Worksheet With Solutions: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | Chemistry Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section A: Fill In The Blanks |

|
| Section B: Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Section C: Assertion and Reason |

|
| Section D: Answer the following Questions |

|
Section A: Fill In The Blanks
Q1: Ethyl bromide on reaction with moist silver gives ____________as the main product. The well-known refrigerant Freon has the structure ____________
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Ethene, CCl₂F₂
Explanation: Ethyl bromide (C₂H₅Br) reacts with moist silver (Ag) to eliminate HBr, forming ethene (C₂H₄) as the main product. Freon-12, a common refrigerant, has the molecular formula CCl₂F₂.
Q2: In SN1 mechanism,____________ are involved as intermediate species. Formation of phenol from chlorobenzene is an example of aromatic substitution.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Carbocations
Explanation: SN1 (Substitution Nucleophilic Unimolecular) reactions involve the formation of a carbocation intermediate. Phenol formation from chlorobenzene is a nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
Q3: Bleaching powder, on treatment with ethanol or acetone, gives____________ .This is an example of____________ reaction. Butane nitrile can be prepared by heating ____________ with alcoholic KCN.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Chloroform, haloform, 1-bromobutane
Explanation: Bleaching powder reacts with ethanol or acetone to give chloroform (CHCl₃) via the haloform reaction. Butane nitrile (CH₃CH₂CH₂CN) is prepared by heating 1-bromobutane with alcoholic potassium cyanide (KCN).
Q4: Vinyl chloride on reaction with dimethyl copper gives ____________. The trade name of carbon tetrachloride is____________ .
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Propene, tetrachloromethane
Explanation: Vinyl chloride (CH₂=CHCl) reacts with dimethyl cuprate to form propene (CH₂=CHCH₃). Carbon tetrachloride (CCl₄) is also known as tetrachloromethane commercially.
Q5: In alkyl halides, due to greater polarity and higher molecular mass as compared to parent hydrocarbons, the intermolecular ____________ and ____________ forces are stronger in halogen derivatives.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Dipole–dipole, van der Waals
Explanation: Alkyl halides exhibit stronger dipole–dipole interactions and van der Waals forces than hydrocarbons due to higher electronegativity and molecular mass of halogens.
Section B: Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. What is the class of the substitution product of LiAlH4 and an alkyl halide reaction?
(a) Haloalkane
(b) Alkyl nitrite
(c) Nitroalkane
(d) Hydrocarbon
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: d
Explanation: The H atom in LiAlH4 acts as a nucleophile, attacking and substituting the halogen in the alkyl halide to generate the basic hydrocarbon.
Q2. Which of the following statements about SN2 mechanisms is incorrect?
(a) The transition state is stable
(b) The complete mechanism takes place in a single step
(c) The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of both reactants
(d) There is an inversion of configuration
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: a
Explanation: The carbon atoms are concurrently attached to the entering nucleophile and the existing group in the transition state of SN2 processes, and are thus connected to five atoms at the same time. It is impossible to isolate such a geometry since it is unstable.
Q3. A mono haloarene is an example of __________
(a) aliphatic halogen compound
(b) side-chain substituted aryl halide
(c) alkyl halide
(d) aromatic halogen compound
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: d
Explanation: A mono haloarene is a halogenated benzene ring with the halogen linked straight to it. Aromatic halogen compounds with the halogen not directly linked to the benzene ring are side chain substituted aryl halides.
Q4. What is 3-Bromopropene’s common name?
(a) Allyl bromide
(b) Vinyl bromide
(c) Tert-Butyl bromide
(d) Propylidene bromide
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: a
Explanation: The parent chain of 3-Bromopropene has three C atoms, with a double bond at C-1 and Br at C-3. As a result, it is an allylic halide because Br is connected to the C adjacent to the C-C double bond.
Q5. Which of the following is the right name for the compound H3C-CHCl2?
(a) 1,2-Dichloroethane
(b) Ethylene dichloride
(c) Ethylidene chloride
(d) Vic-dichloride
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: c
Explanation: Both halogens are on the same carbon atom in the given molecule, making it a dihaloalkane. These are also known as alkylidene halides or gem-dihalides.
Q6. What is the catalyst in the chloroalkane reaction of a primary alcohol with HCl?
(a) red phosphorous
(b) concentrated H2SO4
(c) anhydrous ZnCl2
(d) pyridine
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: c
Explanation: The presence of anhydrous ZnCl2 in alcohols is supposed to disrupt the C-O bond. ZnCl2 is a Lewis acid that reacts with the alcohol group’s oxygen.
Section C: Assertion and Reason
Directions: These questions consist of two statements, each printed as Assertion and Reason. While answering these questions, you are required to choose any one of the following four responses.
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are correct and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(b) If both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
(c) If the Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(d) If both the Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Q1: Assertion : SN2 reaction of an optically active aryl halide with an aqueous solution of KOH always gives an alcohol with opposite sign of rotation.
Reason : SN2 reactions always proceed with inversion of configuration.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d)
Explanation: Assertion is false, because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions. This is due to resonance, because of which the carbon– chlorine bond acquires partial double bond character, hence it becomes shorter and stronger and thus cannot be replaced by nucleophiles. However Reason is true.
Q2: Assertion : Alkylbenzene is not prepared by Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene.
Reason : Alkyl halides are less reactive than acyl halides.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (c)
Explanation: Alkyl halides give polyalkylation products.
Q.3. Assertion : Exposure of ultraviolet rays to human causes the skin cancer, disorder and disrupt the immune system.
Reason : Carbon tetrachloride is released into air it rises to atmosphere and deplets the ozone layer.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (b)
Explanation: Carbon tetrachloride rises to atmosphere and deplete the ozone layer. This depletion of ozone layer increases exposure of UV rays to human being which lead to increase of skin cancer, eye diseases and disorder with disruption of the immune system.
Q4: Assertion : CHCl3 is stored in dark bottles.
Reason : CHCl3 is oxidised in dark.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (c)
Explanation: CHCl3 is stored in dark bottles to prevent oxidation of CHCl3 in presence of sunlight.
Q5: Assertion : CCl4 is not a fire extinguisher.
Reason : CCl4 is insoluble in water.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: (d)
Explanation: CCl4 is used as a fire extinguisher. The dense, non combustible vapours cover the burning substance and prevents the availability of oxygen around burning material.
Section D: Answer the following Questions
Q1: How would you differentiate between S<subN1 and SN2 mechanisms of substitution reactions? Give one example of each.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: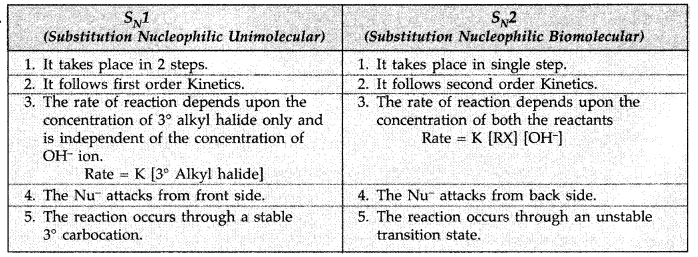
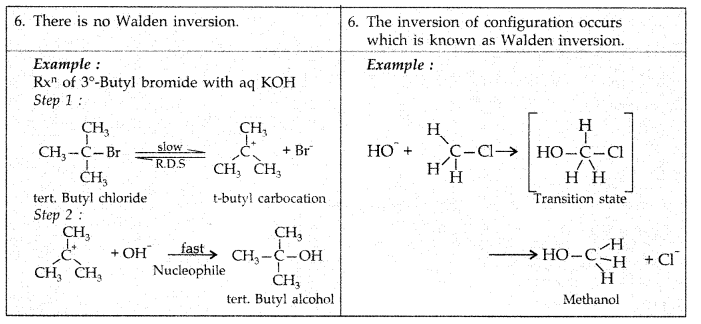
Q2: Rearrange the compounds of each of the following sets in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement :
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) l-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methyl-butane, 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, l-Bromo-2,2-dimethyl-propane, l-Bromo-2-methylbutane
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(i) 1-Bromopentane > 2-Bromopentane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane > 3-Bromo-2 methylbutane > 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane > 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane > 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane.
Q3: Although chlorine is an electron withdrawing group, yet it is ortho-, para-directing in electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Explain why it is so?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:Chlorine withdraws electrons through inductive effect and releases through resonance. Although Cl shows -1 effect but through resonance, Cl tends to stabilize the intermediate carbocation and the effect is more pronounced at ortho and para positions.
This can also be explained diagramatically as: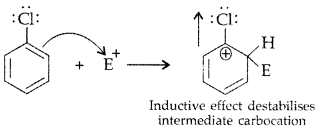
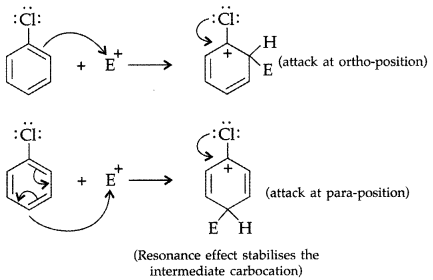
Q4: Answer the following questions:
(i) What is meant by chirality of a compound? Give an example.
(ii) Which one of the following compounds is more easily hydrolyzed by KOH and why?
CH3CHClCH2CH3 or CH3CH2CH2Cl
(iii) Which one undergoes SN2 substitution reaction faster and why?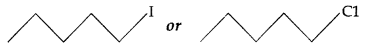
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(i) Chirality : The objects which are non-superimposable on their mirror image are said to be chiral and this property is known as chirality for Butan-2-ol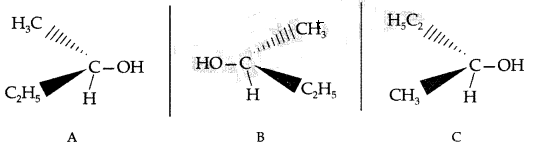 C is non-superimposable on its mirror image A.
C is non-superimposable on its mirror image A. (iii) As I is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophile.
(iii) As I is a better leaving group because of its large size, it will be released at a faster rate in the presence of incoming nucleophile.
Q5: How will you carry out the following conversions :
(i) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(ii) Benzene to p-chloronitrobenzene
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: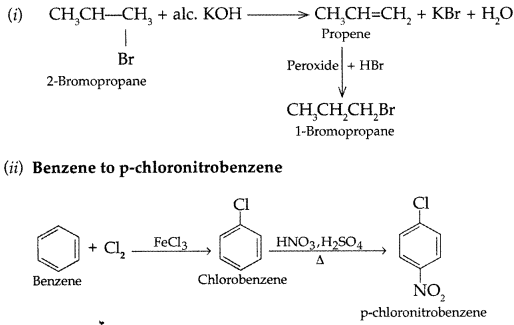
Q6: Answer the following questions:
(i) State one use each of DDT and iodoform.
(ii) Which compound in the following couples will react faster in SN2 displacement and why?
(a) 1-bromopentane or 2-bromopentane
(b) l-bromo-2-methylbutane or 2-bromo-2-methylbutane.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(i) Use of DDT (Dichlorodiphenyl Trichloroethane): As a powerful insecticide, it is widely used for sugarcane and fodder crops to kill mosquitoes, lice which carry pathogens.
Use of iodoform (CHI3) : It is used as an antiseptic for dressing wounds. Its antiseptic action is due to liberation of iodine when iodoform comes in contact with skin but not due to iodoform itself.
(ii) In SN2 reactions, reactivity depends upon steric hindrance
(a) 1-Bromopentane (1° halogen) having less steric hindrance therefore is more reactive than 2-Bromopentane hence undergoes SN2 reactions faster.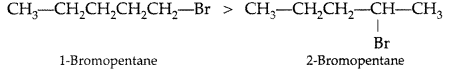 (b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane having less steric hindrance, is thus more reactive towards SN2 reaction than 2-bromo-2-methyl butane (more steric hindrance).
(b) 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane having less steric hindrance, is thus more reactive towards SN2 reaction than 2-bromo-2-methyl butane (more steric hindrance).
Q7: (i) o-nitrophenol has lower b.p. than p-nitro-phenol. Explain.
(ii) Write IUPAC name of the following: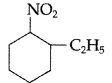
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(i) Ortho-nitrophenol has lower boiling point due to formation of intramolecular H-bonding whereas p-nitrophenol forms intermolecular H-bonding.
(ii) IUPAC name : 2-ethyl-l-nitrocyclohexane
Q8: (a) Write the structural formula of A, B, C and D in the following sequence of reaction: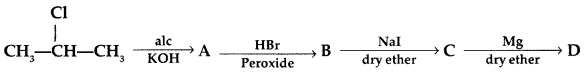 (b) Illustrate Sandmeyer’s reaction with the help of a suitable example.
(b) Illustrate Sandmeyer’s reaction with the help of a suitable example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: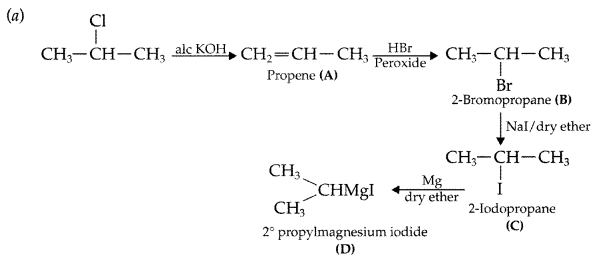 (b) Sandmeyer’s reaction: The substitution of diazo group of benzene diazonium chloride by Chloro, Bromo and Cyano group with the help of solution of CuCl dissolved in HC1, CuBr/HBr and CuCN/KCN respectively is known as Sandmeyer’s reaction.
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction: The substitution of diazo group of benzene diazonium chloride by Chloro, Bromo and Cyano group with the help of solution of CuCl dissolved in HC1, CuBr/HBr and CuCN/KCN respectively is known as Sandmeyer’s reaction.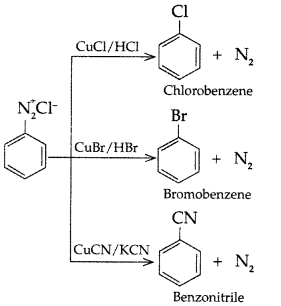
Q9: (a) Account for the following :
(i) Electrophilic substitution reactions in haloarenes occur slowly.
(ii) Haloalkanes, though polar, are insoluble in water.
(b) Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
2-Bromo-2-Methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
(a) (i) Due to -I effect of halogen atom, it withdraws electrons from the benzene ring and thus ring gets deactivated.
(ii) They fail to form hydrogen bonds with water. More energy is required to break hydrogen bonds in water and less energy is released when new attractions are set up.
(b) 2-Bromo-2-Methylbutane < 2-Bromopentane < 1-Bromopentane
Q10: What happens when
(i) CH3—Cl is treated with aqueous KOH?
(ii) CH3—Cl is treated with KCN?
(iii) CH3—Br is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: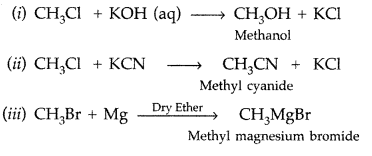
|
75 videos|278 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet With Solutions: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Chemistry Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 2. What are the main methods for synthesizing haloalkanes? |  |
| 3. What are the physical properties of haloalkanes and haloarenes? |  |
| 4. What are the uses of haloalkanes and haloarenes in industry? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of studying haloalkanes and haloarenes in organic chemistry? |  |




















