Commerce Exam > Commerce Notes > Economics Class 11 > Short Notes: Introduction to Microeconomics
Short Notes: Introduction to Microeconomics | Economics Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
What is an Economy?
- An economy is a system of production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services within a region (e.g., a country).
- It determines what to produce, how to produce, and how to distribute resources among people.
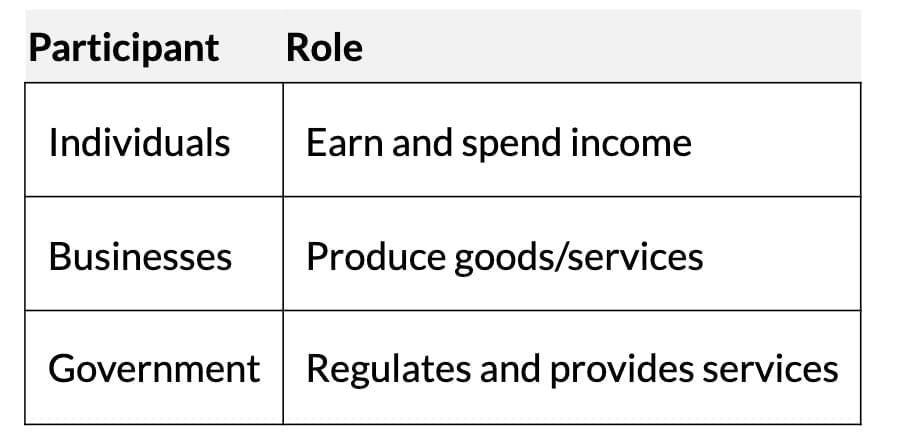
- Key participants:
- Individuals: Earn income through work and spend on goods/services.
- Businesses: Produce goods/services for profit.
- Government: Regulates activities, provides services, collects taxes.
- Markets (physical or virtual) facilitate buying and selling.
- Goal: Efficiently allocate limited resources (land, labour, capital) to meet population needs.
- Example: India’s economy includes farmers, factories, banks, consumers, and government programs like healthcare.
What is Economics?
- Economics studies how people, businesses, and governments make choices about scarce resources.
- Addresses three key questions:
- What to produce? E.g., prioritise education or defence.
- How to produce? E.g., use more machines or workers.
- For whom to produce? E.g., goods for all or only those who can pay.
- Analyses individual behaviour and large-scale economic trends.
- Example: Rising petrol prices may lead people to use public transport, reflecting economic decisions based on price and availability.

Question for Short Notes: Introduction to MicroeconomicsTry yourself: What does economics study?View Solution
A Simple Economy
- Unlimited Needs: People have endless wants (food, clothing, shelter, etc.).
- Limited Resources: Resources (e.g., land, labour, time) are finite, forcing choices.
- Needs Exceed Resources: Individuals prioritise certain goods/services over others.
- Example: A farmer grows crops to sell and buy clothes; a teacher earns a salary to meet needs.
- Mismatches in production and wants lead to overproduction (wasted resources) or underproduction (shortages).
- Proper resource allocation and distribution are critical to avoid economic problems.

Central Problems of an Economy
- Economic Problem: Satisfying unlimited wants with limited resources, having alternative uses.
- Scarcity: Limited resources (money, time, labour, land) vs. unlimited wants force prioritisation.
- Alternative Uses: Resources can serve multiple purposes, requiring trade-offs.
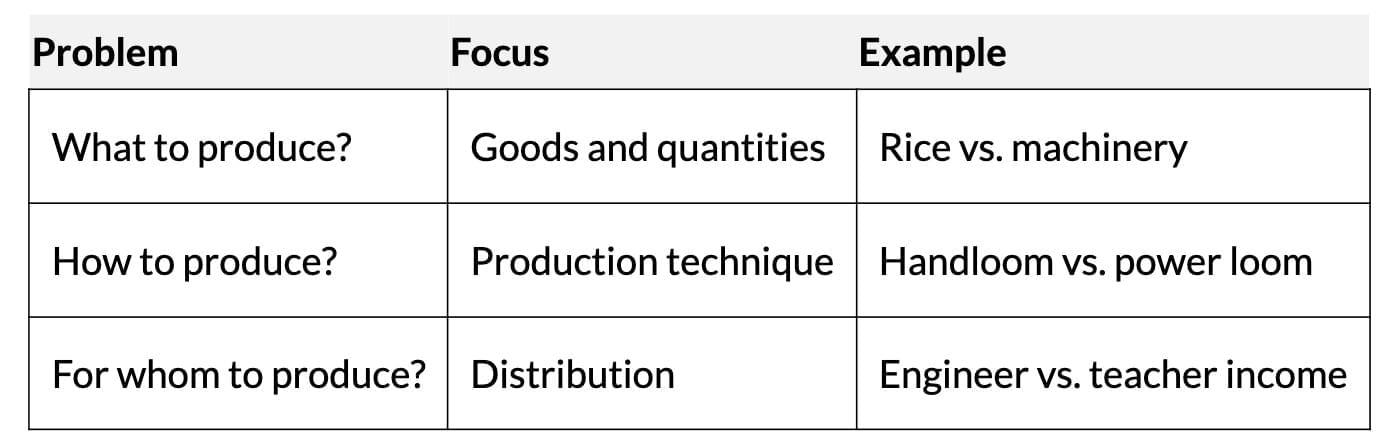
- Three central problems:
- What to produce? Deciding which goods (e.g., consumer vs. capital, civil vs. war) and quantities to produce.
- How to produce? Choosing production techniques (labour-intensive vs. capital-intensive).
- For whom to produce? Determining distribution among individuals (personal) and factors of production (functional).
- Example: Choosing handlooms (labour-intensive) vs. power looms (capital-intensive) for cloth production.
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)
- PPF shows combinations of two goods that an economy can produce using all resources efficiently.
- A concave curve reflects increasing opportunity cost: producing more of one good reduces the other.
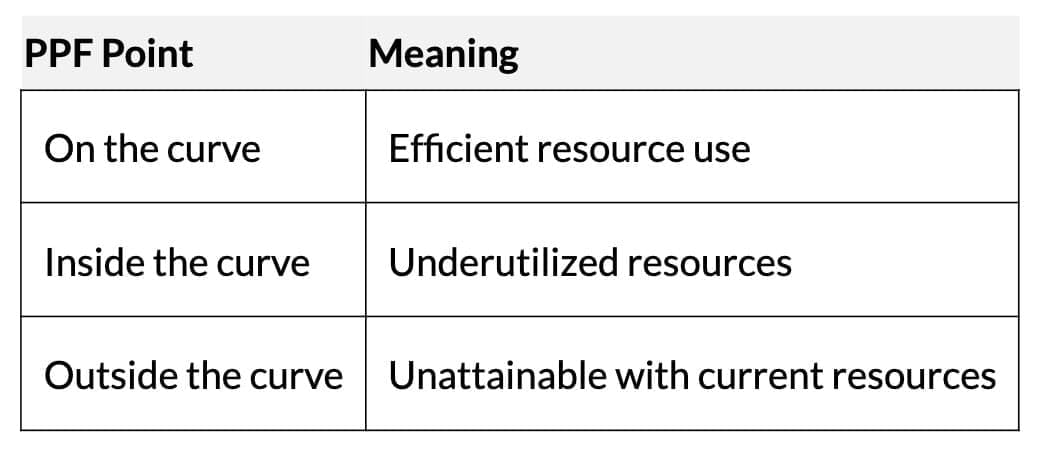
- Key points:
- Efficient Production: Points on the curve (full resource use).
- Underutilisation: Points inside the curve (unused/misused resources).
- Unattainable: Points outside the curve (beyond current resources).
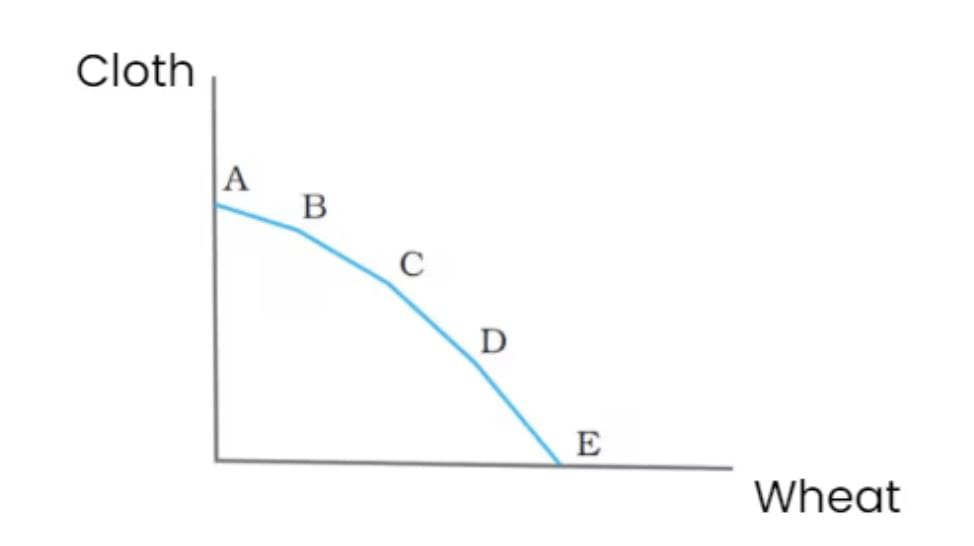
- Opportunity Cost: Value of the next best alternative given up (e.g., producing more wheat reduces cloth output).
- Example: Producing 10 units of cotton leaves no resources for corn; 9 units of cotton allows 1 unit of corn.
Q: What does a concave curve on the PPF indicate about opportunity cost?
 View Answer
View Answer 
A concave curve indicates increasing opportunity cost, meaning producing more of one good reduces the quantity of the other good.
Organisation of Economic Activities
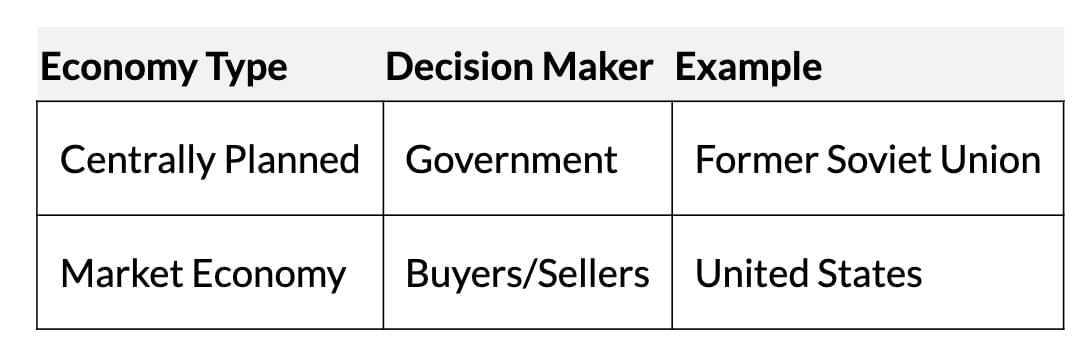
Centrally Planned Economy:- The government makes all decisions on production, exchange, and consumption.
- Aims for equitable resource allocation and distribution.
- Interventions: Subsidies, public enterprises, price controls, rationing.
- Example: The Soviet Union set production targets and controlled prices.
- Decisions made by buyers and sellers via markets (shops, online platforms).
- Prices guide what, how, and for whom to produce.
- Promotes freedom, competition, and efficiency but may require government intervention for fairness (e.g., healthcare, education).
- Example: U.S. emphasises economic freedom; China blends market and government control.
Positive and Normative Economics
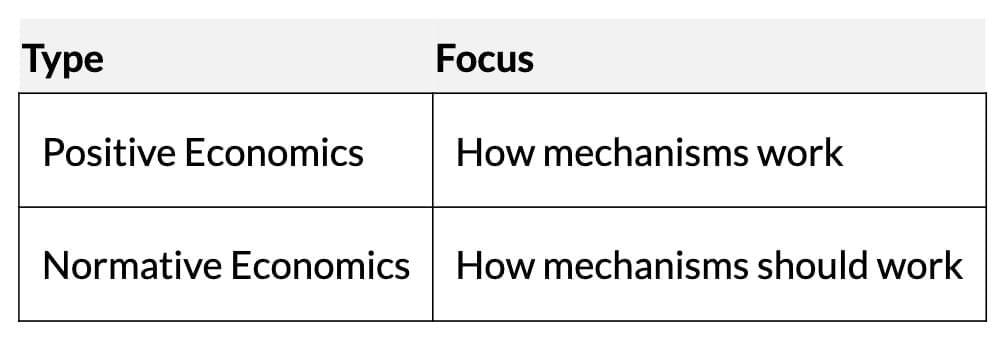
- Positive Economics: Analyses how economic mechanisms function (objective analysis).
- Normative Economics: Evaluates how mechanisms should function (subjective, value-based).
- Both are interconnected; understanding outcomes (positive) informs ideal policies (normative).
- Helps evaluate resource allocation and distribution mechanisms for desirability.
Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
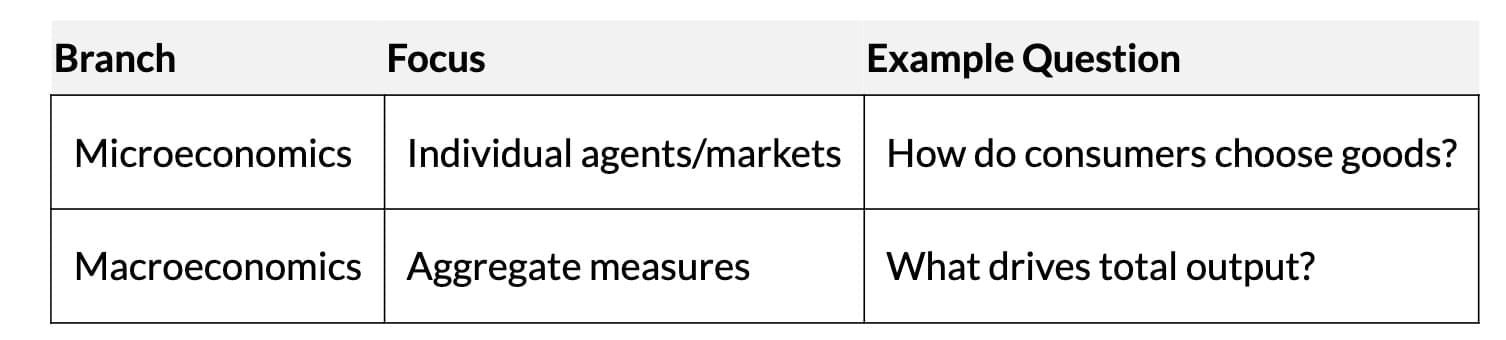
- Microeconomics: Focuses on individual agents (e.g., consumers, firms) and their market interactions.
- Macroeconomics: Examines the economy as a whole, analysing aggregates like total output, employment, and price levels.
- Macro questions: What determines total output? Why do prices rise? Why are resources unemployed?
The document Short Notes: Introduction to Microeconomics | Economics Class 11 - Commerce is a part of the Commerce Course Economics Class 11.
All you need of Commerce at this link: Commerce
|
59 videos|222 docs|43 tests
|
FAQs on Short Notes: Introduction to Microeconomics - Economics Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is the definition of an economy? |  |
Ans. An economy is a system that encompasses the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services within a society. It involves all activities related to how resources are allocated and utilized to meet the needs and wants of individuals and groups.
| 2. What are the central problems of an economy? |  |
Ans. The central problems of an economy typically include what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. These questions arise due to the scarcity of resources, requiring societies to make choices about resource allocation to maximize efficiency and welfare.
| 3. What is the Production Possibility Frontier (PPF)? |  |
Ans. The Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation that shows the maximum feasible amounts of two goods that can be produced within an economy, given available resources and technology. It illustrates the trade-offs and opportunity costs of allocating resources between different production options.
| 4. How do microeconomics and macroeconomics differ? |  |
Ans. Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual consumers and firms, analyzing how they make decisions regarding the allocation of resources and the pricing of goods and services. In contrast, macroeconomics examines the economy as a whole, including national income, overall employment, inflation, and economic growth.
| 5. What is the difference between positive and normative economics? |  |
Ans. Positive economics deals with objective analysis and facts, describing how the economy functions without making judgments about what ought to be. Normative economics, on the other hand, involves subjective statements and opinions, focusing on what should happen and what policies should be implemented based on ethical considerations.
Related Searches
















