Worksheet with Solutions: Principles of Inheritance and Variation | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Section A. Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The units of inheritance proposed by Mendel are now called ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Genes
Q2: The cross between a homozygous tall plant (TT) and a homozygous dwarf plant (tt) is called a ________ cross.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Monohybrid
Q3: The phenomenon where a single gene affects multiple traits is known as ________.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Pleiotropy
Q4: The genetic disorder caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21 is called ________ syndrome.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Down’s
Q5: The sex determination mechanism in honey bees is called ________ system.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Haplodiploid
Section B. Match the Column
Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
1. Law of Segregation | A. Genes on the same chromosome |
2. Incomplete dominance | B. Alleles separate during gamete formation |
3. Linkage | C. Phenotype is intermediate in heterozygotes |
4. Co-dominance | D. Both alleles express in heterozygotes |
5. Pedigree analysis | E. Traces inheritance of traits in families |
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: 1 - B, 2 - C, 3 - A, 4 - D, 5 - E
Section C. Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: What was the phenotypic ratio observed by Mendel in the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross?
(a) 1:2:1
(b) 3:1
(c) 9:3:3:1
(d) 1:1
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 3:1
Q2: Which of the following is an example of co-dominance?
(a) Flower colour in snapdragon
(b) ABO blood groups in humans
(c) Starch synthesis in pea seeds
(d) Skin colour in humans
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) ABO blood groups
Q3: In which type of sex determination do males have only one X-chromosome?
(a) XY type
(b) XO type
(c) ZW type
(d) Haplodiploid type
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) XO type
Q4: Which genetic disorder is caused by a point mutation in the beta-globin gene?
(a) Haemophilia
(b) Sickle-cell anaemia
(c) Phenylketonuria
(d) Down’s syndrome
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) Sickle-cell anaemia
Q5: What is the karyotype of an individual with Klinefelter’s syndrome?
(a) 45, X0
(b) 47, XXY
(c) 47, trisomy 21
(d) 46, XX
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b) 47, XXY
Section D. Assertion Reasoning Questions
Q1: Assertion: In a monohybrid cross, the F1 generation expresses only the dominant trait.
Reason: The dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele in the heterozygous condition.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
In a monohybrid cross (a cross between two individuals with contrasting traits for a single character), the F1 generation is heterozygous. For example, crossing a pure tall (TT) and a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant results in all F1 plants being tall (Tt).
This happens because the dominant allele (T) expresses itself even in the presence of the recessive allele (t). The recessive allele remains unexpressed in the heterozygous condition due to being masked by the dominant one.
Therefore, both the assertion and the reason are true, and the reason correctly explains why the dominant trait appears in the F1 generation.
Q2: Assertion: Linked genes always assort independently during meiosis.
Reason: Linked genes are located on the same chromosome and tend to be inherited together.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) Assertion is true, but the reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d) Assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Linked genes are genes located on the same chromosome, often close to each other. Because of their proximity, they tend to be inherited together and do not follow the principle of independent assortment unless crossing over separates them during meiosis.
The assertion is false because linked genes do not always assort independently—their inheritance is often dependent on their physical proximity.
The reason is true, as it correctly states the definition and behavior of linked genes.
Section E. Case-Based Questions
Case 1: Mendel’s Experiments on Pea Plants
Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on pea plants to study inheritance patterns, using true-breeding lines with contrasting traits like tall and dwarf plants.
(i) Describe the results of a monohybrid cross between a true-breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plant.
(ii) What is the significance of the Law of Segregation in this cross?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
(i) In the F1 generation, all plants were tall (Tt), showing the dominant trait. In the F2 generation, self-pollination of F1 plants resulted in a phenotypic ratio of 3 tall (1 TT, 2 Tt) to 1 dwarf (tt), and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1.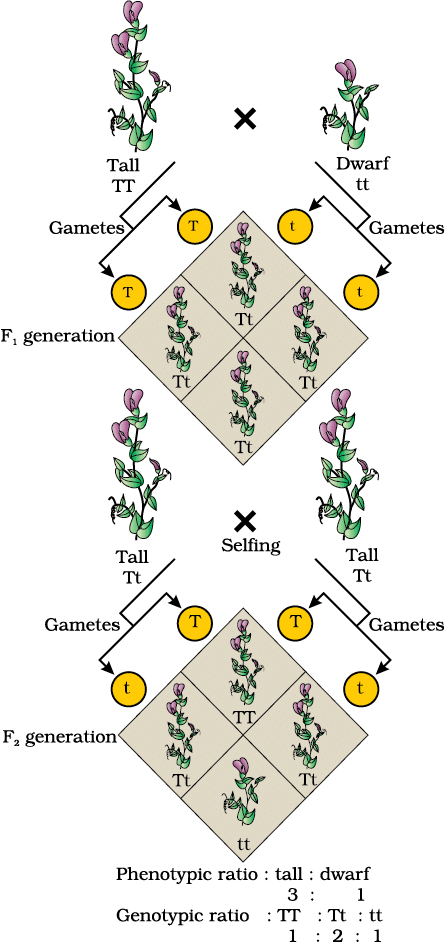
(ii) The Law of Segregation states that alleles of a gene pair segregate during gamete formation, so each gamete carries only one allele. This explains why both tall and dwarf traits reappeared in the F2 generation without blending.
Case 2: Sex Determination Mechanisms
Different organisms exhibit varied mechanisms of sex determination, such as XO, XY, and haplodiploid systems, influencing the genetic makeup of offspring.
(i) Explain the XY type of sex determination in humans.
(ii) How does the haplodiploid system in honey bees differ from the XY system?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Solution:
(i) In humans, females have XX chromosomes, and males have XY. During spermatogenesis, 50% of sperms carry X and 50% carry Y. Fertilisation of an ovum (X) with an X-sperm results in a female (XX), while a Y-sperm results in a male (XY).
(ii) In honey bees, females (queens/workers) are diploid (32 chromosomes) from fertilised eggs, while males (drones) are haploid (16 chromosomes) from unfertilised eggs via parthenogenesis. Males produce sperm by mitosis, unlike the XY system where both sexes are diploid.
Section F. Short Answer Type
Q1: Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Mendel chose pea plants due to their large sampling size, true-breeding varieties, contrasting traits (e.g., tall/dwarf), and ability to perform controlled cross-pollination, ensuring reliable inheritance data.
Q2: Define a test cross and its purpose.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A test cross involves crossing an organism with a dominant phenotype (unknown genotype) with a homozygous recessive parent to determine its genotype. It reveals whether the organism is homozygous (all dominant offspring) or heterozygous (1:1 ratio).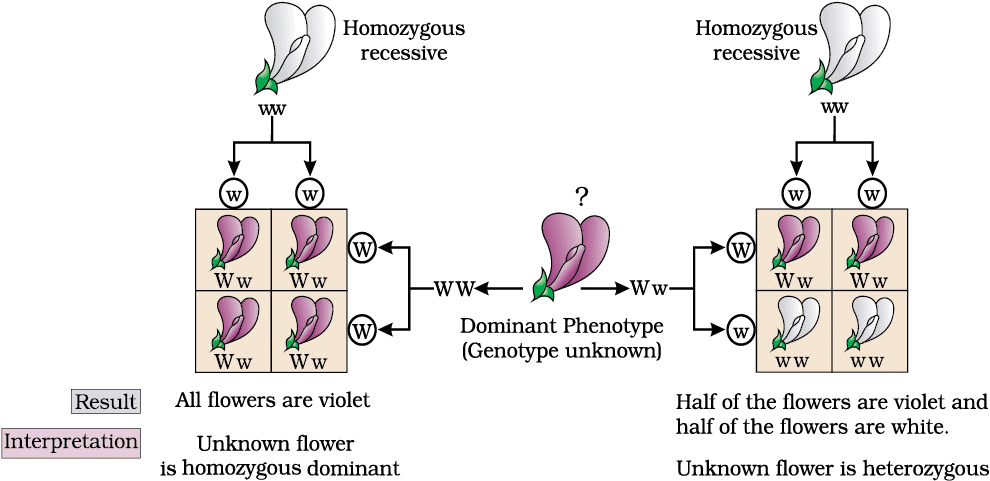
Q3: What is incomplete dominance? Give an example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Incomplete dominance occurs when the F1 heterozygote shows an intermediate phenotype between the two homozygous parents. Example: In snapdragons, red (RR) and white (rr) flowers produce pink (Rr) flowers in the F1 generation.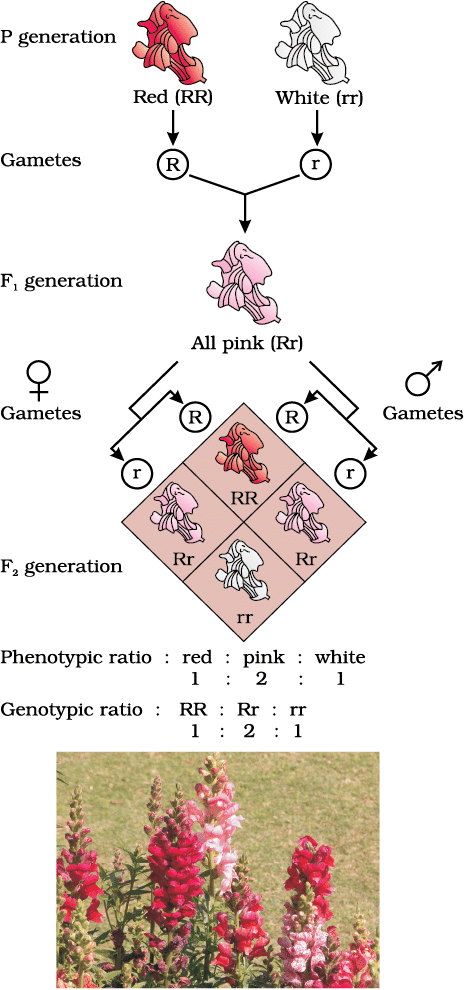
Q4: Explain the concept of linkage in genetics.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Linkage is the physical association of genes on the same chromosome, causing them to be inherited together more often than expected. It reduces recombination, as seen in Morgan’s Drosophila crosses.
Q5: What is a point mutation? Provide an example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: A point mutation is a change in a single base pair of DNA. Example: Sickle-cell anaemia, caused by a single base substitution (GAG to GUG) in the beta-globin gene, altering haemoglobin structure.
Q6: Describe the symptoms of Down’s syndrome.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Down’s syndrome individuals have short stature, a small round head, furrowed tongue, partially open mouth, broad palm with palm crease, and retarded physical, psychomotor, and mental development.
Q7: What is pedigree analysis, and how is it useful?
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Pedigree analysis traces the inheritance of traits across generations in a family tree. It helps identify whether a trait is dominant, recessive, or sex-linked and predicts the risk of genetic disorders in offspring.
Q8: Differentiate between male and female heterogamety.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: Male heterogamety (e.g., XY in humans) involves males producing two types of gametes (X or Y), determining offspring sex. Female heterogamety (e.g., ZW in birds) involves females producing two types of gametes (Z or W), determining sex.
Section G. Long Answer Type
Q1: Explain Mendel’s Law of Dominance and Law of Segregation with a monohybrid cross example.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Law of Dominance: In a heterozygous condition, one allele (dominant) expresses its trait, masking the recessive allele. In a monohybrid cross between true-breeding tall (TT) and dwarf (tt) pea plants, the F1 generation (Tt) is all tall, as T dominates t.
Law of Segregation: Alleles segregate during gamete formation, each gamete carrying one allele. In the F1 (Tt), self-pollination produces F2 with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio (3 tall: 1 dwarf) and 1:2:1 genotypic ratio (TT:Tt:tt), as T and t segregate independently. The recessive trait (dwarf) reappears in F2 without blending.
Q2: Describe the Law of Independent Assortment using a dihybrid cross.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The Law of Independent Assortment states that segregation of one pair of alleles is independent of another pair during gamete formation. In a dihybrid cross between pea plants with round, yellow seeds (RRYY) and wrinkled, green seeds (rryy), the F1 (RrYy) produces four gamete types (RY, Ry, rY, ry). Self-pollination yields F2 with a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio (9 round yellow, 3 wrinkled yellow, 3 round green, 1 wrinkled green), showing independent segregation of seed shape and colour genes.
Q3: Discuss the chromosomal theory of inheritance and its experimental verification.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: The chromosomal theory of inheritance, proposed by Sutton and Boveri, states that genes are located on chromosomes, and their segregation during meiosis explains Mendel’s laws. Chromosomes, like genes, occur in pairs, segregate during gamete formation, and assort independently. Thomas Hunt Morgan verified this using Drosophila, observing sex-linked traits (e.g., white eyes on X-chromosome). His dihybrid crosses showed linked genes on the same chromosome deviate from the 9:3:3:1 ratio, supporting the theory.
Q4: Explain the mechanism of sex determination in humans and birds.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Humans (XY Type): Females have XX chromosomes, males have XY, with 22 pairs of autosomes in both. Males produce 50% X-sperm and 50% Y-sperm. Fertilisation of an X-ovum with X-sperm yields XX (female), and with Y-sperm yields XY (male), determined by the sperm’s genetic makeup.
Birds (ZW Type): Males have ZZ chromosomes, females have ZW, with equal autosomes. Females produce 50% Z-ova and 50% W-ova, determining sex. Z-ovum with Z-sperm yields ZZ (male), and W-ovum with Z-sperm yields ZW (female), showing female heterogamety.
Q5: Describe the genetic basis and symptoms of any two Mendelian disorders.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans:
Haemophilia: A sex-linked recessive disorder caused by a mutation in an X-chromosome gene affecting blood clotting proteins. Males (XY) with the mutant allele show non-stop bleeding from minor cuts. Carrier females (XX with one mutant allele) may pass it to sons. Symptoms include excessive bleeding.
Sickle-cell Anaemia: An autosomal recessive disorder due to a point mutation (GAG to GUG) in the beta-globin gene, substituting glutamic acid with valine. Homozygous (HbSHbS) individuals have sickle-shaped RBCs, causing anaemia and oxygen deficiency. Heterozygotes (HbAHbS) are carriers.
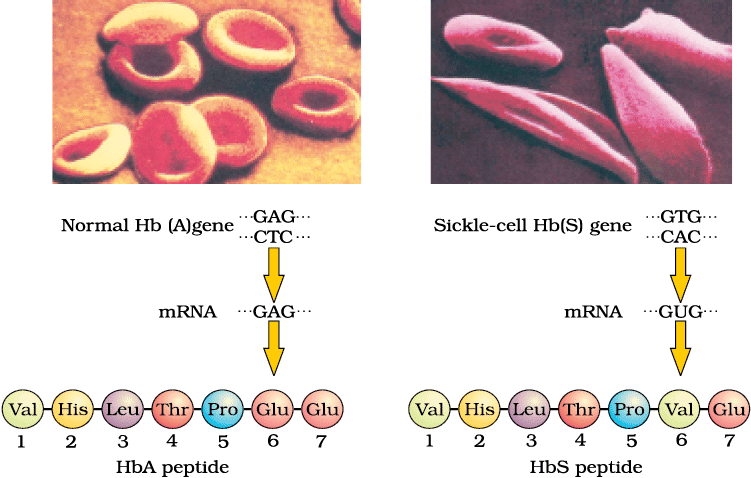 Micrograph of the red blood cells and the amino acid composition of the relevant portion of β-chain of haemoglobin: (a) From a normal individual; (b) From an individual with sickle-cell anaemia
Micrograph of the red blood cells and the amino acid composition of the relevant portion of β-chain of haemoglobin: (a) From a normal individual; (b) From an individual with sickle-cell anaemia
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet with Solutions: Principles of Inheritance and Variation - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What are the fundamental principles of inheritance that are essential for understanding genetics? |  |
| 2. How did Gregor Mendel’s experiments contribute to the field of genetics? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of genetic variation in populations? |  |
| 4. How do mutations affect inheritance and variation in organisms? |  |
| 5. What role do sex chromosomes play in inheritance patterns? |  |
















