NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 11 > Cheat Sheet : Body Fluids and Circulation
Cheat Sheet : Body Fluids and Circulation | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
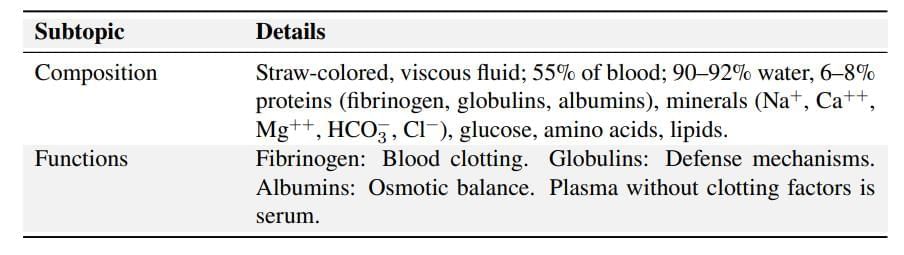
Blood (Plasma)
Formed Elements
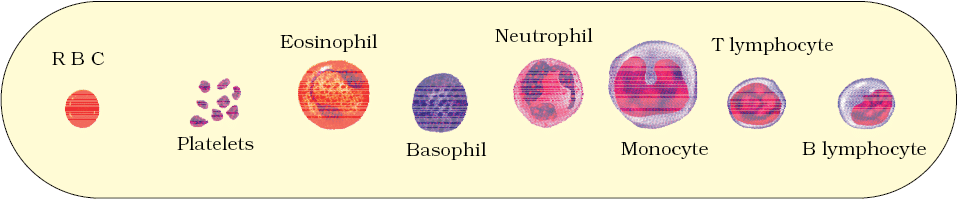 Formed Elements
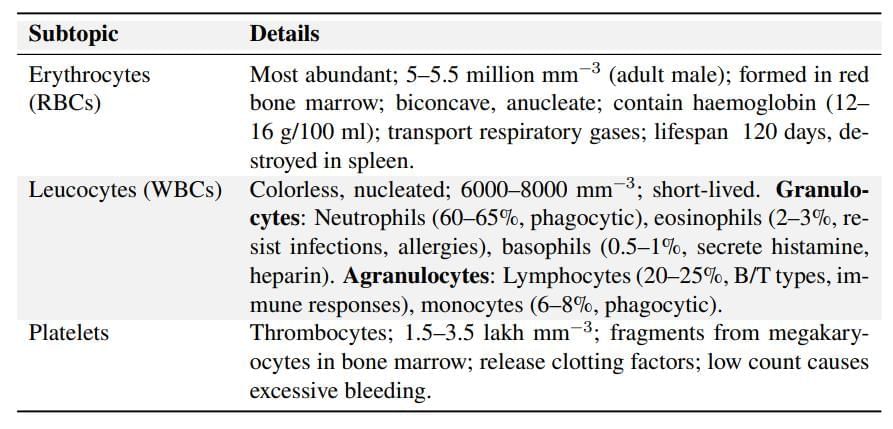
Formed Elements
Blood Groups
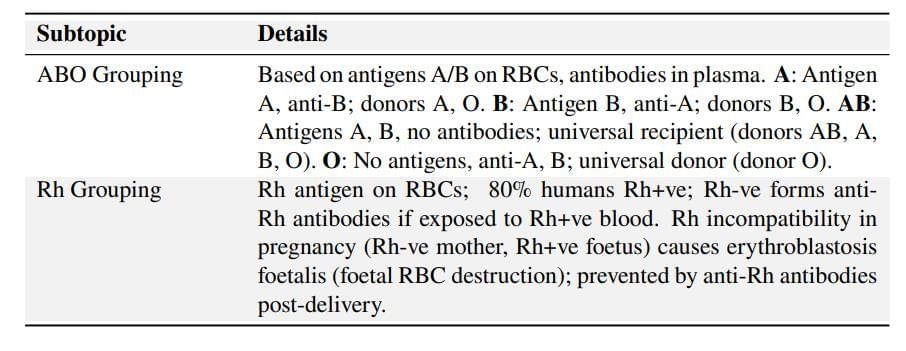
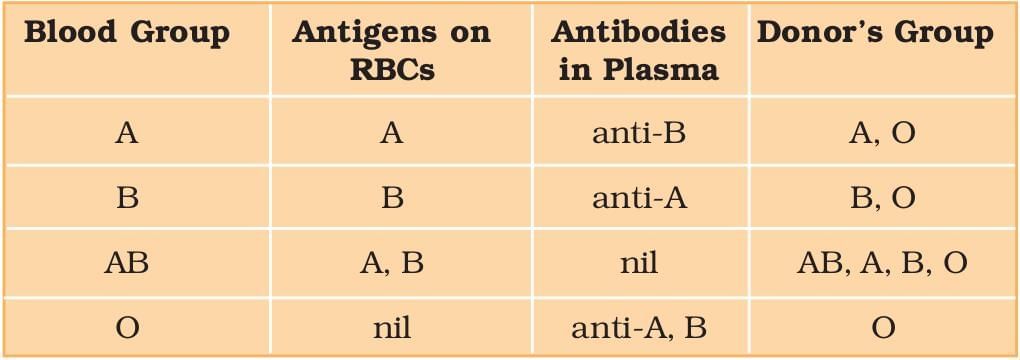 Blood Groups and Donor Compatibility
Blood Groups and Donor Compatibility
Coagulation of Blood
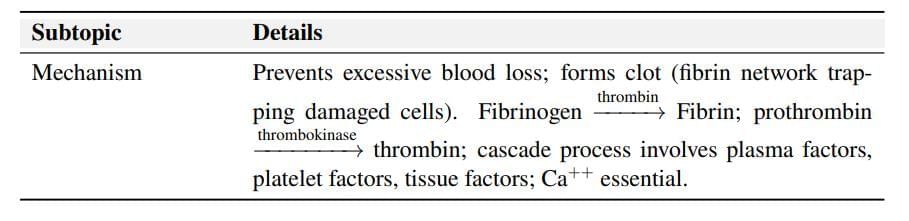
Lymph (Tissue Fluid)
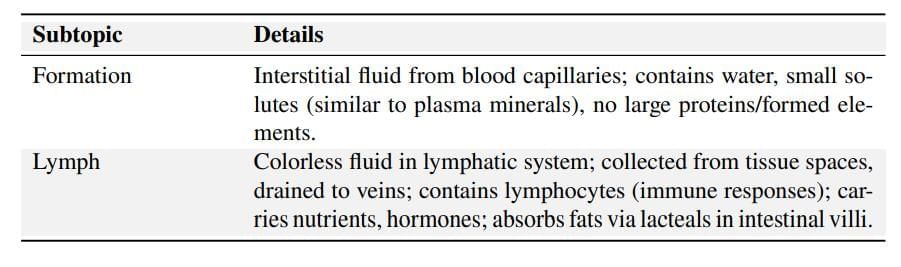
Types of Circulatory Systems
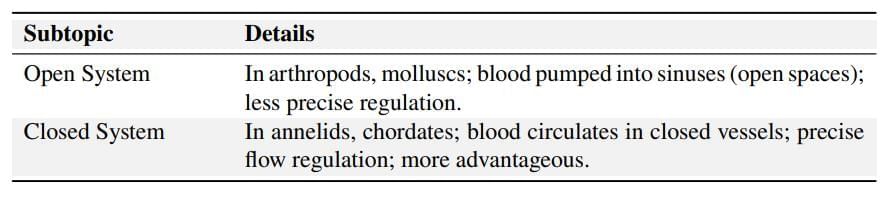
Vertebrate Heart Evolution

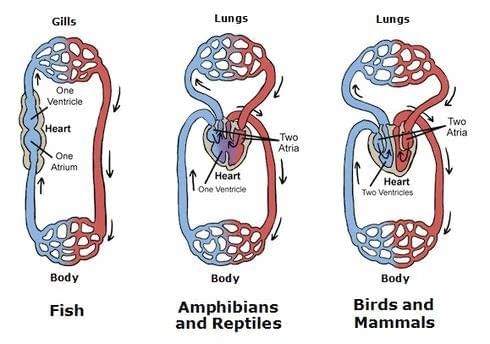 Heart Structures and Circulation in Different Vertebrates
Heart Structures and Circulation in Different Vertebrates
Human Circulatory System
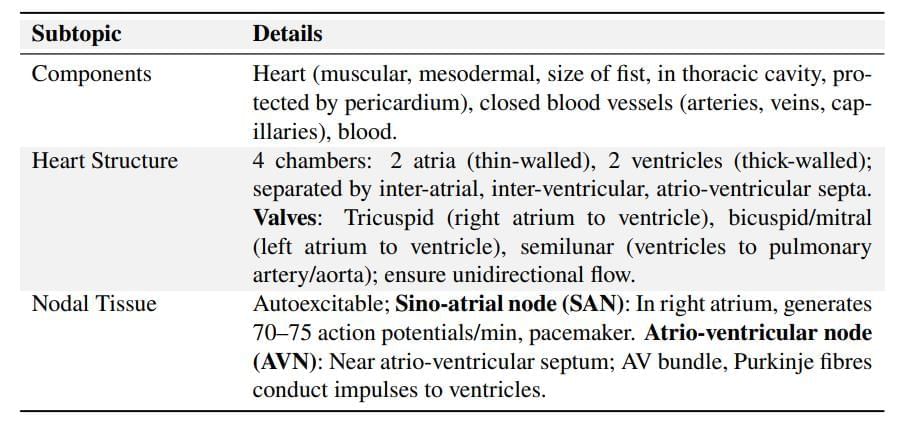
Double Circulation
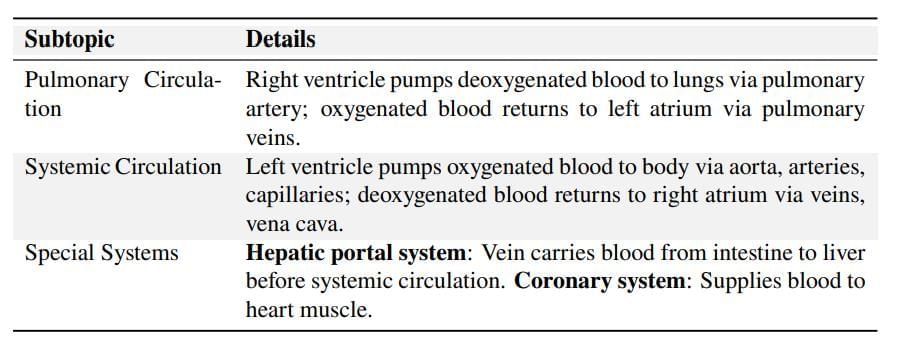
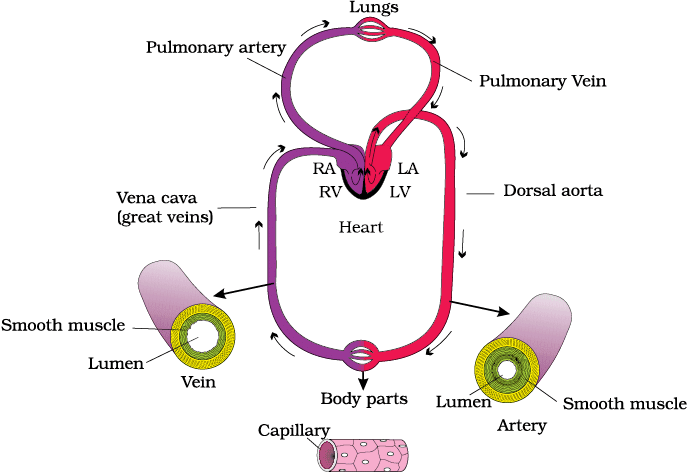 Schematic plan of blood circulation in human
Schematic plan of blood circulation in human
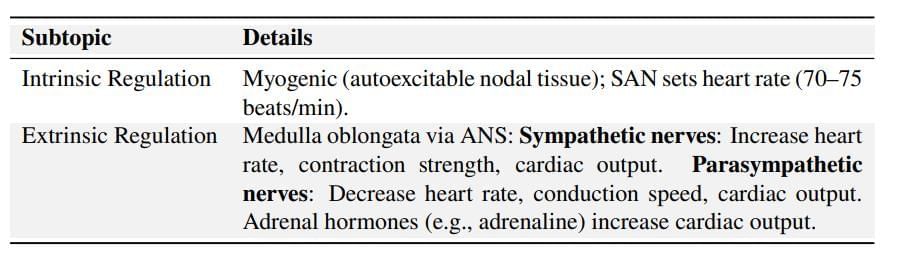
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
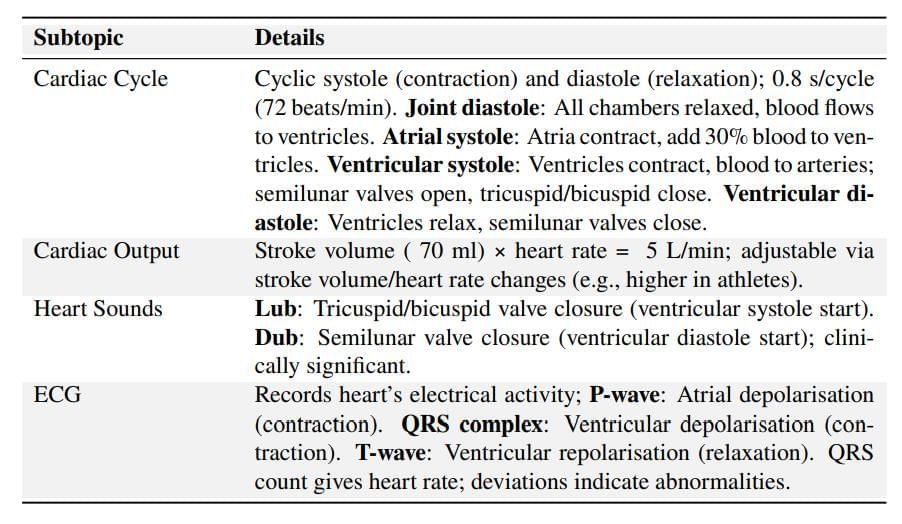
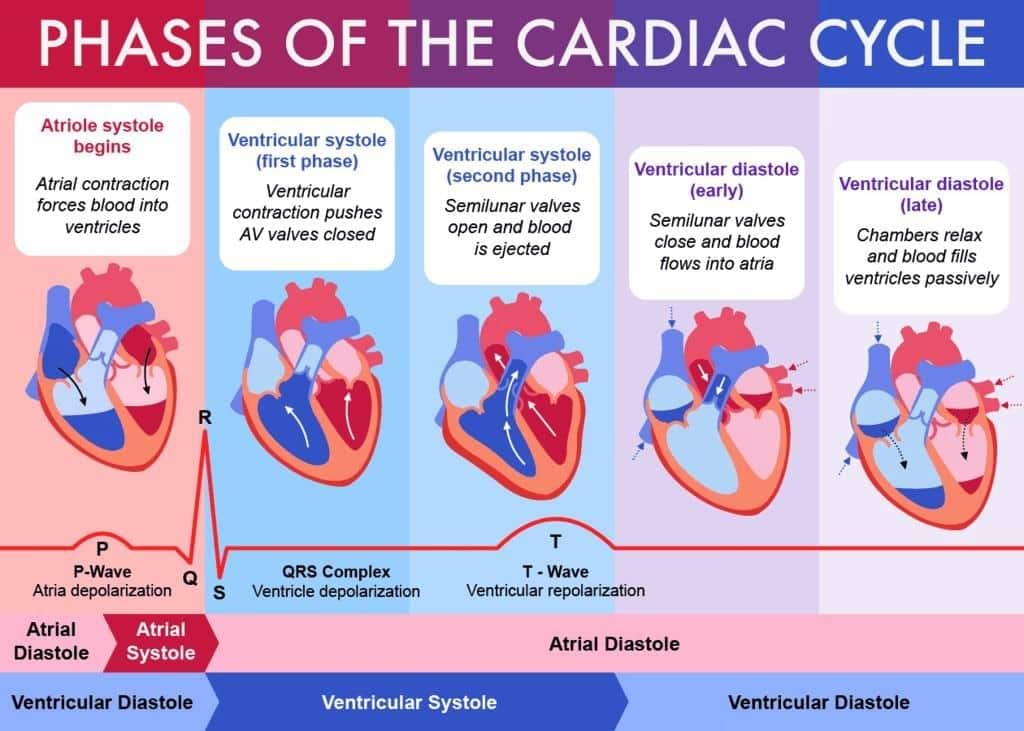
Cardiac Cycle and ECG
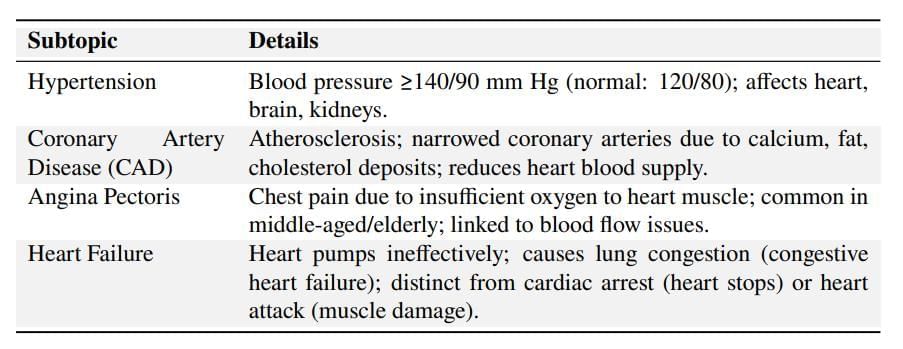
Disorders of Circulatory System
The document Cheat Sheet : Body Fluids and Circulation | Biology Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet : Body Fluids and Circulation - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main components of body fluids? |  |
Ans. The main components of body fluids include water, electrolytes, proteins, nutrients, hormones, and waste products. Water constitutes the largest part of body fluids, while electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are crucial for maintaining fluid balance and nerve function. Proteins such as albumin play key roles in maintaining osmotic pressure and transporting substances.
| 2. How does blood circulation work in the human body? |  |
Ans. Blood circulation in the human body involves two primary circuits: the systemic circulation and the pulmonary circulation. The heart pumps oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle into the aorta, which distributes it throughout the body (systemic circulation). After delivering oxygen and nutrients, blood returns to the right atrium via veins. The right ventricle then pumps this deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation (pulmonary circulation), where carbon dioxide is expelled and oxygen is absorbed before the blood returns to the left atrium to repeat the cycle.
| 3. What is the role of the lymphatic system in body fluid regulation? |  |
Ans. The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in regulating body fluids by collecting excess interstitial fluid from tissues, which helps prevent edema. It transports this fluid, now called lymph, through lymphatic vessels back into the circulatory system. Additionally, the lymphatic system is essential for immune function, as it filters lymph through lymph nodes to remove pathogens and foreign particles.
| 4. What are the differences between arterial and venous blood? |  |
Ans. Arterial blood is oxygen-rich and bright red, as it carries oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues. It is under higher pressure due to the force generated by the heart's pumping action. In contrast, venous blood is oxygen-poor and darker red, transporting carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes back to the heart and lungs for removal. Venous blood operates under lower pressure and has valves to prevent backflow.
| 5. How do body fluids affect homeostasis? |  |
Ans. Body fluids are vital for maintaining homeostasis, which is the body's stable internal environment. They help regulate temperature, pH levels, and electrolyte balance. By facilitating the transport of nutrients, gases, and waste products, body fluids ensure that cells function optimally. Any imbalance in body fluids can disrupt homeostasis, leading to conditions such as dehydration, overhydration, or electrolyte imbalances, which can significantly affect health.
Related Searches
















