Important Questions: The World of Metals and Non-metals | Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT PDF Download
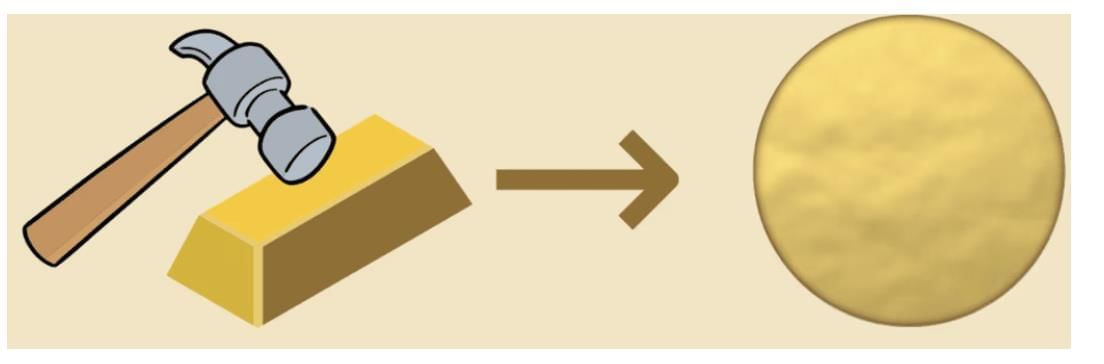
Q1: Which property allows metals to be beaten into thin sheets?
a) Ductility
b) Malleability
c) Sonority
d) Conduction
Ans: b
Malleability is the property that allows metals to be shaped into thin sheets without breaking, unlike ductility, which refers to stretching.
Q2: Which metal is liquid at room temperature?
a) Iron
b) Copper
c) Mercury
d) Aluminium
Ans: c
Mercury is the only metal that remains liquid at room temperature, while the others are solid.
Q3: What sound do metals produce when struck, due to their sonority?
a) Dull thud
b) Ringing sound
c) Squeaking noise
d) No sound
Ans: b
Metals produce a ringing sound when struck, which is a characteristic of their sonority.
Q4: Which non-metal is brittle and breaks when struck?
a) Coal
b) Copper
c) Gold
d) Iron
Ans: a
Coal is a non-metal that is brittle and breaks upon impact, unlike metals which are malleable.
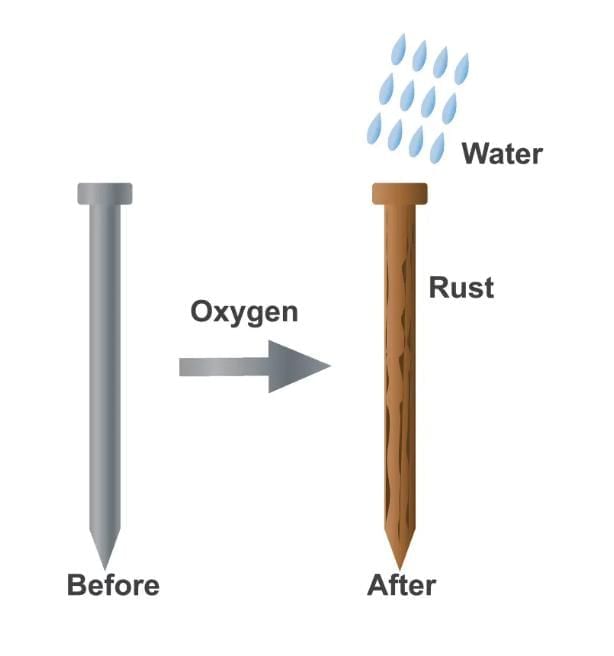
Q5: What is required for iron to rust?
a) Air only
b) Water only
c) Both air and water
d) Heat only
Ans: c
Iron rusts when it comes into contact with both air and water, which facilitates the oxidation process.
Q6: Which metal is stored in kerosene to prevent reaction with air?
a) Magnesium
b) Sodium
c) Aluminium
d) Copper
Ans: b
Sodium is highly reactive with air and water, hence it is stored in kerosene to prevent such reactions.
Q7: What is the nature of sulfur dioxide when dissolved in water?
a) Basic
b) Neutral
c) Acidic
d) Insulating
Ans: c
When dissolved in water, sulfur dioxide forms a solution that is acidic, which can turn blue litmus paper red.
Q8: Which non-metal is essential for breathing?
a) Nitrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Sulfur
d) Phosphorus
Ans: b
Oxygen is vital for respiration in living organisms, unlike the other options which are not essential for breathing.
Q9: What prevents rusting by coating iron with zinc?
a) Painting
b) Greasing
c) Galvanisation
d) Burning
Ans: c
Galvanisation involves coating iron with zinc, which protects it from rusting by preventing moisture and air contact.
Q10: Why was copper used before iron in ancient civilizations?
a) It is stronger
b) It occurs naturally in pure form and has a lower melting point
c) It does not rust
d) It is more ductile
Ans: b
Copper was favored because it can be found in a pure state and has a lower melting point, making it easier to work with than iron.
Q11: Define malleability and give one example of its use in daily life.
Ans: Malleability is the ability of a material to be beaten into thin sheets without breaking. An example is aluminium foil used for wrapping food.
Q12: What is ductility, and name a metal used in electrical wiring due to this property?
Ans: Ductility is the property of a material that allows it to be stretched into thin wires without breaking. One common metal known for its ductility is copper, which is widely used in electrical wiring.
Q13: How does sonority benefit everyday objects, with an example?
Ans: Sonority allows metals to produce ringing sounds when struck; this property is used in objects like school bells, which ring loudly to signal time
Q14: Why is wood considered neither malleable nor brittle?
Ans:Wood is neither malleable because it cannot be flattened like metals, nor brittle because it does not break easily like non-metals, having some flexibility.
Q15: What is rusting, and name one method to prevent it?
Ans: Rusting is the chemical reaction where iron reacts with oxygen and moisture to form rust. One prevention method is painting the iron surface.
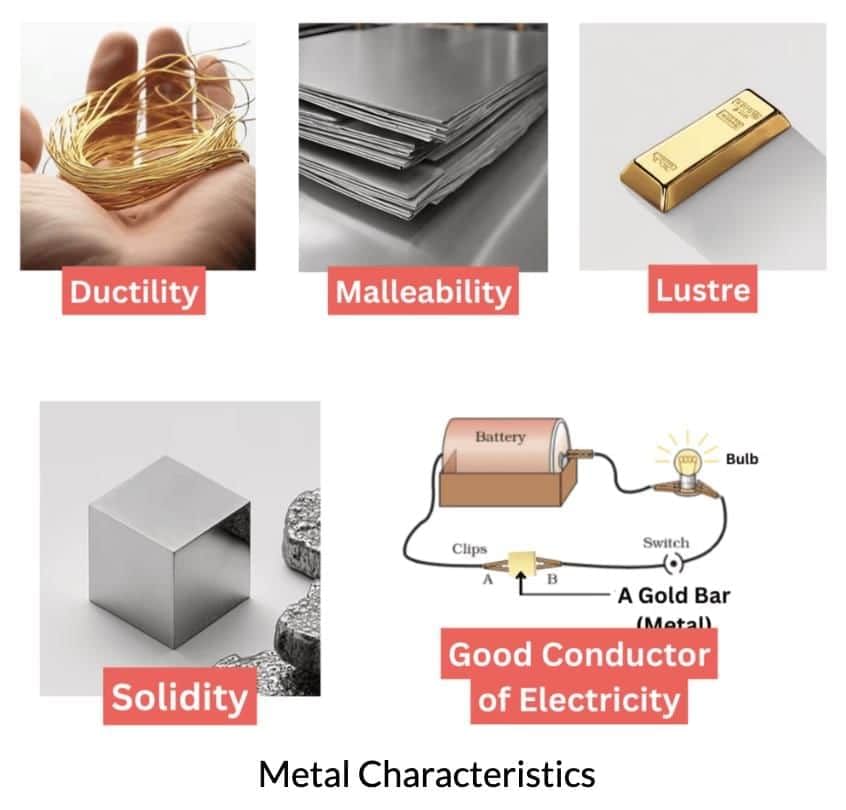
Q16: Explain the properties of metals and non-metals, with examples for each property.
Ans:Metals and non-metals have distinct properties:
Metals:
Malleability: Can be beaten into sheets, e.g., aluminium foil for food wrapping.
Ductility: Can be drawn into wires, e.g., copper for electrical wiring.
Sonority: Produce ringing sounds, e.g., iron in school bells.
Conduction: Good conductors of heat and electricity, e.g., copper in cooking pots.
Lustre: Shiny appearance, e.g., polished silver.
Non-Metals:
Brittleness: Break when struck, e.g., coal shatters.
Non-lustrous: Dull appearance, e.g., sulfur.
Poor conduction: Do not conduct heat/electricity, e.g., wood in pot handles.
Non-sonorous: Produce dull sounds, e.g., wood when dropped.
These properties help classify materials and determine their uses, like metals in tools and non-metals in insulation.
Q17: Describe the process of rusting and its prevention methods, with examples.
Ans: Rusting is a chemical reaction where iron reacts with oxygen and moisture in the air, forming reddish-brown rust, which weakens iron objects like tools or bridges. It requires both air and water; iron does not rust in dry air or water alone. Prevention methods include:
Painting: Coating iron with paint, e.g., painting bridges to block air and moisture.
Oiling/Greasing: Applying oil, e.g., greasing bicycle chains to form a protective layer.
Galvanisation: Coating with zinc, e.g., galvanised iron buckets to prevent rust.
These methods protect iron structures, saving costs on repairs and ensuring safety, as rust makes objects weak and unsafe.
Q18: Discuss the importance of non-metals in daily life, with suitable examples
Ans: Non-metals are essential in daily life despite their differences from metals. Examples include:
Oxygen: Vital for breathing, used in hospitals for patients and in welding processes.
Carbon: The building block of life, found in proteins and carbohydrates for energy and growth.
Nitrogen: Used in fertilizers to help plants grow, supporting agriculture.
Chlorine: Purifies drinking water, ensuring safety.
Iodine: Used as an antiseptic for wounds, preventing infections.
Unlike metals, which are used in tools and wires, non-metals support life, health, and agriculture. Their poor conductivity, like rubber’s use in electrician gloves, ensures safety. These roles highlight non-metals’ critical contributions to human survival and societal functions.
|
80 videos|224 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: The World of Metals and Non-metals - Science (Curiosity) Class 7 - New NCERT
| 1. What are the main differences between metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of common metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How do metals and non-metals react chemically? |  |
| 4. What are the physical properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 5. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |