Worksheet with Solutions: Human Reproduction | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Section A. Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The pouch that maintains the low temperature of the testes is called ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Scrotum
Q2: The process of formation of sperms in the testes is called ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Spermatogenesis
Q3: The female reproductive cycle in primates is known as the ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Menstrual cycle
Q4: The finger-like projections on the trophoblast after implantation are called ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Chorionic villi
Q5: The hormone secreted by the maternal pituitary that induces stronger uterine contractions during parturition is ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Oxytocin
Section B. Match the Column
Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
1. Leydig cells | A. Secretes milk in mammary glands |
2. Sertoli cells | B. Synthesise androgens |
3. Graafian follicle | C. Nourish germ cells |
4. Corpus luteum | D. Releases secondary oocyte |
5. Alveoli | E. Secretes progesterone |
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 1 - B, 2 - C, 3 - D, 4 - E, 5 - A
Section C. Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Which cells in the seminiferous tubules provide nutrition to the developing germ cells?
(a) Leydig cells
(b) Sertoli cells
(c) Spermatogonia
(d) Secondary spermatocytes
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Sertoli cells
Q2: What is the ploidy of the secondary oocyte before fertilisation?
(a) Diploid
(b) Haploid
(c) Triploid
(d) Tetraploid
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Haploid
Q3: Which phase of the menstrual cycle involves the breakdown of the endometrial lining?
(a) Follicular phase
(b) Ovulatory phase
(c) Luteal phase
(d) Menstrual phase
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Menstrual phase
Q4: Where does fertilisation typically occur in the female reproductive system?
(a) Uterus
(b) Ampullary region of fallopian tube
(c) Infundibulum of fallopian tube
(d) Vagina
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Ampullary region of fallopian tube
Q5: Which structure connects the embryo to the placenta during pregnancy?
(a) Chorionic villi
(b) Umbilical cord
(c) Trophoblast
(d) Inner cell mass
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Umbilical cord
Section D. Assertion Reasoning Questions
Q1: Assertion: Spermatogenesis begins at puberty due to increased secretion of GnRH.
Reason: GnRH directly stimulates the testes to produce testosterone.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
At puberty, the hypothalamus increases the secretion of GnRH (Gonadotropin-releasing hormone). GnRH acts on the anterior pituitary, stimulating it to release LH (Luteinizing Hormone) and FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone). These two hormones are essential for spermatogenesis:
LH stimulates Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone.
FSH acts on Sertoli cells, which support and nourish developing sperm.
Therefore, while GnRH initiates the hormonal cascade that leads to spermatogenesis, it does not directly stimulate the testes to produce testosterone—LH does that. Hence, both statements are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Q2: Assertion: Implantation occurs when the blastocyst embeds in the endometrium of the uterus.
Reason: The trophoblast layer of the blastocyst attaches to the endometrium, and uterine cells cover it.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Implantation is the process where the blastocyst embeds itself into the endometrial lining of the uterus, usually around 6–7 days after fertilization. The outer cell layer of the blastocyst, called the trophoblast, plays a key role in this process.
The trophoblast cells secrete enzymes that allow the blastocyst to attach to and invade the endometrium.
As implantation proceeds, uterine endometrial cells proliferate and cover the implanted blastocyst, securing it in place.
Thus, both the assertion and the reason are correct, and the reason clearly explains the mechanism behind implantation.
Section E. Case-Based Questions
Case 1: Gametogenesis in Humans
Gametogenesis is the process of gamete formation in the primary sex organs, differing significantly between males and females. In males, spermatogenesis produces sperms, while in females, oogenesis produces ova. Describe the process of spermatogenesis in males. How does Oogenesis differ from Spermatogenesis?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
Spermatogenesis in Males
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Diploid spermatogonia multiply by mitosis, and some differentiate into primary spermatocytes. Each primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to form two haploid secondary spermatocytes, which undergo meiosis II to produce four haploid spermatids. Spermatids transform into spermatozoa through spermiogenesis and are released via spermiation.
Oogenesis differ from spermatogenesis in following ways
Oogenesis begins during embryonic development, forming primary oocytes that arrest in prophase-I until puberty. At puberty, primary oocytes complete meiosis I to form a secondary oocyte and a first polar body. The secondary oocyte arrests in meiosis II until fertilisation, producing an ovum and a second polar body. Unlike spermatogenesis, oogenesis produces one functional ovum per cycle, with unequal cytoplasmic division, and ceases at menopause.
Case 2: Fertilisation and Implantation
Fertilisation and implantation are critical reproductive events that lead to pregnancy, occurring in specific regions of the female reproductive system. Explain the process of fertilisation in humans and What is implantation, and where does it occur?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
Process of Fertilisation
During coitus, sperms are released into the vagina and swim through the cervix and uterus to reach the ampullary region of the fallopian tube, where fertilisation occurs. A sperm contacts the zona pellucida of the secondary oocyte, and acrosomal enzymes facilitate penetration. The sperm and ovum nuclei fuse to form a diploid zygote, with the ovum completing meiosis II to form an ootid and a second polar body.
Implantation
Implantation is the embedding of the blastocyst in the endometrium of the uterus. The blastocyst, formed from the zygote through cleavage, consists of a trophoblast and inner cell mass. The trophoblast attaches to the endometrium, and uterine cells cover the blastocyst, completing implantation.
Section F. Short Answer Type
Q1: What is the role of the scrotum in the male reproductive system?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The scrotum maintains the testes at a temperature 2–2.5°C lower than the body temperature, which is necessary for spermatogenesis.
Q2: Describe the structure of the uterus in females.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The uterus is a single, pear-shaped organ with three layers: an outer perimetrium, a middle myometrium (smooth muscle), and an inner endometrium (glandular, undergoes cyclical changes). It opens into the vagina through a narrow cervix, forming part of the birth canal.
Q3: What triggers ovulation during the menstrual cycle?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Ovulation is triggered by a rapid secretion of luteinising hormone (LH) during the mid-cycle, known as the LH surge, which induces rupture of the Graafian follicle to release the secondary oocyte.
Q4: How is the sex of the baby determined during fertilisation?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The sex is determined by the sperm’s sex chromosome (X or Y). If an X-carrying sperm fertilises the ovum (X), the zygote is XX (female); if a Y-carrying sperm fertilises, the zygote is XY (male).
Q5: What is the function of the placenta during pregnancy?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The placenta supplies oxygen and nutrients to the embryo, removes carbon dioxide and waste, and produces hormones like hCG, hPL, estrogens, and progestogens to support pregnancy.
Q6: What is parturition, and what initiates it?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Parturition is the process of childbirth, involving the expulsion of the foetus. It is initiated by signals from the foetus and placenta, causing a foetal ejection reflex that triggers oxytocin release, leading to stronger uterine contractions.
Q7: What is colostrum, and why is it important?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Colostrum is the milk produced in the initial days of lactation, rich in antibodies that provide immunity to the newborn, essential for developing resistance.
Q8: How does the corpus luteum contribute to pregnancy?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The corpus luteum, formed from the Graafian follicle after ovulation, secretes progesterone, which maintains the endometrium for implantation and pregnancy until the placenta takes over.
Section G. Long Answer Type
Q1: Describe the structure and function of the male reproductive system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Structure: The male reproductive system includes a pair of testes (in the scrotum), accessory ducts (rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct, urethra), accessory glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands), and external genitalia (penis). Each testis has 250 testicular lobules with seminiferous tubules lined by spermatogonia and Sertoli cells. Interstitial spaces contain Leydig cells. The penis has special tissue for erection, with the glans penis covered by foreskin .
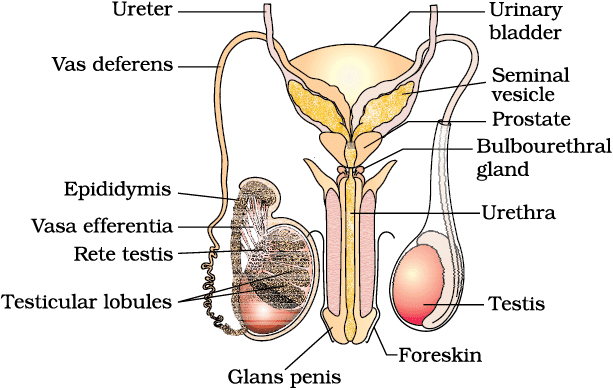
Function: The testes produce sperms via spermatogenesis and androgens via Leydig cells. Sertoli cells nourish germ cells. Accessory ducts store and transport sperms, while accessory glands produce seminal plasma (rich in fructose, calcium, enzymes) for sperm motility and maturation. The penis facilitates insemination by delivering semen into the female reproductive tract.
Q2: Explain the process of oogenesis and the hormonal regulation of the menstrual cycle.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
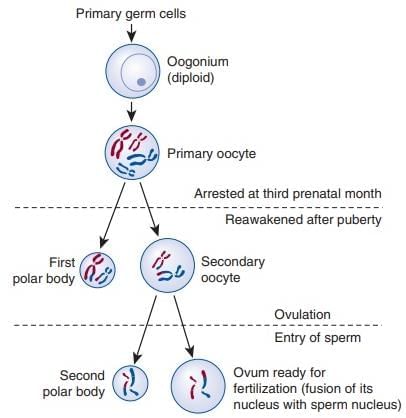
Oogenesis: Oogenesis begins in the fetal ovary, forming oogonia that develop into primary oocytes, arrested in prophase-I. At puberty, primary oocytes in primary follicles complete meiosis I, forming a haploid secondary oocyte and a first polar body. The secondary oocyte, surrounded by the zona pellucida in the Graafian follicle, is released during ovulation and arrests in meiosis II until fertilisation, forming an ovum and a second polar body.
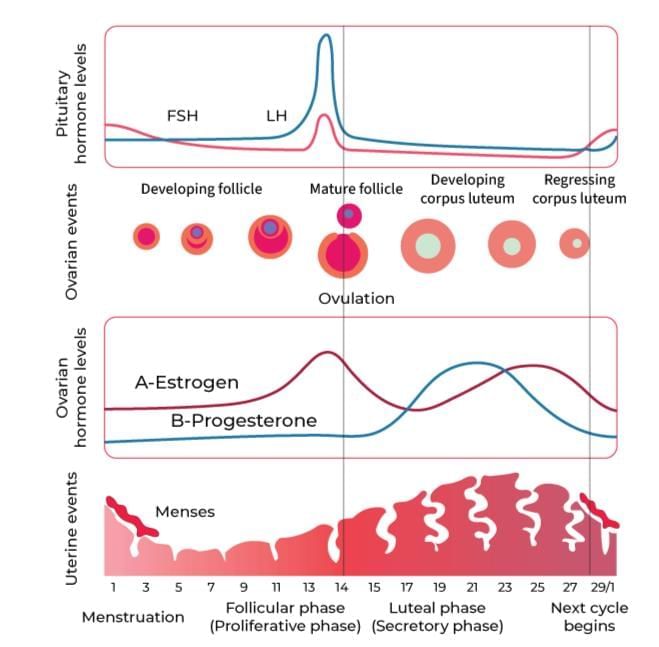
Menstrual Cycle Regulation: The menstrual cycle (28/29 days) starts with the menstrual phase (3-5 days, endometrial breakdown). The follicular phase follows, with FSH and LH stimulating follicle growth and estrogen secretion, regenerating the endometrium. The LH surge around day 14 triggers ovulation. The luteal phase involves corpus luteum formation, secreting progesterone to maintain the endometrium. If fertilisation does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to menstruation.
Q3: Discuss the process of fertilisation and implantation in humans.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Fertilisation: During coitus, semen is released into the vagina, and motile sperms swim through the cervix and uterus to the ampullary region of the fallopian tube. A sperm contacts the secondary oocyte’s zona pellucida, and acrosomal enzymes enable penetration, blocking additional sperms. The sperm nucleus fuses with the ovum’s nucleus, forming a diploid zygote, and the ovum completes meiosis II.
Implantation: The zygote undergoes cleavage in the oviduct, forming a morula, then a blastocyst with a trophoblast and inner cell mass. The blastocyst reaches the uterus, and the trophoblast attaches to the endometrium. Uterine cells cover the blastocyst, embedding it in the endometrium, completing implantation and initiating pregnancy.
Q4: Describe the role of the placenta and the major stages of embryonic development during pregnancy.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Placenta Role: The placenta, formed by interdigitated chorionic villi and uterine tissue, supplies oxygen and nutrients to the embryo, removes waste, and produces hormones (hCG, hPL, estrogens, progestogens) to support fetal growth and pregnancy. It is connected to the embryo via the umbilical cord.
Embryonic Development Stages: After one month, the embryo’s heart forms. By the end of the second month, limbs and digits develop. By 12 weeks (first trimester), major organ systems, including limbs and external genitalia, are formed. During the fifth month, fetal movements and hair appear. By 24 weeks (second trimester), the body has fine hair, eyelids separate, and eyelashes form. By nine months, the foetus is fully developed for delivery.
Q5: Explain the process of parturition and the significance of lactation in humans.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Parturition: Parturition is the delivery of the foetus after a nine-month gestation period, induced by a neuroendocrine mechanism. Signals from the foetus and placenta trigger a foetal ejection reflex, stimulating oxytocin release from the maternal pituitary. Oxytocin causes stronger uterine contractions, which further stimulate oxytocin release, leading to expulsion of the baby and placenta through the birth canal.
Lactation Significance: Lactation is the production of milk by mammary glands, starting towards the end of pregnancy. The initial milk, colostrum, is rich in antibodies, providing immunity to the newborn. Breast-feeding is recommended for the initial months to ensure healthy infant growth and resistance to infections.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet with Solutions: Human Reproduction - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the main stages of human reproduction? |  |
| 2. What is the role of hormones in human reproduction? |  |
| 3. How does fertilization occur in humans? |  |
| 4. What are common reproductive health issues individuals may face? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of prenatal care during pregnancy? |  |





















