Class 2 Exam > Class 2 Notes > EVS for Class 2 > Mind Map: Plants
Mind Map: Plants | EVS for Class 2 PDF Download
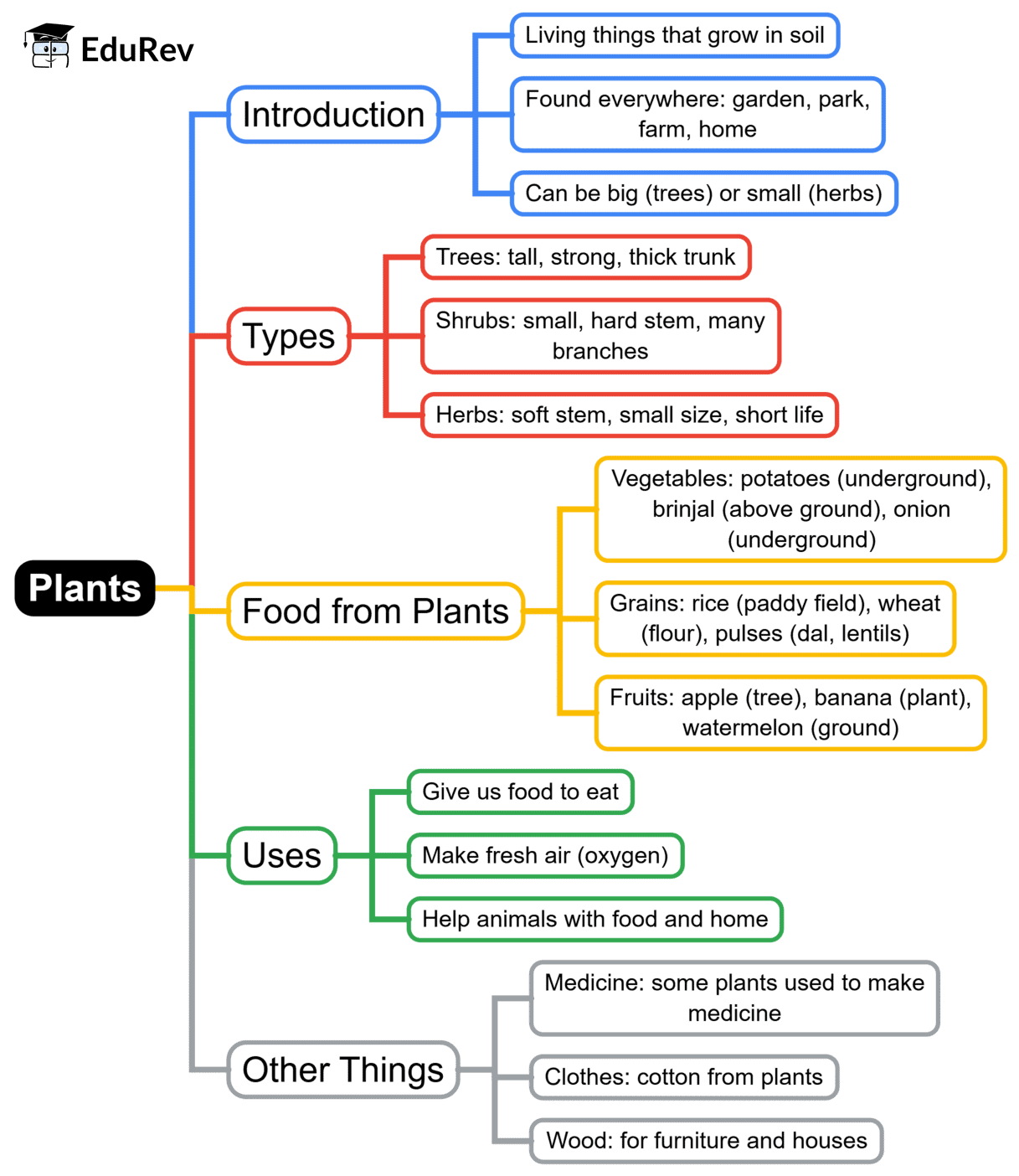
The document Mind Map: Plants | EVS for Class 2 is a part of the Class 2 Course EVS for Class 2.
All you need of Class 2 at this link: Class 2
|
30 videos|243 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Plants - EVS for Class 2
| 1. What are the different types of plants and how are they classified? |  |
Ans.Plants are primarily classified into three main categories: vascular plants, non-vascular plants, and seed plants. Vascular plants, which include ferns, gymnosperms, and angiosperms, have specialized tissues for transporting water and nutrients. Non-vascular plants, such as mosses and liverworts, lack these tissues and generally thrive in moist environments. Seed plants are further divided into two groups: gymnosperms, which produce seeds not enclosed in an ovary, and angiosperms, which produce seeds within fruits.
| 2. What is photosynthesis and why is it important for plants? |  |
Ans.Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, using carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen. This process is crucial for plants as it allows them to create their own food, serving as a primary energy source. Additionally, photosynthesis plays a vital role in regulating atmospheric oxygen levels and supporting life on Earth by providing food and oxygen to other organisms.
| 3. How do plants reproduce, and what are the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction? |  |
Ans.Plants can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of male and female gametes, leading to the formation of seeds. This method promotes genetic diversity. In contrast, asexual reproduction occurs without the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent plant. Common methods of asexual reproduction include budding, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation. Each method has its advantages, such as rapid population increase in asexual reproduction, while sexual reproduction enhances adaptability.
| 4. What role do plants play in an ecosystem? |  |
Ans.Plants play a fundamental role in ecosystems by acting as primary producers. They convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis, forming the base of the food chain. Plants also provide habitat and food for numerous organisms, contribute to soil health through nutrient cycling, and help regulate water cycles. Additionally, they play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, which is essential for mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
| 5. How can I care for indoor plants to ensure they thrive? |  |
Ans.Caring for indoor plants involves several key practices. First, ensure they receive adequate light, as different plants have varying light requirements. Regular watering is essential, but overwatering should be avoided; check the soil moisture before watering. Additionally, use appropriate soil and fertilizers to provide necessary nutrients. It's also important to maintain humidity levels and monitor for pests. Regularly pruning dead leaves and stems can promote healthy growth and improve the plant's overall appearance.
Related Searches
















