Hydrosphere Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 5 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Meaning of Hydrosphere and Tides |

|
| Ocean Currents |

|
| Important Ocean Currents and Their Effects |

|
| Ocean Currents: Their Circulation Pattern |

|
The hydrosphere refers to the total amount of water on Earth, including all its forms such as liquid, solid, and vapour. It encompasses oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers, and even the moisture in the atmosphere. Water covers over 70% of the Earth’s surface, playing a vital role in supporting life and regulating the planet’s climate.
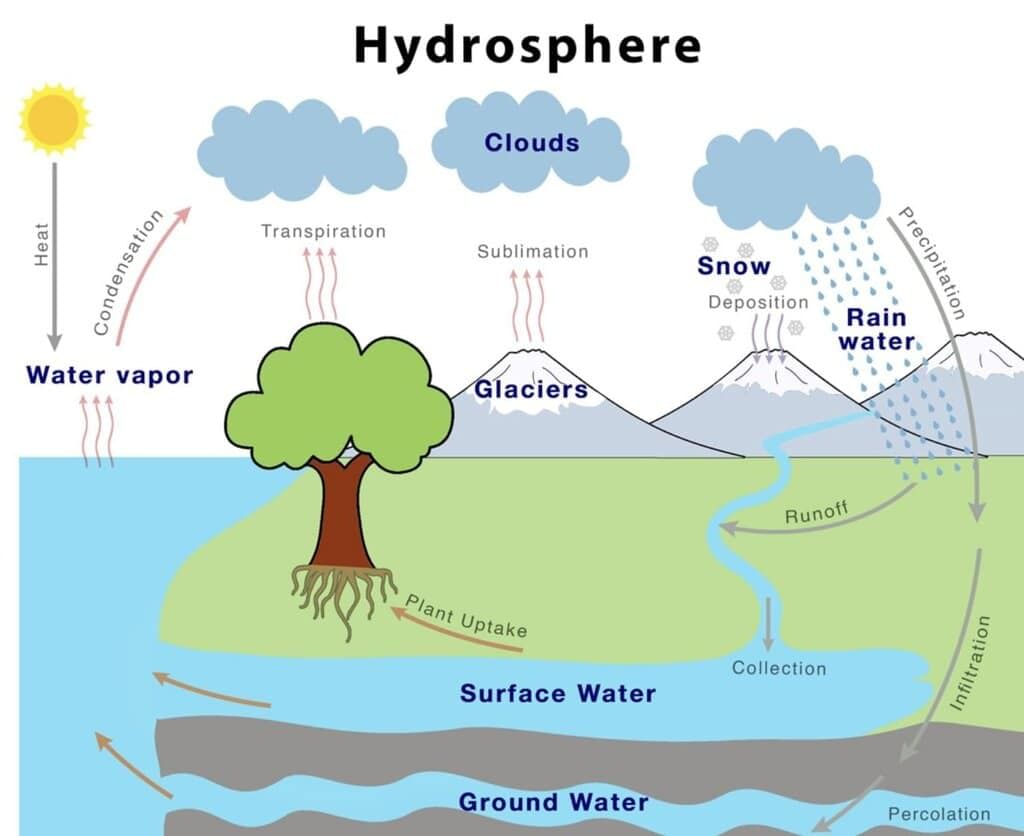
The hydrosphere is not just a passive blanket of water; it is dynamic and constantly interacting with other spheres of the Earth, such as the atmosphere (air), lithosphere (land), and biosphere (living organisms). This interaction is crucial for maintaining the balance of ecosystems and supporting various life forms.
Key Elements of the Hydrosphere
- Water Bodies: The hydrosphere includes all water bodies on Earth, such as vast oceans, flowing rivers, serene lakes, and massive glaciers.
- Climate Regulation: The hydrosphere plays a vital role in regulating the climate and weather patterns of our planet. It helps maintain a balance in temperature and precipitation, which are crucial for sustaining life.
- Tides: Tides are a natural phenomenon within the hydrosphere, influenced by the gravitational pull of the Moon. This pull creates a rhythmic rise and fall of ocean water levels, impacting coastal ecosystems and human activities.
- Ocean Currents: Ocean currents are powerful streams of water within the oceans that help distribute heat and nutrients across the globe. These currents are essential for regulating climate and supporting marine life.
- Interaction with Other Spheres: The hydrosphere does not exist in isolation. It interacts with the atmosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere, creating diverse ecosystems. For example, the evaporation of water from oceans contributes to atmospheric moisture, which in turn affects weather patterns and supports plant life on land.
Meaning of Hydrosphere and Tides
- The hydrosphere is the total mass of water on Earth, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and other water bodies.
- It covers about 71% of Earth's surface, with oceans occupying nearly three-fourths of the total area.
- Ocean water moves in three main ways: waves, ocean currents, and tides.
- Waves are formed by winds blowing over the ocean surface, creating a series of swells that move forward.
- Tides are the regular rise and fall of ocean water levels caused by the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon.
- There are two high tides and two low tides in a 24-hour period, occurring roughly every 6 hours.
- The Moon’s gravitational pull causes a bulge in the ocean water directly beneath it and another bulge on the opposite side of the Earth due to varying gravitational forces. For example, when the Moon is directly overhead, the ocean water in a coastal city like Mumbai bulges towards it, resulting in a high tide. Simultaneously, another high tide occurs on the opposite side of Earth, such as in the Pacific Ocean, due to a weaker gravitational pull.
- High tides occur about 50 minutes later each day because the Moon rises later, and this cycle repeats every 12 hours and 26 minutes.
- The difference in water level between high and low tides, known as the tidal range or amplitude, typically ranges from 1 to 3 meters.
- In open oceans, the tidal range is about 0.5 meters, but in shallow seas, it can reach up to 10 meters.
- Tides change due to the shifting positions of the Sun and Moon relative to Earth, leading to two types: Spring Tides and Neap Tides.
Spring Tides
- Spring tides are higher-than-normal high tides with a range 20% greater than average tides.
- They occur when the Sun, Moon, and Earth are aligned, maximising the combined gravitational pull.
- They happen twice a month, just after the new Moon and full Moon.
- During spring tides, high tides are very high, and low tides are very low.
Neap Tides
- Neap tides are lower-than-normal high tides with a range 20% less than average tides.
- They occur when the Sun, Earth, and Moon form a right angle (quadrature), causing the Sun's gravitational pull to counteract the Moon's.
- They happen twice a month during the first and last quarters of the Moon's cycle.
- During neap tides, high tides are lower, and low tides are higher than normal.
King Tide
- King tides are the highest spring tides, occurring when the Moon is at perigee (closest to Earth) and Earth is at perihelion (closest to the Sun), around January 1st or 2nd.
Effects of Tides
Environmental Effects/Importance
- Tides move coastal debris into the sea, helping to erode coastlines and form creeks and inlets.
- They keep harbours clean by carrying debris and sewage out to sea.
- The mixing of salty seawater and freshwater from rivers during high tides creates unique ecosystems, such as tidal forests like the Sundarbans.
- Sea creatures like oysters and mussels rely on tides to bring food from the sea.
- In polar regions, the constant motion of salty tidal waters prevents harbours from freezing, keeping them ice-free.
Economic Importance
- Tidal energy, which is a renewable energy source, can be harnessed to produce electricity in areas like the Gulf of Khambhat and Kutch in Gujarat.
- Tides facilitate the work of fishermen by making it easier for their boats to go out to sea and return.
- In polar regions, tidal movements create shallow coastal areas where water is gathered for salt production.
- Major ports such as London (on the River Thames) and Kolkata (on the Hooghly River) rely on tides to assist with ship movement during high tides.
Key Words
- Amplitude of tides: Average difference in water levels between high and low tides.
- Perigee: The point in the Moon’s orbit when it is closest to Earth.
- Perihelion: The point in Earth’s orbit when it is closest to the Sun.
- Quadrature: The position of the Moon or a planet when it is 90° from the Sun as seen from Earth.
- Creek: A narrow inlet of the sea along the shore.
- Renewable Energy: Energy from natural sources like sunlight, wind, tides, waves, and geothermal heat.
- Estuarine river: A river with an estuary at its mouth.
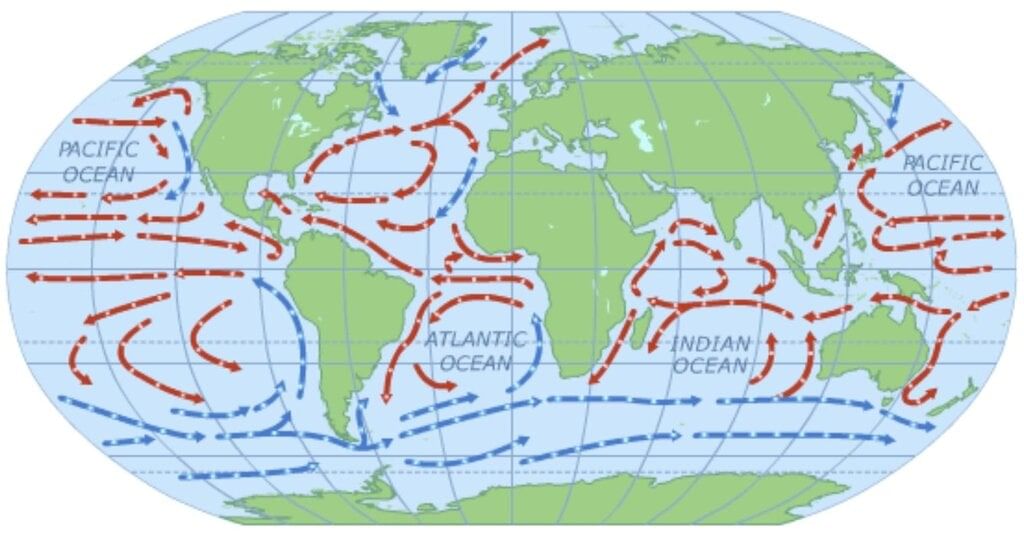
Ocean Currents
- Ocean currents are regular movements of ocean water along specific paths over long distances.
- They are classified into warm and cold currents based on water temperature.
- Example: The Gulf Stream, a warm current, flows along the eastern coast of the USA, raising coastal temperatures, while the Labrador Current, a cold current, cools the Canadian coast.
 Ocean Currents
Ocean Currents
Factors Influencing Ocean Currents
- Prevailing Winds: Winds play a crucial role in driving ocean currents. For example, the North-East Trade Winds push the North Equatorial Current, which warms Japan’s coast. Similarly, the Westerlies carry the Gulf Stream towards Europe, where it becomes the North Atlantic Drift.
- Sea Water Temperature: Warm currents typically start at the Equator and flow towards the poles at the surface, while colder, denser water from polar regions moves towards the Equator at deeper levels.
- Salinity: The salinity of seawater affects its density. Water with low salinity is lighter and tends to flow above denser, high-salinity water. For instance, North Atlantic currents with lower salinity enter the Mediterranean Sea through the Strait of Gibraltar.
- Earth’s Rotation and Coriolis Force: The Coriolis Effect, resulting from Earth’s rotation, causes ocean currents to deflect to the right (clockwise) in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left (anti-clockwise) in the Southern Hemisphere, as explained by Ferrel’s Law.
- Configuration of Landmasses: The shape and configuration of landmasses influence the paths of ocean currents. For example, the shape of South America divides the North Equatorial Current into the Cayenne Current (flowing northward) and the Brazilian Current (flowing southward).
- Gyres: Gyres are large circular patterns of ocean currents formed by the surrounding continents and water bodies. These are particularly prominent in the Northern Hemisphere. Gyres play a vital role in ocean circulation and ecosystems by distributing nutrients and heat. For instance, the North Atlantic gyre includes the Gulf Stream, North Atlantic Drift, and Canary Current, encircling the Sargasso Sea, which is filled with floating seaweed.
Important Ocean Currents and Their Effects
Atlantic Ocean
Gulf Stream (Warm):
- Flows along Florida and eastern USA coasts up to the Grand Banks.
- Raises coastal temperatures in Florida and the USA.
- Meets the cold Labrador Current near Newfoundland, creating fog that hinders shipping but supports fishing at the Grand Banks due to nutrient mixing.
North Atlantic Drift (Warm):
- Flows eastward to Britain and northward along the Scandinavian coast.
- Keeps Western Europe, especially the UK, warm.
- Keeps the Norwegian coast ice-free, aiding navigation and shipping.
Labrador Current (Cold):
- Flows southeast along Greenland and Canada’s northeast coast.
- Brings icebergs, cooling the Canadian coast.
- Meets the Gulf Stream, causing fog that affects shipping but promotes plankton growth, creating the Grand Banks fishing ground.
Pacific Ocean
Kuroshio (Warm):
- Flows along Japan’s east coast.
- Raises coastal temperatures, preventing freezing in January.
- Supports Japan’s coral reefs and makes southern Alaska’s weather milder.
Oyashio (Cold):
- Flows south from the Okhotsk Sea, meeting the Kuroshio off Hokkaido.
- Lowers temperatures in northwest Japan and northeast Russia.
- Creates fog and nutrient-rich waters, supporting the world’s richest fishing grounds due to plankton growth.
Effects of Ocean Currents
Environmental/Climatic Effects
- Warm currents raise coastal temperatures and bring rainfall, while cold currents lower temperatures and dry the air, e.g., the Atacama and Kalahari Deserts are dry due to cold currents.
- Currents influence cyclonic storm paths, with violent storms following the meeting points of warm and cold currents.
- The mixing of warm and cold currents creates dense fog, which is hazardous for shipping due to water vapor condensation.
Economic Effects
- Mixing of warm and cold currents creates ideal temperatures for plankton growth, supporting fishing industries.
- Currents aid faster ship movement, improving trans-oceanic communication.
- Warm currents keep harbours in cold regions ice-free, enabling year-round trade.
Ocean Currents: Their Circulation Pattern
- Ocean currents transfer heat from the Equator to the poles, regulating climate.
- They carry nutrients and food to stationary marine organisms and spread reproductive cells to new areas.
- Ocean circulation is driven by two types:
- Wind-driven circulation: Powered by wind stress on the sea surface, creating vigorous gyres in the surface layer.
- Thermohaline circulation: Driven by variations in water density due to heat and water exchange with the atmosphere, moving slowly (1 cm/s or 0.4 inch/s) but extending to the sea floor, forming global patterns.
- Wind-driven and thermohaline circulations are interconnected, as sea-air exchanges depend on wind speed.
Key Words
- Configuration of landmass: The arrangement or shape of landmasses.
- Seismic waves: Earthquake waves.
- Gyre: Large circulating ocean current systems influenced by the Coriolis Effect.
- Plankton: Small, microscopic organisms drifting in the sea or freshwater.
|
44 videos|128 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Hydrosphere Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 5
| 1. What is the hydrosphere and what are its main components? |  |
| 2. How do tides occur and what factors influence them? |  |
| 3. What are ocean currents and why are they important? |  |
| 4. Can you name some important ocean currents and their effects on climate and marine life? |  |
| 5. What are the circulation patterns of ocean currents and how do they affect global climate? |  |




















