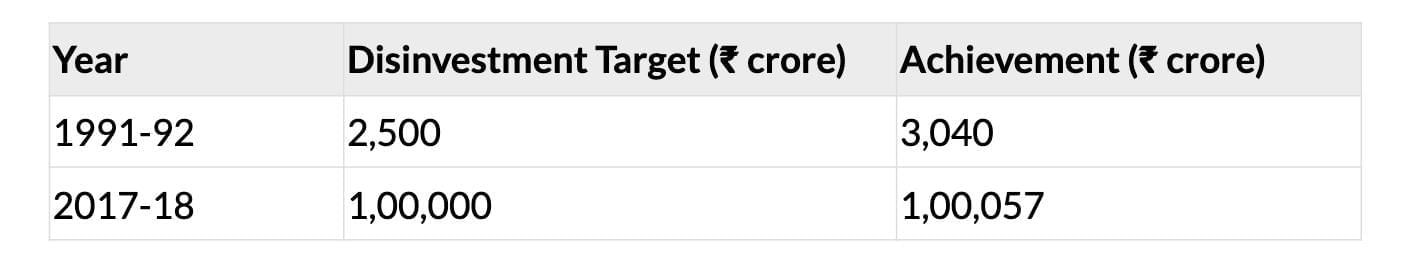
- Disinvestment: Selling public sector equity to the public.
- Objectives: Improve financial discipline, modernise, leverage private expertise, boost FDI.
- Measures: Granted PSUs autonomy; designated maharatnas, navratnas, miniratnas.
Globalisation
- Definition: Integration with the global economy, fostering interdependence across boundaries.
- Outsourcing: Companies hire services (e.g., IT, call centres) from India due to low costs, skilled labour, enabled by IT advancements.
World Trade Organisation (WTO)
- Established: 1995, succeeding GATT (1948).
- Objectives: Rule-based trade, expand service trade, optimise resources, and protect the environment.
- India’s Role: Liberalised trade, reduced tariffs, advocates for developing countries.
- Criticism: Limited benefits due to trade favouring developed nations, unfair subsidy complaints, and market access imbalances.
Indian Economy During Reforms: An Assessment
Growth
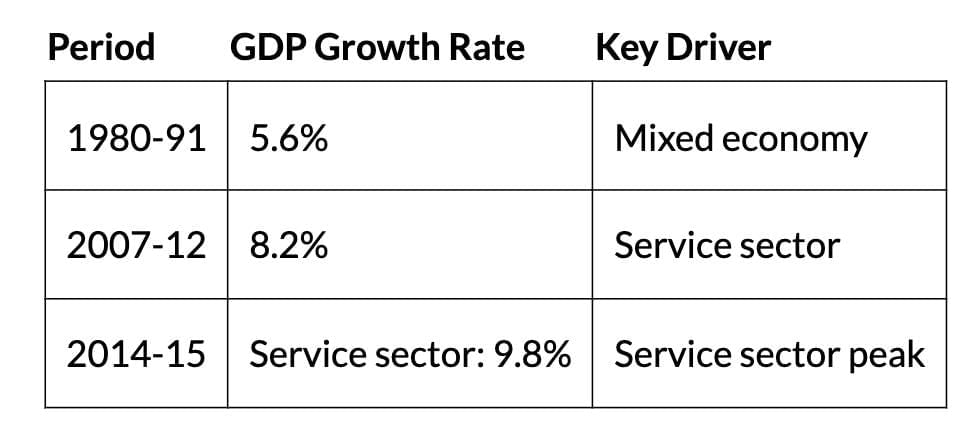
- Service sector led growth; agriculture slowed; industry fluctuated.
- Decline in 2012-15; agriculture peaked in 2013-14.
Foreign Investment and Exchange Reserves
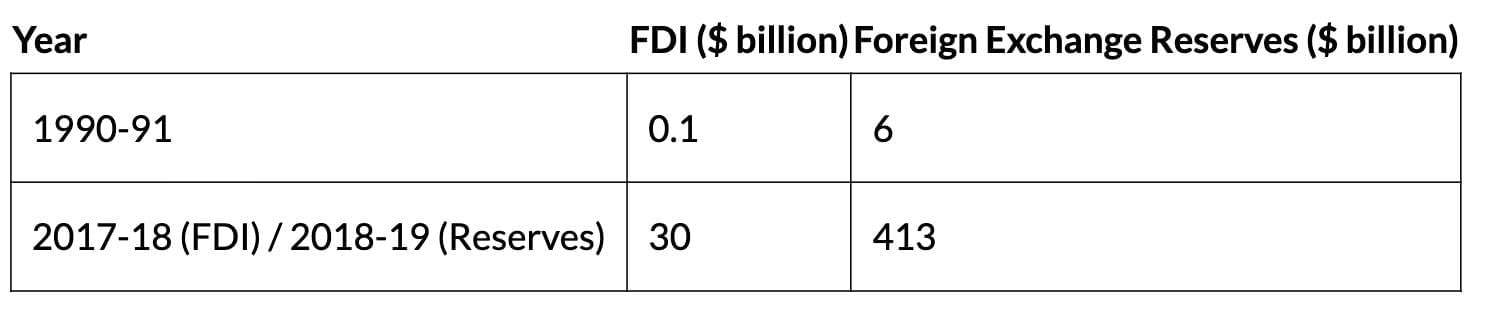
Exports and Challenges
- Strengths: Exports in auto parts, pharmaceuticals, IT, textiles; controlled inflation.
- Weaknesses: Inadequate focus on employment, agriculture, industry, infrastructure, and fiscal management.
Growth and Employment
- High GDP growth but insufficient job creation.
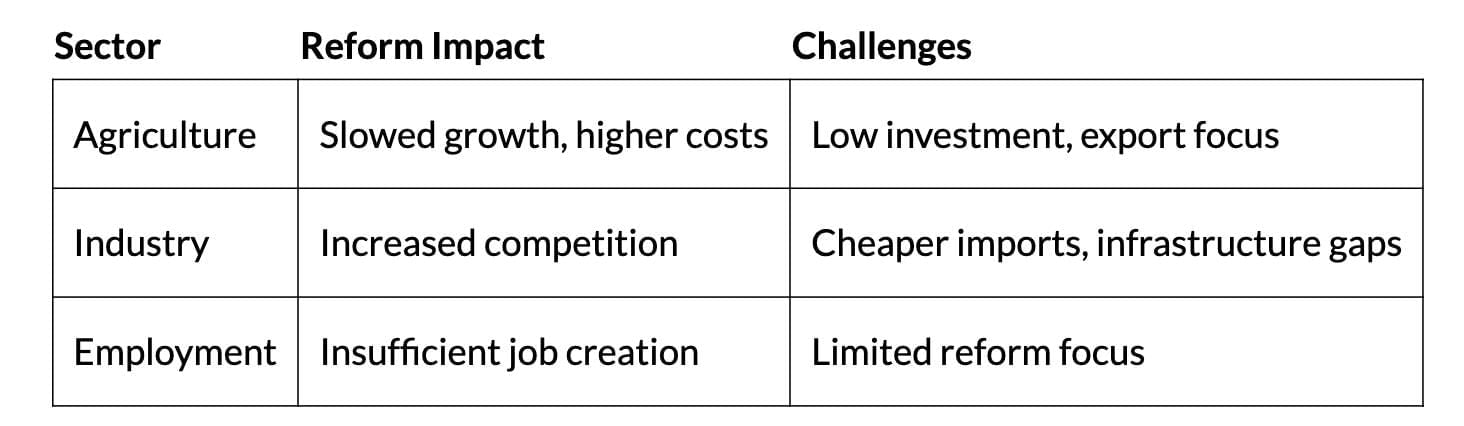
Reforms in Agriculture
- Slowed growth; reduced public investment.
- Higher costs from partial fertiliser subsidy removal; increased competition from import policy changes.
- Export focus raised domestic food prices.
Reforms in Industry
- Slowed due to low demand, cheaper imports, and poor infrastructure.
- Globalization increased competition; non-tariff barriers (e.g., US textile quotas) limited market access.
Disinvestment
- Criticism: Undervalued PSU assets sold; proceeds covered revenue shortfalls, not reinvested.
Reforms and Fiscal Policies
- Limited social sector spending; tax cuts, tariff reductions, and investor incentives reduced revenue.
- Impacted developmental/welfare expenditures.
The document Cheat Sheet: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal | Economics Class 12 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Economics Class 12.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
64 videos|308 docs|51 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Liberalisation, Privatisation and Globalisation : An Appraisal - Economics Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What are the main objectives of liberalisation in the Indian economy? |  |
Ans. The main objectives of liberalisation in the Indian economy include reducing government restrictions on the economy, promoting free trade and investment, enhancing competition, and encouraging private enterprise. The aim was to create a more open and market-driven economy, allowing for greater efficiency and innovation.
| 2. How has privatisation impacted the public sector in India? |  |
Ans. Privatisation in India has led to the transfer of ownership and management of state-owned enterprises to private entities. This has resulted in increased efficiency, better service delivery, and improved financial performance of these enterprises. However, it has also raised concerns about job losses and the potential neglect of social objectives.
| 3. What role does globalisation play in shaping the Indian economy? |  |
Ans. Globalisation has played a significant role in integrating the Indian economy with the global market. It has facilitated the inflow of foreign direct investment, increased exports, and provided access to international technology and markets. This integration has stimulated economic growth but has also exposed the economy to global competition and external shocks.
| 4. What are the key reforms introduced during the liberalisation period in India? |  |
Ans. Key reforms introduced during the liberalisation period include the dismantling of the License Raj, reduction of import tariffs, deregulation of industries, and the introduction of foreign investment policies. These reforms aimed to create a more conducive environment for business and attract investments.
| 5. What are the criticisms associated with the liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation policies in India? |  |
Ans. Criticisms of these policies include increasing income inequality, marginalisation of small industries, and concerns over job security in the public sector. Critics argue that while these policies have led to economic growth, they have also resulted in social disparities and a focus on profit over public welfare.
Related Searches




















